Andreas Zeller
Synthesizing Realistic Test Data without Breaking Privacy
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:There is a need for synthetic training and test datasets that replicate statistical distributions of original datasets without compromising their confidentiality. A lot of research has been done in leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for synthetic data generation. However, the resulting models are either not accurate enough or are still vulnerable to membership inference attacks (MIA) or dataset reconstruction attacks since the original data has been leveraged in the training process. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of producing a synthetic test dataset with the same statistical properties as the original one, with only indirectly leveraging the original data in the generation process. The approach is inspired by GANs, with a generation step and a discrimination step. However, in our approach, we use a test generator (a fuzzer) to produce test data from an input specification, preserving constraints set by the original data; a discriminator model determines how close we are to the original data. By evolving samples and determining "good samples" with the discriminator, we can generate privacy-preserving data that follows the same statistical distributions are the original dataset, leading to a similar utility as the original data. We evaluated our approach on four datasets that have been used to evaluate the state-of-the-art techniques. Our experiments highlight the potential of our approach towards generating synthetic datasets that have high utility while preserving privacy.
Will AI replace Software Engineers? Hold your Breath
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology such as Large Language Models (LLMs) have become extremely popular in creating code. This has led to the conjecture that future software jobs will be exclusively conducted by LLMs, and the software industry will cease to exist. But software engineering is much more than producing code -- notably, \emph{maintaining} large software and keeping it reliable is a major part of software engineering, which LLMs are not yet capable of.
Learning Program Behavioral Models from Synthesized Input-Output Pairs
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Modelizer - a novel framework that, given a black-box program, learns a _model from its input/output behavior_ using _neural machine translation_. The resulting model _mocks_ the original program: Given an input, the model predicts the output that would have been produced by the program. However, the model is also _reversible_ - that is, the model can predict the input that would have produced a given output. Finally, the model is _differentiable_ and can be efficiently restricted to predict only a certain aspect of the program behavior. Modelizer uses _grammars_ to synthesize inputs and to parse the resulting outputs, allowing it to learn sequence-to-sequence associations between token streams. Other than input and output grammars, Modelizer only requires the ability to execute the program. The resulting models are _small_, requiring fewer than 6.3 million parameters for languages such as Markdown or HTML; and they are _accurate_, achieving up to 95.4% accuracy and a BLEU score of 0.98 with standard error 0.04 in mocking real-world applications. We foresee several _applications_ of these models, especially as the output of the program can be any aspect of program behavior. Besides mocking and predicting program behavior, the model can also synthesize inputs that are likely to produce a particular behavior, such as failures or coverage.
Revisiting Neural Program Smoothing for Fuzzing
Sep 28, 2023Abstract:Testing with randomly generated inputs (fuzzing) has gained significant traction due to its capacity to expose program vulnerabilities automatically. Fuzz testing campaigns generate large amounts of data, making them ideal for the application of machine learning (ML). Neural program smoothing (NPS), a specific family of ML-guided fuzzers, aims to use a neural network as a smooth approximation of the program target for new test case generation. In this paper, we conduct the most extensive evaluation of NPS fuzzers against standard gray-box fuzzers (>11 CPU years and >5.5 GPU years), and make the following contributions: (1) We find that the original performance claims for NPS fuzzers do not hold; a gap we relate to fundamental, implementation, and experimental limitations of prior works. (2) We contribute the first in-depth analysis of the contribution of machine learning and gradient-based mutations in NPS. (3) We implement Neuzz++, which shows that addressing the practical limitations of NPS fuzzers improves performance, but that standard gray-box fuzzers almost always surpass NPS-based fuzzers. (4) As a consequence, we propose new guidelines targeted at benchmarking fuzzing based on machine learning, and present MLFuzz, a platform with GPU access for easy and reproducible evaluation of ML-based fuzzers. Neuzz++, MLFuzz, and all our data are public.
Exposing Backdoors in Robust Machine Learning Models
Feb 25, 2020
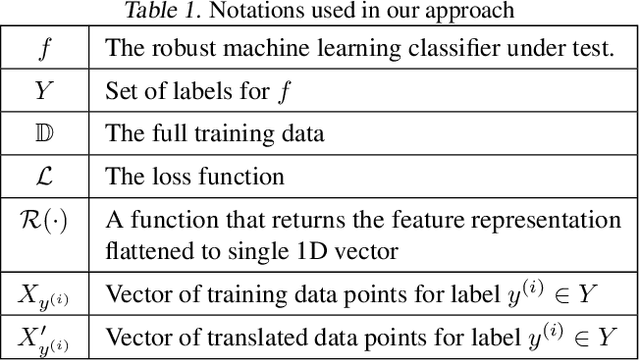
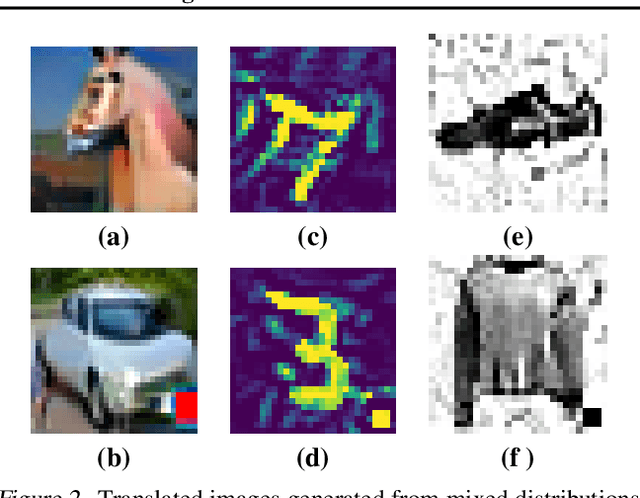

Abstract:The introduction of robust optimisation has pushed the state-of-the-art in defending against adversarial attacks. However, the behaviour of such optimisation has not been studied in the light of a fundamentally different class of attacks called backdoors. In this paper, we demonstrate that adversarially robust models are susceptible to backdoor attacks. Subsequently, we observe that backdoors are reflected in the feature representation of such models. Then, this is leveraged to detect backdoor-infected models. Specifically, we use feature clustering to effectively detect backdoor-infected robust Deep Neural Networks (DNNs). In our evaluation of major classification tasks, our approach effectively detects robust DNNs infected with backdoors. Our investigation reveals that salient features of adversarially robust DNNs break the stealthy nature of backdoor attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge