Arafat Rahman
Fairness in Machine Learning-based Hand Load Estimation: A Case Study on Load Carriage Tasks
Apr 08, 2025



Abstract:Predicting external hand load from sensor data is essential for ergonomic exposure assessments, as obtaining this information typically requires direct observation or supplementary data. While machine learning methods have been used to estimate external hand load from worker postures or force exertion data, our findings reveal systematic bias in these predictions due to individual differences such as age and biological sex. To explore this issue, we examined bias in hand load prediction by varying the sex ratio in the training dataset. We found substantial sex disparity in predictive performance, especially when the training dataset is more sex-imbalanced. To address this bias, we developed and evaluated a fair predictive model for hand load estimation that leverages a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) with feature disentanglement. This approach is designed to separate sex-agnostic and sex-specific latent features, minimizing feature overlap. The disentanglement capability enables the model to make predictions based solely on sex-agnostic features of motion patterns, ensuring fair prediction for both biological sexes. Our proposed fair algorithm outperformed conventional machine learning methods (e.g., Random Forests) in both fairness and predictive accuracy, achieving a lower mean absolute error (MAE) difference across male and female sets and improved fairness metrics such as statistical parity (SP) and positive and negative residual differences (PRD and NRD), even when trained on imbalanced sex datasets. These findings emphasize the importance of fairness-aware machine learning algorithms to prevent potential disadvantages in workplace health and safety for certain worker populations.
A Shape-Based Functional Index for Objective Assessment of Pediatric Motor Function
Jan 02, 2025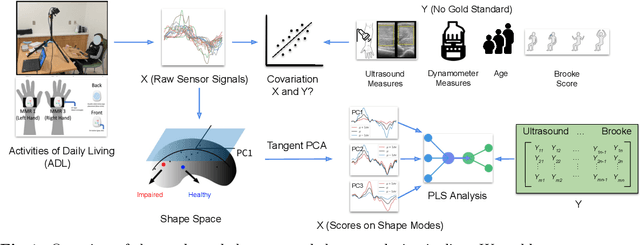
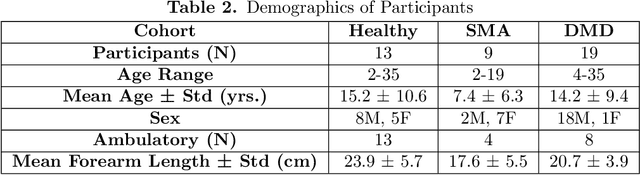
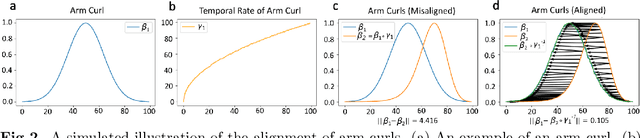
Abstract:Clinical assessments for neuromuscular disorders, such as Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), continue to rely on subjective measures to monitor treatment response and disease progression. We introduce a novel method using wearable sensors to objectively assess motor function during daily activities in 19 patients with DMD, 9 with SMA, and 13 age-matched controls. Pediatric movement data is complex due to confounding factors such as limb length variations in growing children and variability in movement speed. Our approach uses Shape-based Principal Component Analysis to align movement trajectories and identify distinct kinematic patterns, including variations in motion speed and asymmetry. Both DMD and SMA cohorts have individuals with motor function on par with healthy controls. Notably, patients with SMA showed greater activation of the motion asymmetry pattern. We further combined projections on these principal components with partial least squares (PLS) to identify a covariation mode with a canonical correlation of r = 0.78 (95% CI: [0.34, 0.94]) with muscle fat infiltration, the Brooke score (a motor function score), and age-related degenerative changes, proposing a novel motor function index. This data-driven method can be deployed in home settings, enabling better longitudinal tracking of treatment efficacy for children with neuromuscular disorders.
Multimodal EEG and Keystroke Dynamics Based Biometric System Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Mar 10, 2021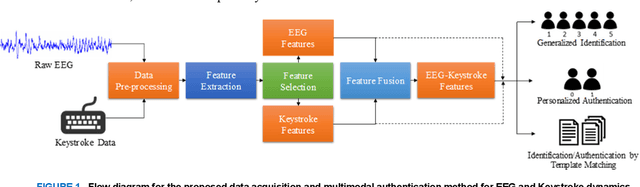
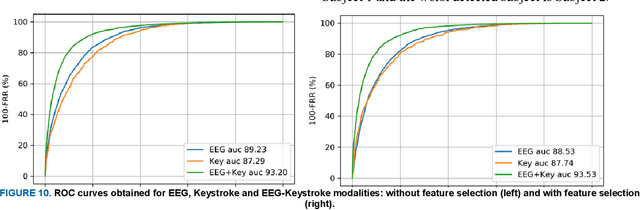
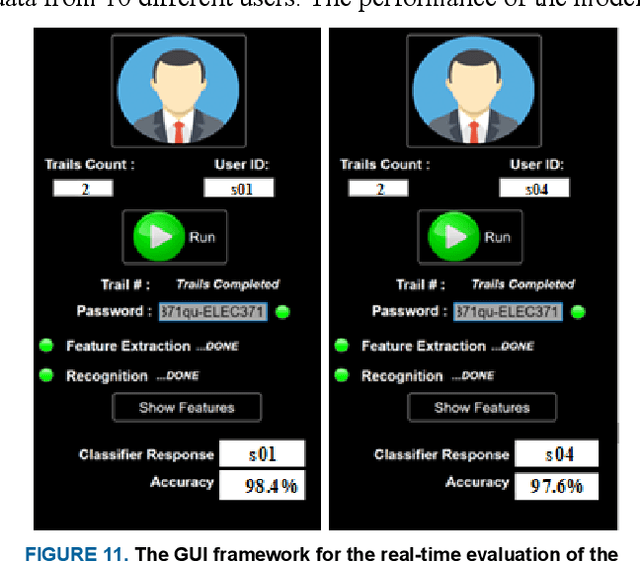
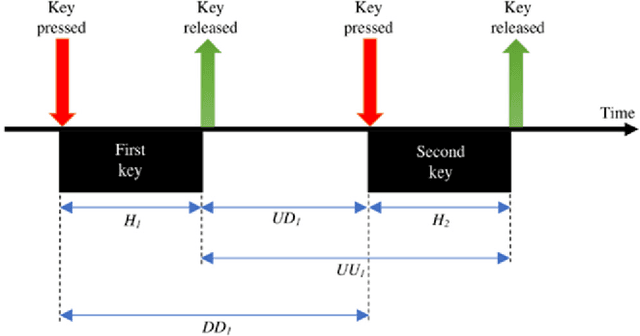
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of technology, different biometric user authentication, and identification systems are emerging. Traditional biometric systems like face, fingerprint, and iris recognition, keystroke dynamics, etc. are prone to cyber-attacks and suffer from different disadvantages. Electroencephalography (EEG) based authentication has shown promise in overcoming these limitations. However, EEG-based authentication is less accurate due to signal variability at different psychological and physiological conditions. On the other hand, keystroke dynamics-based identification offers high accuracy but suffers from different spoofing attacks. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel multimodal biometric system combining EEG and keystroke dynamics. Firstly, a dataset was created by acquiring both keystroke dynamics and EEG signals from 10 users with 500 trials per user at 10 different sessions. Different statistical, time, and frequency domain features were extracted and ranked from the EEG signals and key features were extracted from the keystroke dynamics. Different classifiers were trained, validated, and tested for both individual and combined modalities for two different classification strategies - personalized and generalized. Results show that very high accuracy can be achieved both in generalized and personalized cases for the combination of EEG and keystroke dynamics. The identification and authentication accuracies were found to be 99.80% and 99.68% for Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) and Random Forest classifiers, respectively which outperform the individual modalities with a significant margin (around 5 percent). We also developed a binary template matching-based algorithm, which gives 93.64% accuracy 6X faster. The proposed method is secured and reliable for any kind of biometric authentication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge