Anush Mattapalli
Speculative RAG: Enhancing Retrieval Augmented Generation through Drafting
Jul 11, 2024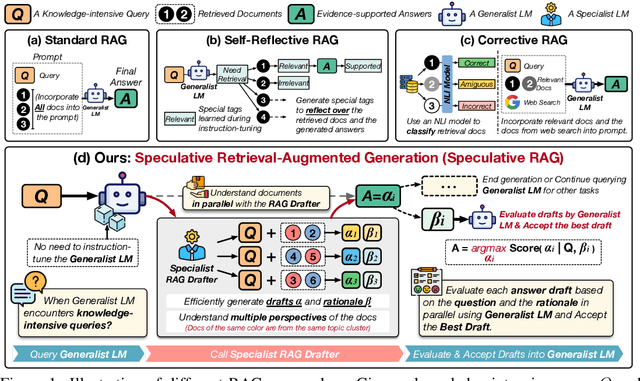
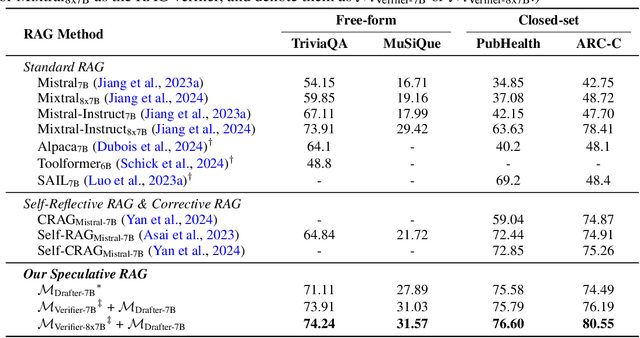
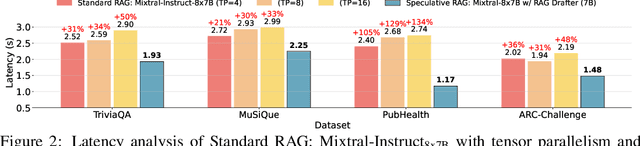
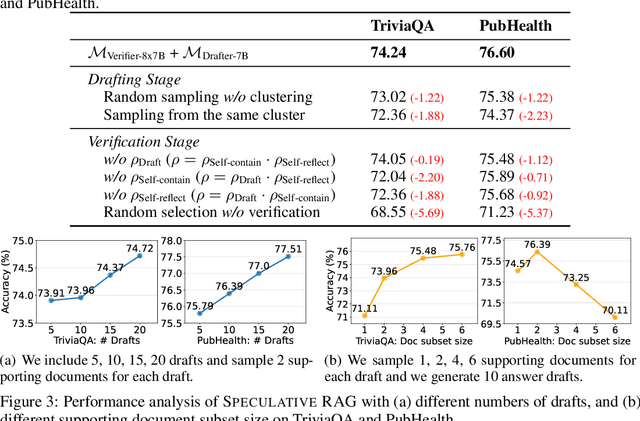
Abstract:Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) combines the generative abilities of large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge sources to provide more accurate and up-to-date responses. Recent RAG advancements focus on improving retrieval outcomes through iterative LLM refinement or self-critique capabilities acquired through additional instruction tuning of LLMs. In this work, we introduce Speculative RAG - a framework that leverages a larger generalist LM to efficiently verify multiple RAG drafts produced in parallel by a smaller, distilled specialist LM. Each draft is generated from a distinct subset of retrieved documents, offering diverse perspectives on the evidence while reducing input token counts per draft. This approach enhances comprehension of each subset and mitigates potential position bias over long context. Our method accelerates RAG by delegating drafting to the smaller specialist LM, with the larger generalist LM performing a single verification pass over the drafts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Speculative RAG achieves state-of-the-art performance with reduced latency on TriviaQA, MuSiQue, PubHealth, and ARC-Challenge benchmarks. It notably enhances accuracy by up to 12.97% while reducing latency by 51% compared to conventional RAG systems on PubHealth.
Understanding the Humans Behind Online Misinformation: An Observational Study Through the Lens of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Oct 12, 2023



Abstract:The proliferation of online misinformation has emerged as one of the biggest threats to society. Considerable efforts have focused on building misinformation detection models, still the perils of misinformation remain abound. Mitigating online misinformation and its ramifications requires a holistic approach that encompasses not only an understanding of its intricate landscape in relation to the complex issue and topic-rich information ecosystem online, but also the psychological drivers of individuals behind it. Adopting a time series analytic technique and robust causal inference-based design, we conduct a large-scale observational study analyzing over 32 million COVID-19 tweets and 16 million historical timeline tweets. We focus on understanding the behavior and psychology of users disseminating misinformation during COVID-19 and its relationship with the historical inclinations towards sharing misinformation on Non-COVID topics before the pandemic. Our analysis underscores the intricacies inherent to cross-topic misinformation, and highlights that users' historical inclination toward sharing misinformation is positively associated with their present behavior pertaining to misinformation sharing on emergent topics and beyond. This work may serve as a valuable foundation for designing user-centric inoculation strategies and ecologically-grounded agile interventions for effectively tackling online misinformation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge