A Simulation Benchmark for Vision-based Autonomous Navigation
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2022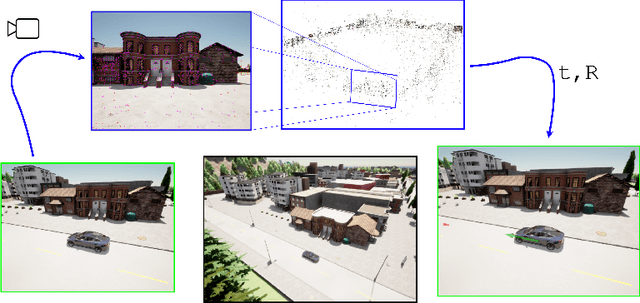
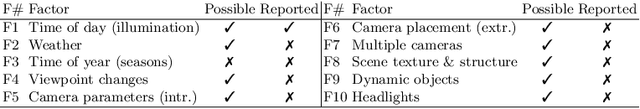
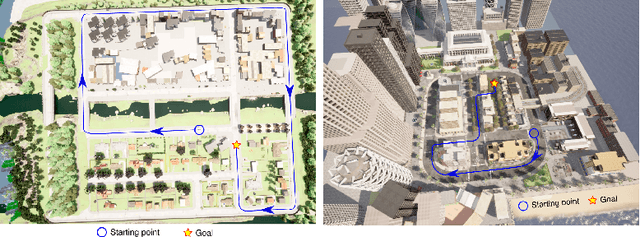
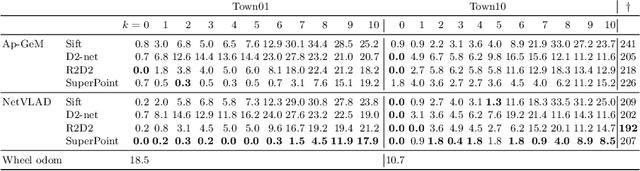
This work introduces a simulator benchmark for vision-based autonomous navigation. The simulator offers control over real world variables such as the environment, time of day, weather and traffic. The benchmark includes a modular integration of different components of a full autonomous visual navigation stack. In the experimental part of the paper, state-of-the-art visual localization methods are evaluated as a part of the stack in realistic navigation tasks. To the authors' best knowledge, the proposed benchmark is the first to study modern visual localization methods as part of a full autonomous visual navigation stack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge