Anh Thi Luu
Bias and Diversity in Synthetic-based Face Recognition
Nov 07, 2023



Abstract:Synthetic data is emerging as a substitute for authentic data to solve ethical and legal challenges in handling authentic face data. The current models can create real-looking face images of people who do not exist. However, it is a known and sensitive problem that face recognition systems are susceptible to bias, i.e. performance differences between different demographic and non-demographics attributes, which can lead to unfair decisions. In this work, we investigate how the diversity of synthetic face recognition datasets compares to authentic datasets, and how the distribution of the training data of the generative models affects the distribution of the synthetic data. To do this, we looked at the distribution of gender, ethnicity, age, and head position. Furthermore, we investigated the concrete bias of three recent synthetic-based face recognition models on the studied attributes in comparison to a baseline model trained on authentic data. Our results show that the generator generate a similar distribution as the used training data in terms of the different attributes. With regard to bias, it can be seen that the synthetic-based models share a similar bias behavior with the authentic-based models. However, with the uncovered lower intra-identity attribute consistency seems to be beneficial in reducing bias.
Efficient Explainable Face Verification based on Similarity Score Argument Backpropagation
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Explainable Face Recognition is gaining growing attention as the use of the technology is gaining ground in security-critical applications. Understanding why two faces images are matched or not matched by a given face recognition system is important to operators, users, anddevelopers to increase trust, accountability, develop better systems, and highlight unfair behavior. In this work, we propose xSSAB, an approach to back-propagate similarity score-based arguments that support or oppose the face matching decision to visualize spatial maps that indicate similar and dissimilar areas as interpreted by the underlying FR model. Furthermore, we present Patch-LFW, a new explainable face verification benchmark that enables along with a novel evaluation protocol, the first quantitative evaluation of the validity of similarity and dissimilarity maps in explainable face recognition approaches. We compare our efficient approach to state-of-the-art approaches demonstrating a superior trade-off between efficiency and performance. The code as well as the proposed Patch-LFW is publicly available at: https://github.com/marcohuber/xSSAB.
SYN-MAD 2022: Competition on Face Morphing Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data
Aug 15, 2022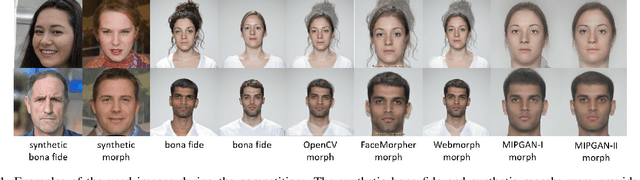
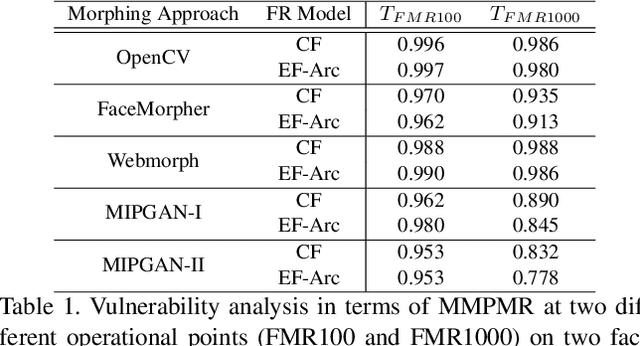
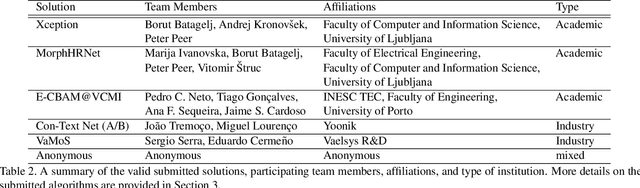
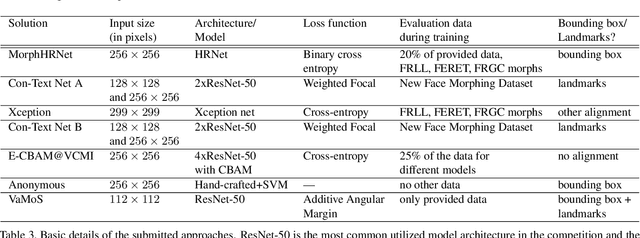
Abstract:This paper presents a summary of the Competition on Face Morphing Attack Detection Based on Privacy-aware Synthetic Training Data (SYN-MAD) held at the 2022 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB 2022). The competition attracted a total of 12 participating teams, both from academia and industry and present in 11 different countries. In the end, seven valid submissions were submitted by the participating teams and evaluated by the organizers. The competition was held to present and attract solutions that deal with detecting face morphing attacks while protecting people's privacy for ethical and legal reasons. To ensure this, the training data was limited to synthetic data provided by the organizers. The submitted solutions presented innovations that led to outperforming the considered baseline in many experimental settings. The evaluation benchmark is now available at: https://github.com/marcohuber/SYN-MAD-2022.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge