Anastasia Voznyuk
Feature-Level Insights into Artificial Text Detection with Sparse Autoencoders
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Artificial Text Detection (ATD) is becoming increasingly important with the rise of advanced Large Language Models (LLMs). Despite numerous efforts, no single algorithm performs consistently well across different types of unseen text or guarantees effective generalization to new LLMs. Interpretability plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. In this study, we enhance ATD interpretability by using Sparse Autoencoders (SAE) to extract features from Gemma-2-2b residual stream. We identify both interpretable and efficient features, analyzing their semantics and relevance through domain- and model-specific statistics, a steering approach, and manual or LLM-based interpretation. Our methods offer valuable insights into how texts from various models differ from human-written content. We show that modern LLMs have a distinct writing style, especially in information-dense domains, even though they can produce human-like outputs with personalized prompts.
Quantifying Logical Consistency in Transformers via Query-Key Alignment
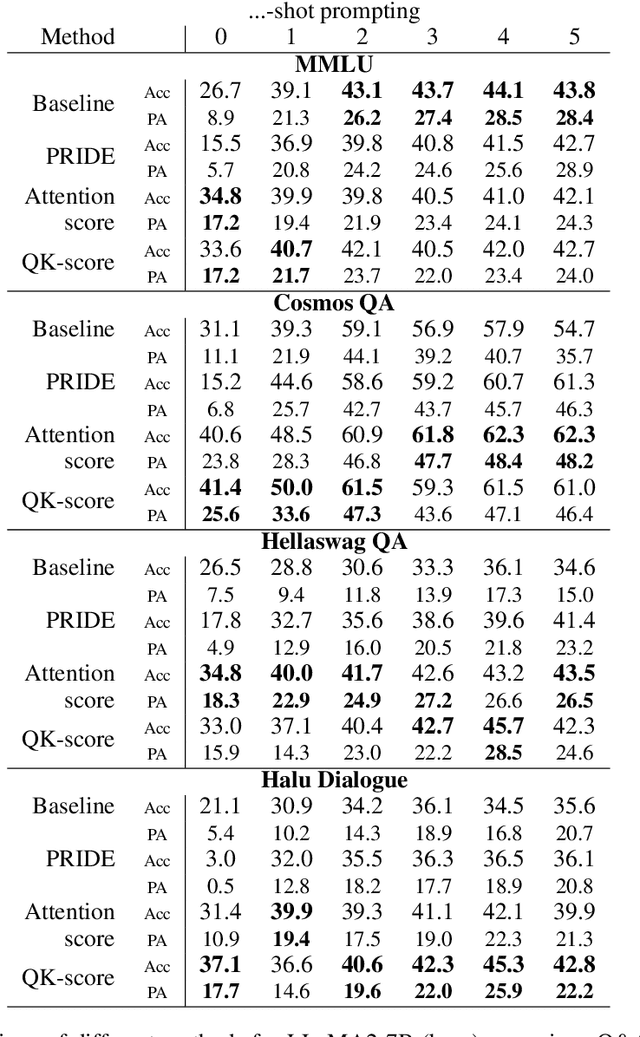
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in various natural language processing tasks, yet their ability to perform multi-step logical reasoning remains an open challenge. Although Chain-of-Thought prompting has improved logical reasoning by enabling models to generate intermediate steps, it lacks mechanisms to assess the coherence of these logical transitions. In this paper, we propose a novel, lightweight evaluation strategy for logical reasoning that uses query-key alignments inside transformer attention heads. By computing a single forward pass and extracting a "QK-score" from carefully chosen heads, our method reveals latent representations that reliably separate valid from invalid inferences, offering a scalable alternative to traditional ablation-based techniques. We also provide an empirical validation on multiple logical reasoning benchmarks, demonstrating improved robustness of our evaluation method against distractors and increased reasoning depth. The experiments were conducted on a diverse set of models, ranging from 1.5B to 70B parameters.
Advacheck at GenAI Detection Task 1: AI Detection Powered by Domain-Aware Multi-Tasking
Nov 18, 2024
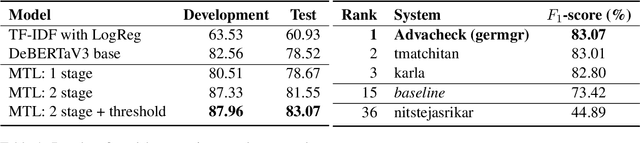
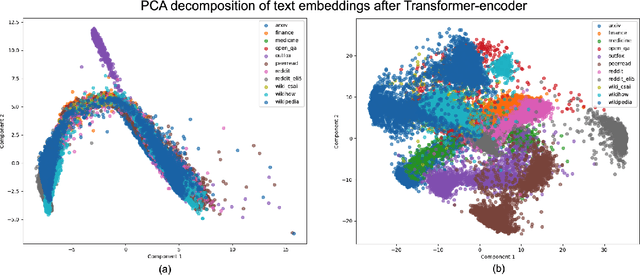
Abstract:The paper describes a system designed by Advacheck team to recognise machine-generated and human-written texts in the monolingual subtask of GenAI Detection Task 1 competition. Our developed system is a multi-task architecture with shared Transformer Encoder between several classification heads. One head is responsible for binary classification between human-written and machine-generated texts, while the other heads are auxiliary multiclass classifiers for texts of different domains from particular datasets. As multiclass heads were trained to distinguish the domains presented in the data, they provide a better understanding of the samples. This approach led us to achieve the first place in the official ranking with 83.07% macro F1-score on the test set and bypass the baseline by 10%. We further study obtained system through ablation, error and representation analyses, finding that multi-task learning outperforms single-task mode and simultaneous tasks form a cluster structure in embeddings space.
Are AI Detectors Good Enough? A Survey on Quality of Datasets With Machine-Generated Texts
Oct 18, 2024
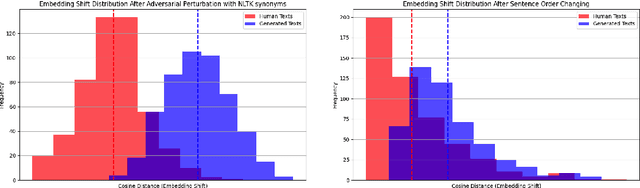
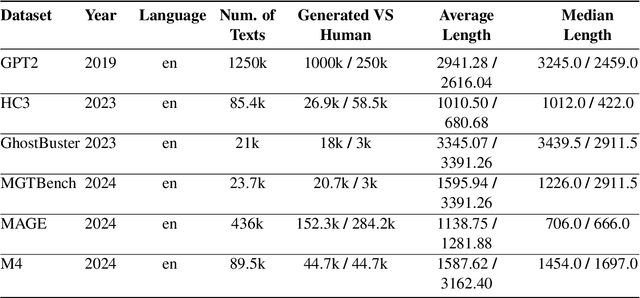
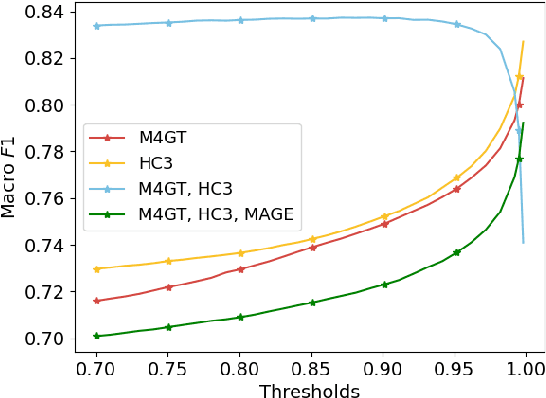
Abstract:The rapid development of autoregressive Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly improved the quality of generated texts, necessitating reliable machine-generated text detectors. A huge number of detectors and collections with AI fragments have emerged, and several detection methods even showed recognition quality up to 99.9% according to the target metrics in such collections. However, the quality of such detectors tends to drop dramatically in the wild, posing a question: Are detectors actually highly trustworthy or do their high benchmark scores come from the poor quality of evaluation datasets? In this paper, we emphasise the need for robust and qualitative methods for evaluating generated data to be secure against bias and low generalising ability of future model. We present a systematic review of datasets from competitions dedicated to AI-generated content detection and propose methods for evaluating the quality of datasets containing AI-generated fragments. In addition, we discuss the possibility of using high-quality generated data to achieve two goals: improving the training of detection models and improving the training datasets themselves. Our contribution aims to facilitate a better understanding of the dynamics between human and machine text, which will ultimately support the integrity of information in an increasingly automated world.
Listening to the Wise Few: Select-and-Copy Attention Heads for Multiple-Choice QA
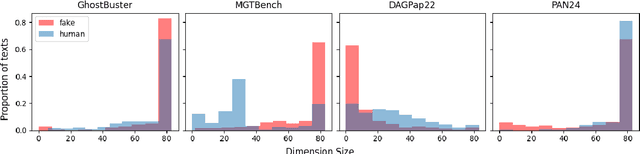
Oct 03, 2024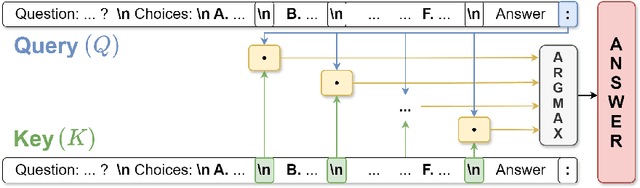
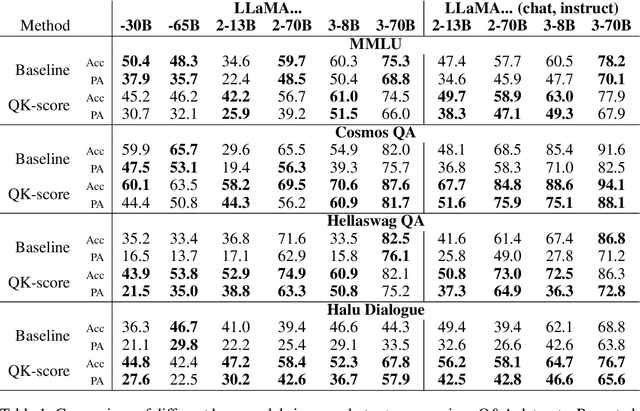
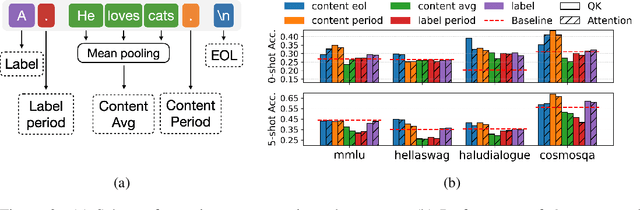
Abstract:A standard way to evaluate the abilities of LLM involves presenting a multiple-choice question and selecting the option with the highest logit as the model's predicted answer. However, such a format for evaluating LLMs has limitations, since even if the model knows the correct answer, it may struggle to select the corresponding letter simply due to difficulties in following this rigid format. To address this, we introduce new scores that better capture and reveal model's underlying knowledge: the Query-Key Score (QK-score), derived from the interaction between query and key representations in attention heads, and the Attention Score, based on attention weights. These scores are extracted from specific \textit{select-and-copy} heads, which show consistent performance across popular Multi-Choice Question Answering (MCQA) datasets. Based on these scores, our method improves knowledge extraction, yielding up to 16\% gain for LLaMA2-7B and up to 10\% for larger models on popular MCQA benchmarks. At the same time, the accuracy on a simple synthetic dataset, where the model explicitly knows the right answer, increases by almost 60\%, achieving nearly perfect accuracy, therefore demonstrating the method's efficiency in mitigating MCQA format limitations. To support our claims, we conduct experiments on models ranging from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters in both zero- and few-shot setups.
DeepPavlov at SemEval-2024 Task 8: Leveraging Transfer Learning for Detecting Boundaries of Machine-Generated Texts
May 17, 2024



Abstract:The Multigenerator, Multidomain, and Multilingual Black-Box Machine-Generated Text Detection shared task in the SemEval-2024 competition aims to tackle the problem of misusing collaborative human-AI writing. Although there are a lot of existing detectors of AI content, they are often designed to give a binary answer and thus may not be suitable for more nuanced problem of finding the boundaries between human-written and machine-generated texts, while hybrid human-AI writing becomes more and more popular. In this paper, we address the boundary detection problem. Particularly, we present a pipeline for augmenting data for supervised fine-tuning of DeBERTaV3. We receive new best MAE score, according to the leaderboard of the competition, with this pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge