Anna Widiger
European Commission - Joint Research Centre
Geocoding multilingual texts: Recognition, disambiguation and visualisation
Sep 12, 2006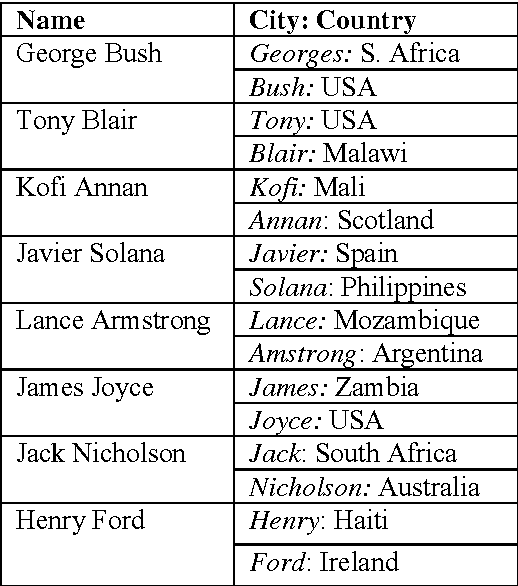
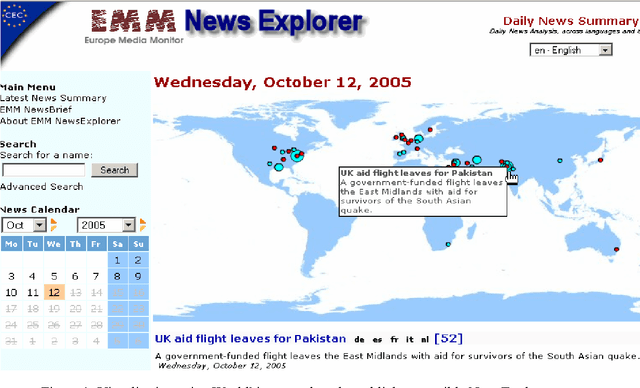
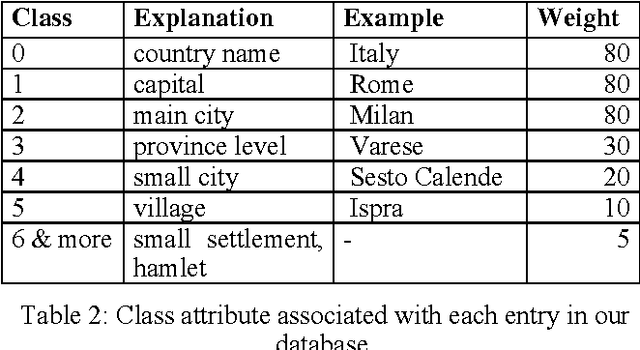
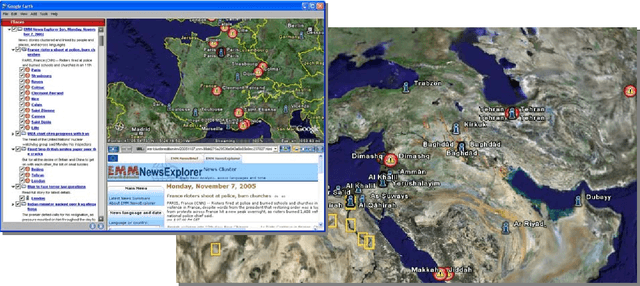
Abstract:We are presenting a method to recognise geographical references in free text. Our tool must work on various languages with a minimum of language-dependent resources, except a gazetteer. The main difficulty is to disambiguate these place names by distinguishing places from persons and by selecting the most likely place out of a list of homographic place names world-wide. The system uses a number of language-independent clues and heuristics to disambiguate place name homographs. The final aim is to index texts with the countries and cities they mention and to automatically visualise this information on geographical maps using various tools.
* 6 pages
The JRC-Acquis: A multilingual aligned parallel corpus with 20+ languages
Sep 12, 2006

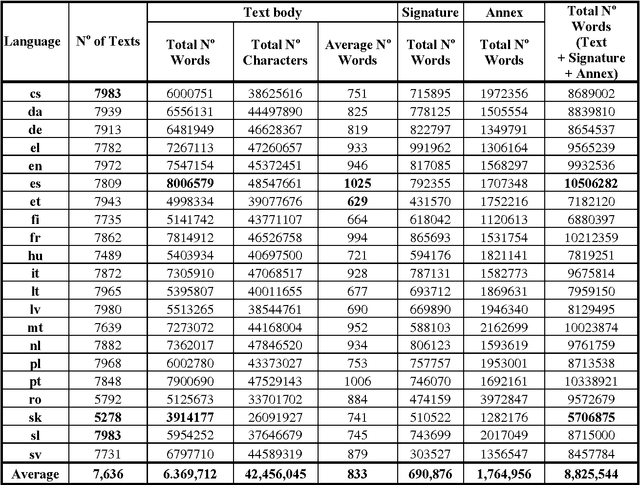

Abstract:We present a new, unique and freely available parallel corpus containing European Union (EU) documents of mostly legal nature. It is available in all 20 official EUanguages, with additional documents being available in the languages of the EU candidate countries. The corpus consists of almost 8,000 documents per language, with an average size of nearly 9 million words per language. Pair-wise paragraph alignment information produced by two different aligners (Vanilla and HunAlign) is available for all 190+ language pair combinations. Most texts have been manually classified according to the EUROVOC subject domains so that the collection can also be used to train and test multi-label classification algorithms and keyword-assignment software. The corpus is encoded in XML, according to the Text Encoding Initiative Guidelines. Due to the large number of parallel texts in many languages, the JRC-Acquis is particularly suitable to carry out all types of cross-language research, as well as to test and benchmark text analysis software across different languages (for instance for alignment, sentence splitting and term extraction).
* A multilingual textual resource with meta-data freely available for download at http://langtech.jrc.it/JRC-Acquis.html
Multilingual person name recognition and transliteration
Sep 11, 2006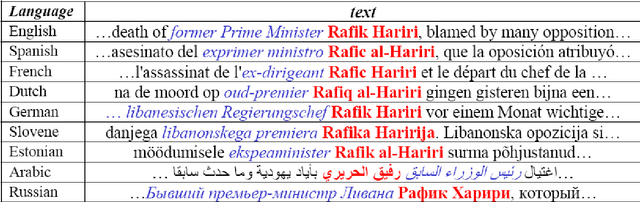
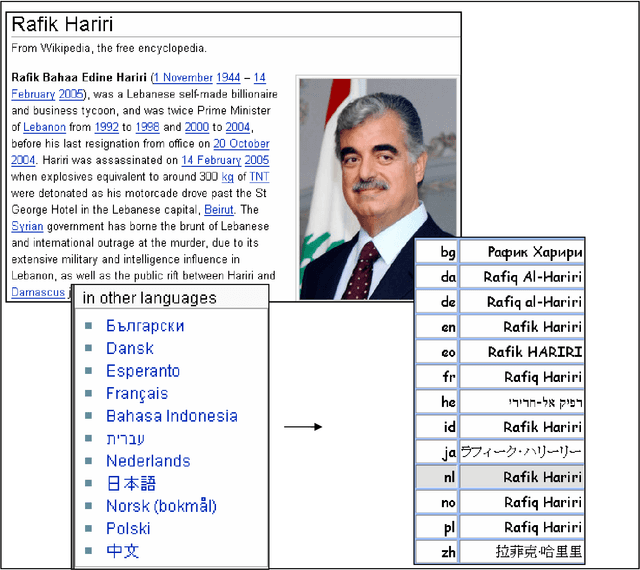
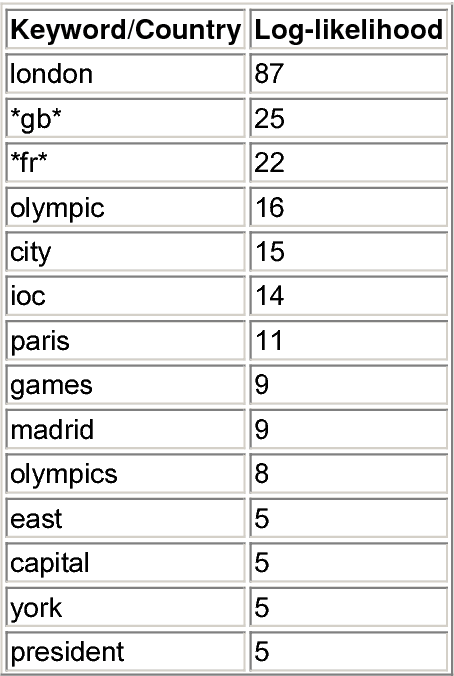
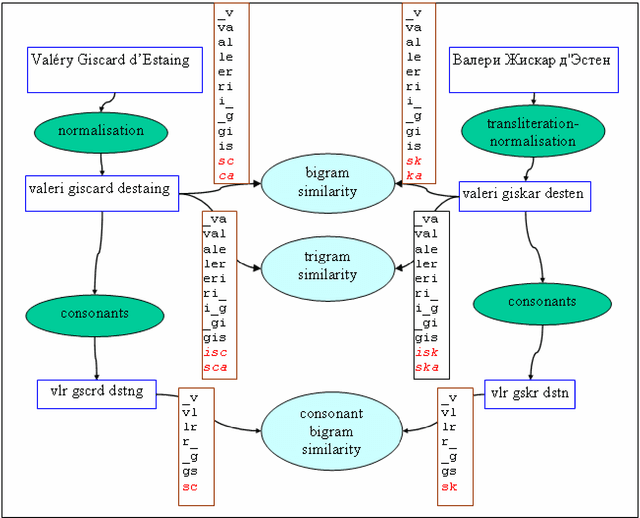
Abstract:We present an exploratory tool that extracts person names from multilingual news collections, matches name variants referring to the same person, and infers relationships between people based on the co-occurrence of their names in related news. A novel feature is the matching of name variants across languages and writing systems, including names written with the Greek, Cyrillic and Arabic writing system. Due to our highly multilingual setting, we use an internal standard representation for name representation and matching, instead of adopting the traditional bilingual approach to transliteration. This work is part of the news analysis system NewsExplorer that clusters an average of 25,000 news articles per day to detect related news within the same and across different languages.
* Explains the technology behind the JRC's NewsExplorer application, which is freely accessible at http://press.jrc.it/NewsExplorer
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge