Anil Goyal
AMA, LHC
RE-GrievanceAssist: Enhancing Customer Experience through ML-Powered Complaint Management
Apr 29, 2024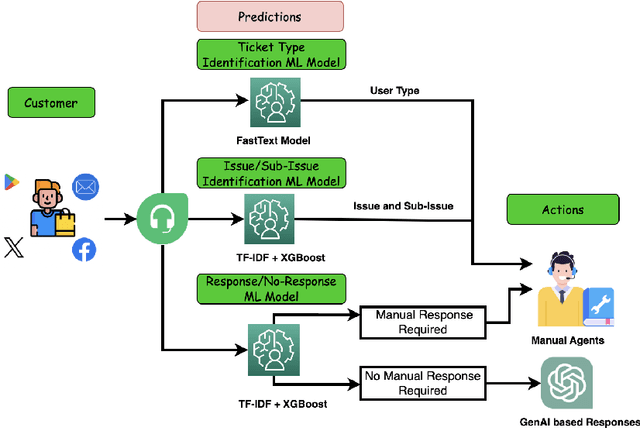
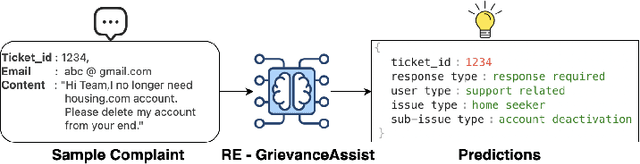
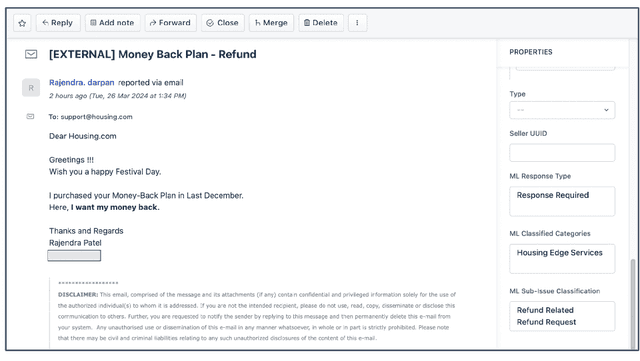
Abstract:In recent years, digital platform companies have faced increasing challenges in managing customer complaints, driven by widespread consumer adoption. This paper introduces an end-to-end pipeline, named RE-GrievanceAssist, designed specifically for real estate customer complaint management. The pipeline consists of three key components: i) response/no-response ML model using TF-IDF vectorization and XGBoost classifier ; ii) user type classifier using fasttext classifier; iii) issue/sub-issue classifier using TF-IDF vectorization and XGBoost classifier. Finally, it has been deployed as a batch job in Databricks, resulting in a remarkable 40% reduction in overall manual effort with monthly cost reduction of Rs 1,50,000 since August 2023.
RE-RFME: Real-Estate RFME Model for customer segmentation
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:Marketing is one of the high-cost activities for any online platform. With the increase in the number of customers, it is crucial to understand customers based on their dynamic behaviors to design effective marketing strategies. Customer segmentation is a widely used approach to group customers into different categories and design the marketing strategy targeting each group individually. Therefore, in this paper, we propose an end-to-end pipeline RE-RFME for segmenting customers into 4 groups: high value, promising, need attention, and need activation. Concretely, we propose a novel RFME (Recency, Frequency, Monetary and Engagement) model to track behavioral features of customers and segment them into different categories. Finally, we train the K-means clustering algorithm to cluster the user into one of the 4 categories. We show the effectiveness of the proposed approach on real-world Housing.com datasets for both website and mobile application users.
RE-RecSys: An End-to-End system for recommending properties in Real-Estate domain
Apr 25, 2024
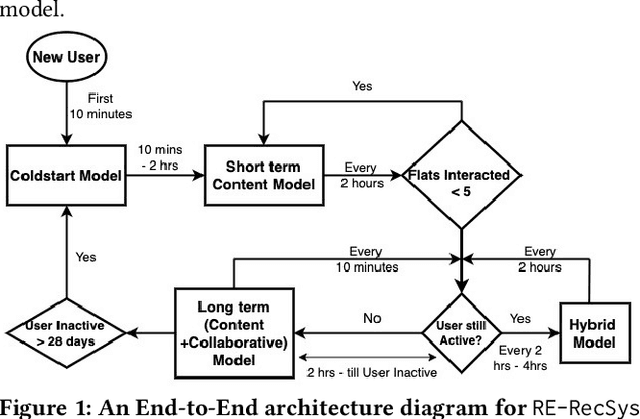
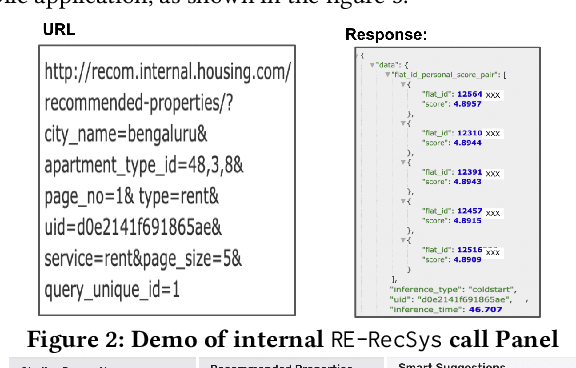
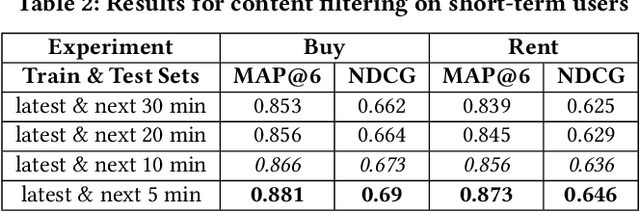
Abstract:We propose an end-to-end real-estate recommendation system, RE-RecSys, which has been productionized in real-world industry setting. We categorize any user into 4 categories based on available historical data: i) cold-start users; ii) short-term users; iii) long-term users; and iv) short-long term users. For cold-start users, we propose a novel rule-based engine that is based on the popularity of locality and user preferences. For short-term users, we propose to use content-filtering model which recommends properties based on recent interactions of users. For long-term and short-long term users, we propose a novel combination of content and collaborative filtering based approach which can be easily productionized in the real-world scenario. Moreover, based on the conversion rate, we have designed a novel weighing scheme for different impressions done by users on the platform for the training of content and collaborative models. Finally, we show the efficiency of the proposed pipeline, RE-RecSys, on a real-world property and clickstream dataset collected from leading real-estate platform in India. We show that the proposed pipeline is deployable in real-world scenario with an average latency of <40 ms serving 1000 rpm.
DIGITOUR: Automatic Digital Tours for Real-Estate Properties
Jan 17, 2023



Abstract:A virtual or digital tour is a form of virtual reality technology which allows a user to experience a specific location remotely. Currently, these virtual tours are created by following a 2-step strategy. First, a photographer clicks a 360 degree equirectangular image; then, a team of annotators manually links these images for the "walkthrough" user experience. The major challenge in the mass adoption of virtual tours is the time and cost involved in manual annotation/linking of images. Therefore, this paper presents an end-to-end pipeline to automate the generation of 3D virtual tours using equirectangular images for real-estate properties. We propose a novel HSV-based coloring scheme for paper tags that need to be placed at different locations before clicking the equirectangular images using 360 degree cameras. These tags have two characteristics: i) they are numbered to help the photographer for placement of tags in sequence and; ii) bi-colored, which allows better learning of tag detection (using YOLOv5 architecture) in an image and digit recognition (using custom MobileNet architecture) tasks. Finally, we link/connect all the equirectangular images based on detected tags. We show the efficiency of the proposed pipeline on a real-world equirectangular image dataset collected from the Housing.com database.
DEXTER: An end-to-end system to extract table contents from electronic medical health documents
Jul 18, 2022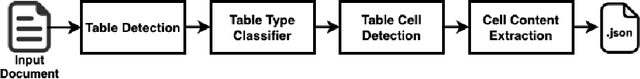

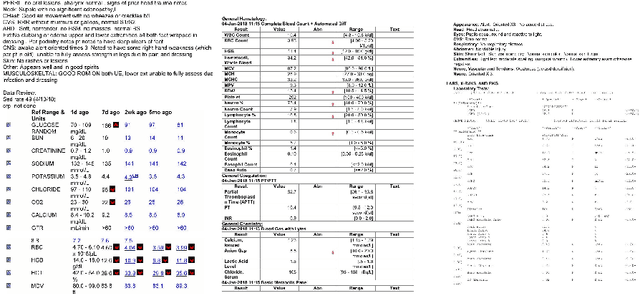

Abstract:In this paper, we propose DEXTER, an end to end system to extract information from tables present in medical health documents, such as electronic health records (EHR) and explanation of benefits (EOB). DEXTER consists of four sub-system stages: i) table detection ii) table type classification iii) cell detection; and iv) cell content extraction. We propose a two-stage transfer learning-based approach using CDeC-Net architecture along with Non-Maximal suppression for table detection. We design a conventional computer vision-based approach for table type classification and cell detection using parameterized kernels based on image size for detecting rows and columns. Finally, we extract the text from the detected cells using pre-existing OCR engine Tessaract. To evaluate our system, we manually annotated a sample of the real-world medical dataset (referred to as Meddata) consisting of wide variations of documents (in terms of appearance) covering different table structures, such as bordered, partially bordered, borderless, or coloured tables. We experimentally show that DEXTER outperforms the commercially available Amazon Textract and Microsoft Azure Form Recognizer systems on the annotated real-world medical dataset
RE-Tagger: A light-weight Real-Estate Image Classifier
Jul 12, 2022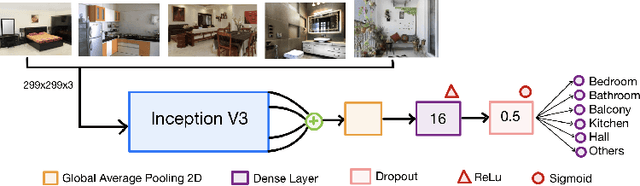
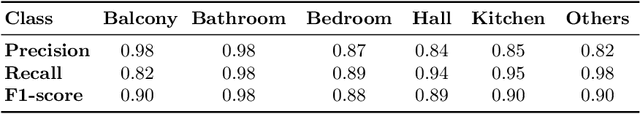
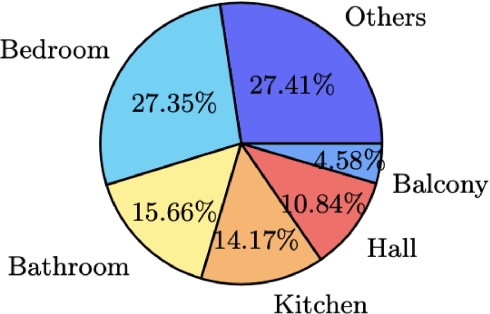

Abstract:Real-estate image tagging is one of the essential use-cases to save efforts involved in manual annotation and enhance the user experience. This paper proposes an end-to-end pipeline (referred to as RE-Tagger) for the real-estate image classification problem. We present a two-stage transfer learning approach using custom InceptionV3 architecture to classify images into different categories (i.e., bedroom, bathroom, kitchen, balcony, hall, and others). Finally, we released the application as REST API hosted as a web application running on 2 cores machine with 2 GB RAM. The demo video is available here.
Diversity-Aware Weighted Majority Vote Classifier for Imbalanced Data
Apr 16, 2020
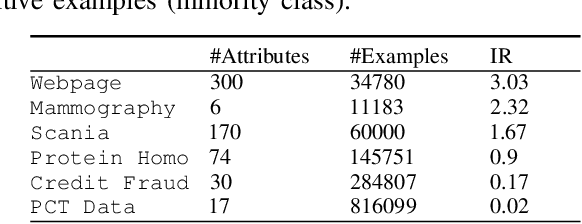
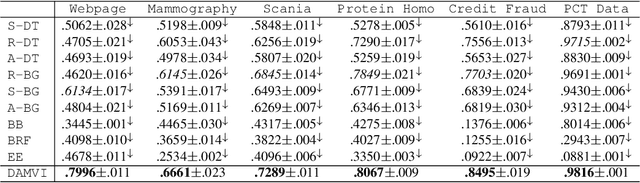

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a diversity-aware ensemble learning based algorithm, referred to as DAMVI, to deal with imbalanced binary classification tasks. Specifically, after learning base classifiers, the algorithm i) increases the weights of positive examples (minority class) which are "hard" to classify with uniformly weighted base classifiers; and ii) then learns weights over base classifiers by optimizing the PAC-Bayesian C-Bound that takes into account the accuracy and diversity between the classifiers. We show efficiency of the proposed approach with respect to state-of-art models on predictive maintenance task, credit card fraud detection, webpage classification and medical applications.
Multiview Boosting by Controlling the Diversity and the Accuracy of View-specific Voters
Aug 27, 2018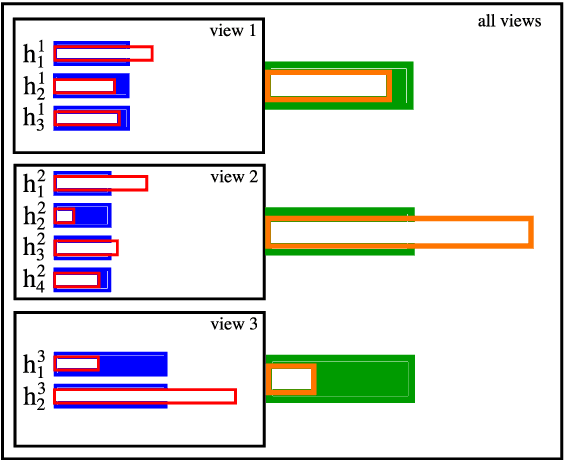
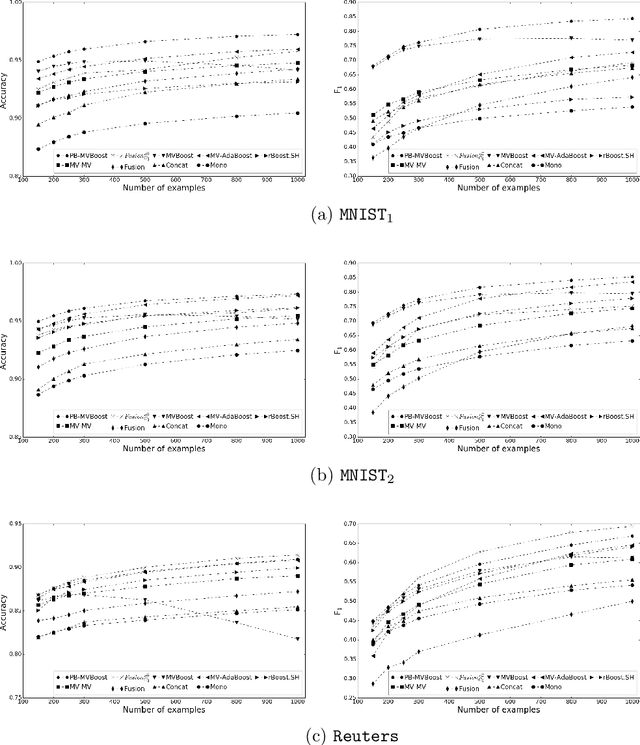
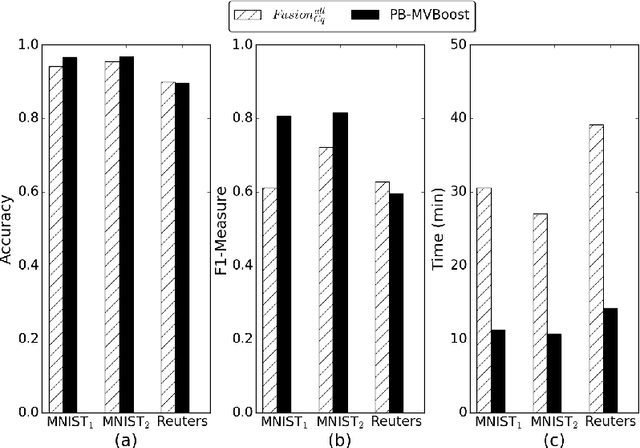
Abstract:In this paper we propose a boosting based multiview learning algorithm, referred to as PB-MVBoost, which iteratively learns i) weights over view-specific voters capturing view-specific information; and ii) weights over views by optimizing a PAC-Bayes multiview C-Bound that takes into account the accuracy of view-specific classifiers and the diversity between the views. We derive a generalization bound for this strategy following the PAC-Bayes theory which is a suitable tool to deal with models expressed as weighted combination over a set of voters. Different experiments on three publicly available datasets show the efficiency of the proposed approach with respect to state-of-art models.
Multiview Learning of Weighted Majority Vote by Bregman Divergence Minimization
May 25, 2018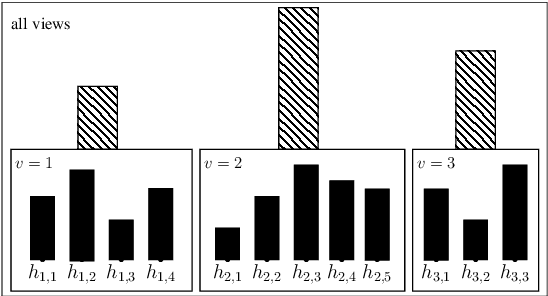

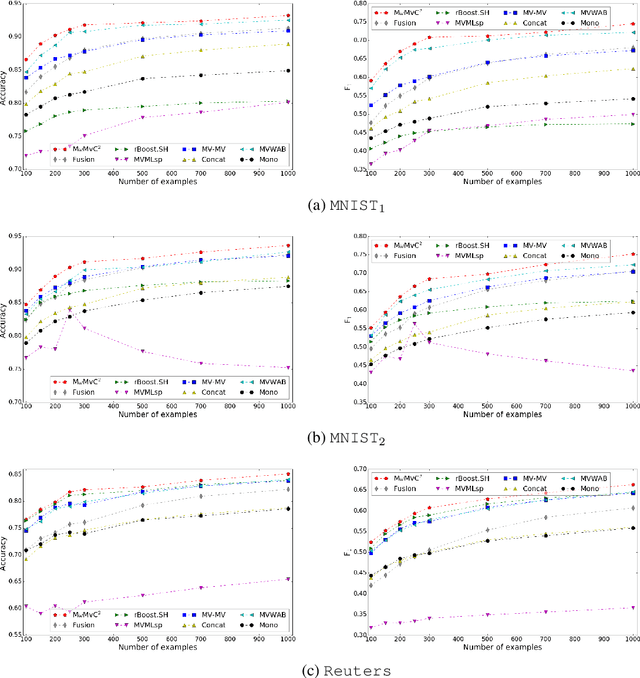
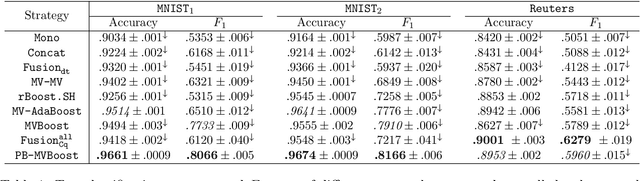
Abstract:We tackle the issue of classifier combinations when observations have multiple views. Our method jointly learns view-specific weighted majority vote classifiers (i.e. for each view) over a set of base voters, and a second weighted majority vote classifier over the set of these view-specific weighted majority vote classifiers. We show that the empirical risk minimization of the final majority vote given a multiview training set can be cast as the minimization of Bregman divergences. This allows us to derive a parallel-update optimization algorithm for learning our multiview model. We empirically study our algorithm with a particular focus on the impact of the training set size on the multiview learning results. The experiments show that our approach is able to overcome the lack of labeled information.
PAC-Bayesian Analysis for a two-step Hierarchical Multiview Learning Approach
Jul 13, 2017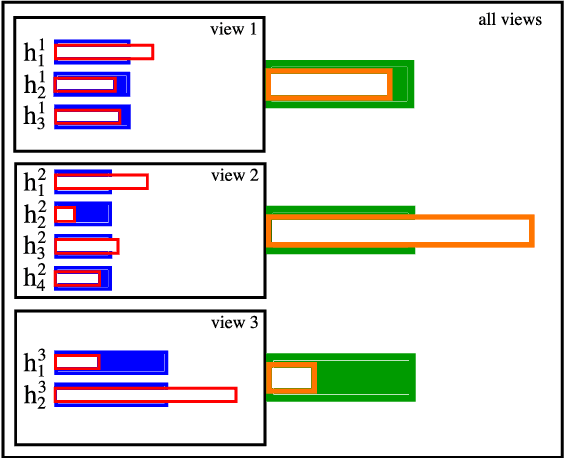
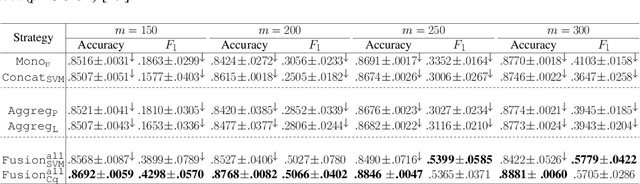
Abstract:We study a two-level multiview learning with more than two views under the PAC-Bayesian framework. This approach, sometimes referred as late fusion, consists in learning sequentially multiple view-specific classifiers at the first level, and then combining these view-specific classifiers at the second level. Our main theoretical result is a generalization bound on the risk of the majority vote which exhibits a term of diversity in the predictions of the view-specific classifiers. From this result it comes out that controlling the trade-off between diversity and accuracy is a key element for multiview learning, which complements other results in multiview learning. Finally, we experiment our principle on multiview datasets extracted from the Reuters RCV1/RCV2 collection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge