Anh-Quan Cao
Driving on Registers
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present DrivoR, a simple and efficient transformer-based architecture for end-to-end autonomous driving. Our approach builds on pretrained Vision Transformers (ViTs) and introduces camera-aware register tokens that compress multi-camera features into a compact scene representation, significantly reducing downstream computation without sacrificing accuracy. These tokens drive two lightweight transformer decoders that generate and then score candidate trajectories. The scoring decoder learns to mimic an oracle and predicts interpretable sub-scores representing aspects such as safety, comfort, and efficiency, enabling behavior-conditioned driving at inference. Despite its minimal design, DrivoR outperforms or matches strong contemporary baselines across NAVSIM-v1, NAVSIM-v2, and the photorealistic closed-loop HUGSIM benchmark. Our results show that a pure-transformer architecture, combined with targeted token compression, is sufficient for accurate, efficient, and adaptive end-to-end driving. Code and checkpoints will be made available via the project page.
StableMTL: Repurposing Latent Diffusion Models for Multi-Task Learning from Partially Annotated Synthetic Datasets
Jun 09, 2025
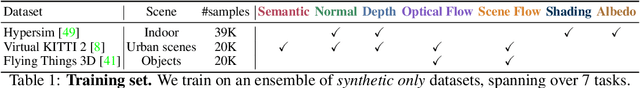
Abstract:Multi-task learning for dense prediction is limited by the need for extensive annotation for every task, though recent works have explored training with partial task labels. Leveraging the generalization power of diffusion models, we extend the partial learning setup to a zero-shot setting, training a multi-task model on multiple synthetic datasets, each labeled for only a subset of tasks. Our method, StableMTL, repurposes image generators for latent regression. Adapting a denoising framework with task encoding, per-task conditioning and a tailored training scheme. Instead of per-task losses requiring careful balancing, a unified latent loss is adopted, enabling seamless scaling to more tasks. To encourage inter-task synergy, we introduce a multi-stream model with a task-attention mechanism that converts N-to-N task interactions into efficient 1-to-N attention, promoting effective cross-task sharing. StableMTL outperforms baselines on 7 tasks across 8 benchmarks.
LatteCLIP: Unsupervised CLIP Fine-Tuning via LMM-Synthetic Texts
Oct 10, 2024
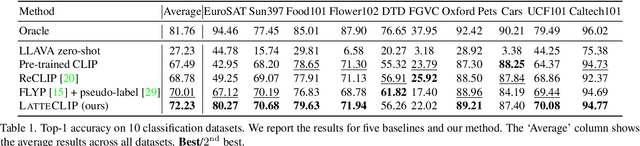

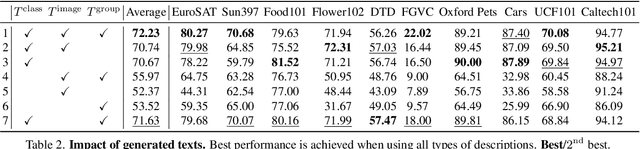
Abstract:Large-scale vision-language pre-trained (VLP) models (e.g., CLIP) are renowned for their versatility, as they can be applied to diverse applications in a zero-shot setup. However, when these models are used in specific domains, their performance often falls short due to domain gaps or the under-representation of these domains in the training data. While fine-tuning VLP models on custom datasets with human-annotated labels can address this issue, annotating even a small-scale dataset (e.g., 100k samples) can be an expensive endeavor, often requiring expert annotators if the task is complex. To address these challenges, we propose LatteCLIP, an unsupervised method for fine-tuning CLIP models on classification with known class names in custom domains, without relying on human annotations. Our method leverages Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to generate expressive textual descriptions for both individual images and groups of images. These provide additional contextual information to guide the fine-tuning process in the custom domains. Since LMM-generated descriptions are prone to hallucination or missing details, we introduce a novel strategy to distill only the useful information and stabilize the training. Specifically, we learn rich per-class prototype representations from noisy generated texts and dual pseudo-labels. Our experiments on 10 domain-specific datasets show that LatteCLIP outperforms pre-trained zero-shot methods by an average improvement of +4.74 points in top-1 accuracy and other state-of-the-art unsupervised methods by +3.45 points.
PaSCo: Urban 3D Panoptic Scene Completion with Uncertainty Awareness
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:We propose the task of Panoptic Scene Completion (PSC) which extends the recently popular Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) task with instance-level information to produce a richer understanding of the 3D scene. Our PSC proposal utilizes a hybrid mask-based technique on the non-empty voxels from sparse multi-scale completions. Whereas the SSC literature overlooks uncertainty which is critical for robotics applications, we instead propose an efficient ensembling to estimate both voxel-wise and instance-wise uncertainties along PSC. This is achieved by building on a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) strategy, while improving performance and yielding better uncertainty for little additional compute. Additionally, we introduce a technique to aggregate permutation-invariant mask predictions. Our experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses all baselines in both Panoptic Scene Completion and uncertainty estimation on three large-scale autonomous driving datasets. Our code and data are available at https://astra-vision.github.io/PaSCo .
SceneRF: Self-Supervised Monocular 3D Scene Reconstruction with Radiance Fields
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:In the literature, 3D reconstruction from 2D image has been extensively addressed but often still requires geometrical supervision. In this paper, we propose SceneRF, a self-supervised monocular scene reconstruction method with neural radiance fields (NeRF) learned from multiple image sequences with pose. To improve geometry prediction, we introduce new geometry constraints and a novel probabilistic sampling strategy that efficiently update radiance fields. As the latter are conditioned on a single frame, scene reconstruction is achieved from the fusion of multiple synthesized novel depth views. This is enabled by our spherical-decoder, which allows hallucination beyond the input frame field of view. Thorough experiments demonstrate that we outperform all baselines on all metrics for novel depth views synthesis and scene reconstruction. Our code is available at https://astra-vision.github.io/SceneRF.
COARSE3D: Class-Prototypes for Contrastive Learning in Weakly-Supervised 3D Point Cloud Segmentation
Oct 08, 2022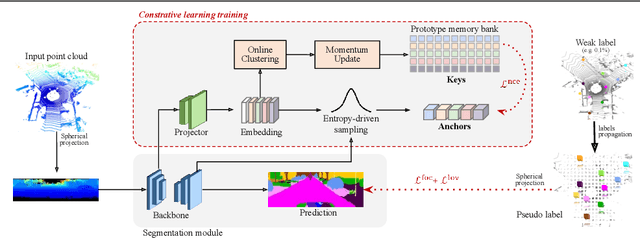
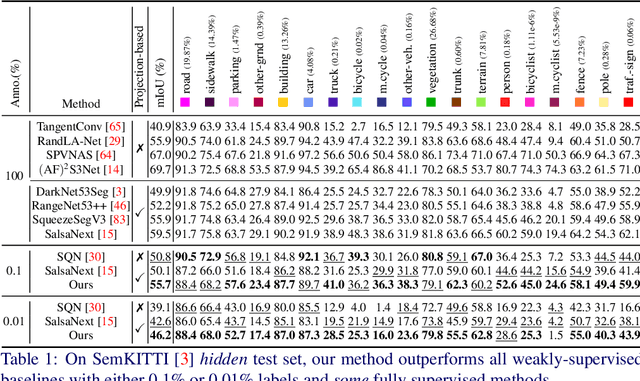
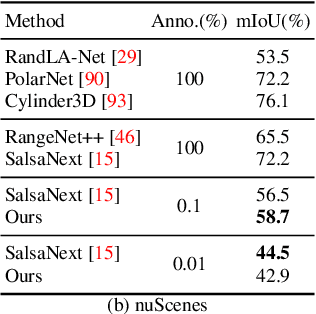
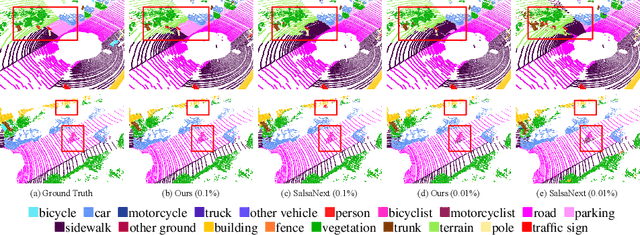
Abstract:Annotation of large-scale 3D data is notoriously cumbersome and costly. As an alternative, weakly-supervised learning alleviates such a need by reducing the annotation by several order of magnitudes. We propose COARSE3D, a novel architecture-agnostic contrastive learning strategy for 3D segmentation. Since contrastive learning requires rich and diverse examples as keys and anchors, we leverage a prototype memory bank capturing class-wise global dataset information efficiently into a small number of prototypes acting as keys. An entropy-driven sampling technique then allows us to select good pixels from predictions as anchors. Experiments on three projection-based backbones show we outperform baselines on three challenging real-world outdoor datasets, working with as low as 0.001% annotations.
MonoScene: Monocular 3D Semantic Scene Completion
Dec 01, 2021

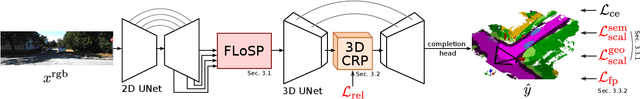

Abstract:MonoScene proposes a 3D Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) framework, where the dense geometry and semantics of a scene are inferred from a single monocular RGB image. Different from the SSC literature, relying on 2.5 or 3D input, we solve the complex problem of 2D to 3D scene reconstruction while jointly inferring its semantics. Our framework relies on successive 2D and 3D UNets bridged by a novel 2D-3D features projection inspiring from optics and introduces a 3D context relation prior to enforce spatio-semantic consistency. Along with architectural contributions, we introduce novel global scene and local frustums losses. Experiments show we outperform the literature on all metrics and datasets while hallucinating plausible scenery even beyond the camera field of view. Our code and trained models are available at https://github.com/cv-rits/MonoScene
PCAM: Product of Cross-Attention Matrices for Rigid Registration of Point Clouds
Oct 04, 2021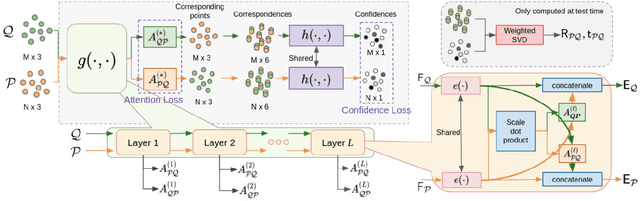
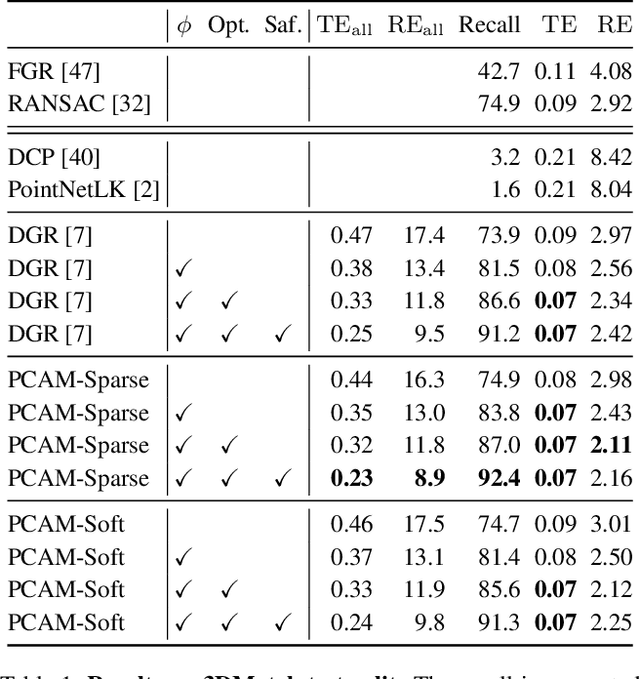
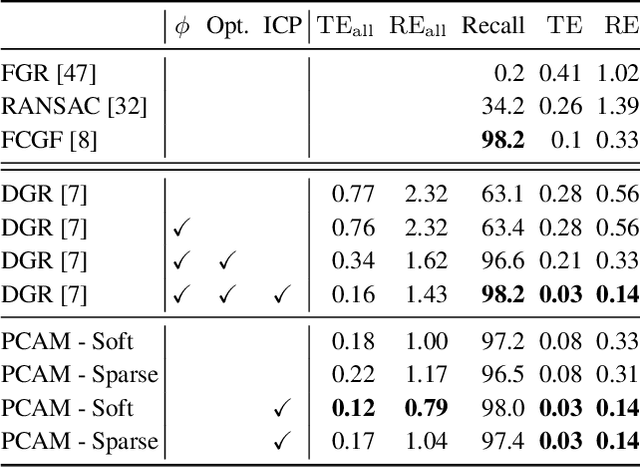
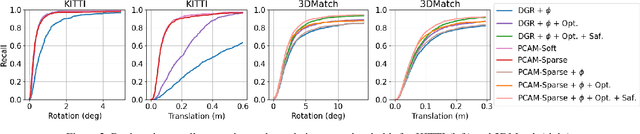
Abstract:Rigid registration of point clouds with partial overlaps is a longstanding problem usually solved in two steps: (a) finding correspondences between the point clouds; (b) filtering these correspondences to keep only the most reliable ones to estimate the transformation. Recently, several deep nets have been proposed to solve these steps jointly. We built upon these works and propose PCAM: a neural network whose key element is a pointwise product of cross-attention matrices that permits to mix both low-level geometric and high-level contextual information to find point correspondences. These cross-attention matrices also permits the exchange of context information between the point clouds, at each layer, allowing the network construct better matching features within the overlapping regions. The experiments show that PCAM achieves state-of-the-art results among methods which, like us, solve steps (a) and (b) jointly via deepnets. Our code and trained models are available at https://github.com/valeoai/PCAM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge