DEXTER: An end-to-end system to extract table contents from electronic medical health documents
Paper and Code
Jul 18, 2022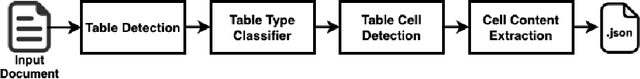

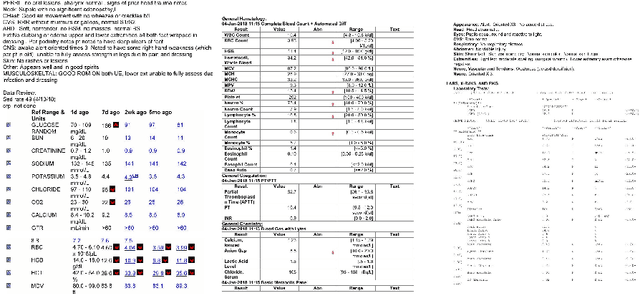

In this paper, we propose DEXTER, an end to end system to extract information from tables present in medical health documents, such as electronic health records (EHR) and explanation of benefits (EOB). DEXTER consists of four sub-system stages: i) table detection ii) table type classification iii) cell detection; and iv) cell content extraction. We propose a two-stage transfer learning-based approach using CDeC-Net architecture along with Non-Maximal suppression for table detection. We design a conventional computer vision-based approach for table type classification and cell detection using parameterized kernels based on image size for detecting rows and columns. Finally, we extract the text from the detected cells using pre-existing OCR engine Tessaract. To evaluate our system, we manually annotated a sample of the real-world medical dataset (referred to as Meddata) consisting of wide variations of documents (in terms of appearance) covering different table structures, such as bordered, partially bordered, borderless, or coloured tables. We experimentally show that DEXTER outperforms the commercially available Amazon Textract and Microsoft Azure Form Recognizer systems on the annotated real-world medical dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge