Anastasia Giachanou
Utrecht University
Evaluating GRPO and DPO for Faithful Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning has emerged as a powerful technique for improving the problem-solving capabilities of large language models (LLMs), particularly for tasks requiring multi-step reasoning. However, recent studies show that CoT explanations often fail to reflect the model's actual reasoning process, as models may produce coherent yet misleading justifications or modify answers without acknowledging external cues. Such discrepancies undermine the reliability of CoT-based methods for safety supervision and alignment monitoring, as models can generate plausible but deceptive rationales for incorrect answers. To better understand this limitation, we evaluate two optimization methods, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), in their ability to improve CoT faithfulness. Our experiments show that GRPO achieves higher performance than DPO in larger models, with the Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct model attaining the best results across all evaluation metrics. Both approaches exhibit positive correlations between model size and performance, but GRPO shows greater potential for improving faithfulness metrics, albeit with less stable behavior at smaller scales. These results suggest that GRPO offers a promising direction for developing more transparent and trustworthy reasoning in LLMs.
Assessing the Reliability of LLMs Annotations in the Context of Demographic Bias and Model Explanation
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Understanding the sources of variability in annotations is crucial for developing fair NLP systems, especially for tasks like sexism detection where demographic bias is a concern. This study investigates the extent to which annotator demographic features influence labeling decisions compared to text content. Using a Generalized Linear Mixed Model, we quantify this inf luence, finding that while statistically present, demographic factors account for a minor fraction ( 8%) of the observed variance, with tweet content being the dominant factor. We then assess the reliability of Generative AI (GenAI) models as annotators, specifically evaluating if guiding them with demographic personas improves alignment with human judgments. Our results indicate that simplistic persona prompting often fails to enhance, and sometimes degrades, performance compared to baseline models. Furthermore, explainable AI (XAI) techniques reveal that model predictions rely heavily on content-specific tokens related to sexism, rather than correlates of demographic characteristics. We argue that focusing on content-driven explanations and robust annotation protocols offers a more reliable path towards fairness than potentially persona simulation.
From Data-Driven to Purpose-Driven Artificial Intelligence: Systems Thinking for Data-Analytic Automation of Patient Care
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:In this work, we reflect on the data-driven modeling paradigm that is gaining ground in AI-driven automation of patient care. We argue that the repurposing of existing real-world patient datasets for machine learning may not always represent an optimal approach to model development as it could lead to undesirable outcomes in patient care. We reflect on the history of data analysis to explain how the data-driven paradigm rose to popularity, and we envision ways in which systems thinking and clinical domain theory could complement the existing model development approaches in reaching human-centric outcomes. We call for a purpose-driven machine learning paradigm that is grounded in clinical theory and the sociotechnical realities of real-world operational contexts. We argue that understanding the utility of existing patient datasets requires looking in two directions: upstream towards the data generation, and downstream towards the automation objectives. This purpose-driven perspective to AI system development opens up new methodological opportunities and holds promise for AI automation of patient care.
Explainability-Based Token Replacement on LLM-Generated Text
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Generative models, especially large language models (LLMs), have shown remarkable progress in producing text that appears human-like. However, they often exhibit patterns that make their output easier to detect than text written by humans. In this paper, we investigate how explainable AI (XAI) methods can be used to reduce the detectability of AI-generated text (AIGT) while also introducing a robust ensemble-based detection approach. We begin by training an ensemble classifier to distinguish AIGT from human-written text, then apply SHAP and LIME to identify tokens that most strongly influence its predictions. We propose four explainability-based token replacement strategies to modify these influential tokens. Our findings show that these token replacement approaches can significantly diminish a single classifier's ability to detect AIGT. However, our ensemble classifier maintains strong performance across multiple languages and domains, showing that a multi-model approach can mitigate the impact of token-level manipulations. These results show that XAI methods can make AIGT harder to detect by focusing on the most influential tokens. At the same time, they highlight the need for robust, ensemble-based detection strategies that can adapt to evolving approaches for hiding AIGT.
Stereotype Detection in Natural Language Processing
May 23, 2025Abstract:Stereotypes influence social perceptions and can escalate into discrimination and violence. While NLP research has extensively addressed gender bias and hate speech, stereotype detection remains an emerging field with significant societal implications. In this work is presented a survey of existing research, analyzing definitions from psychology, sociology, and philosophy. A semi-automatic literature review was performed by using Semantic Scholar. We retrieved and filtered over 6,000 papers (in the year range 2000-2025), identifying key trends, methodologies, challenges and future directions. The findings emphasize stereotype detection as a potential early-monitoring tool to prevent bias escalation and the rise of hate speech. Conclusions highlight the need for a broader, multilingual, and intersectional approach in NLP studies.
Explainability in Practice: A Survey of Explainable NLP Across Various Domains
Feb 02, 2025



Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) has become a cornerstone in many critical sectors, including healthcare, finance, and customer relationship management. This is especially true with the development and use of advanced models such as GPT-based architectures and BERT, which are widely used in decision-making processes. However, the black-box nature of these advanced NLP models has created an urgent need for transparency and explainability. This review explores explainable NLP (XNLP) with a focus on its practical deployment and real-world applications, examining its implementation and the challenges faced in domain-specific contexts. The paper underscores the importance of explainability in NLP and provides a comprehensive perspective on how XNLP can be designed to meet the unique demands of various sectors, from healthcare's need for clear insights to finance's emphasis on fraud detection and risk assessment. Additionally, this review aims to bridge the knowledge gap in XNLP literature by offering a domain-specific exploration and discussing underrepresented areas such as real-world applicability, metric evaluation, and the role of human interaction in model assessment. The paper concludes by suggesting future research directions that could enhance the understanding and broader application of XNLP.
On Text-based Personality Computing: Challenges and Future Directions
Dec 14, 2022Abstract:Text-based personality computing (TPC) has gained many research interests in NLP. In this paper, we describe 15 challenges that we consider deserving the attention of the research community. These challenges are organized by the following topics: personality taxonomies, measurement quality, datasets, performance evaluation, modelling choices, as well as ethics and fairness. When addressing each challenge, not only do we combine perspectives from both NLP and social sciences, but also offer concrete suggestions towards more valid and reliable TPC research.
Modelling Stance Detection as Textual Entailment Recognition and Leveraging Measurement Knowledge from Social Sciences
Dec 13, 2022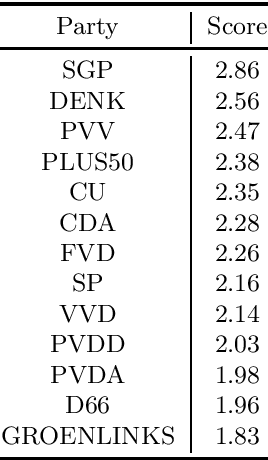
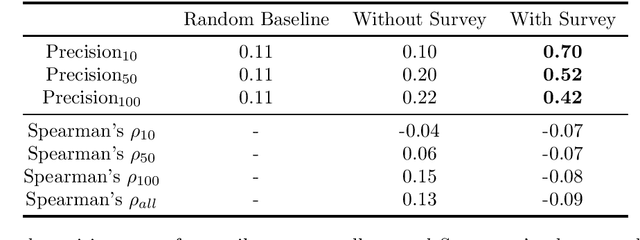
Abstract:Stance detection (SD) can be considered a special case of textual entailment recognition (TER), a generic natural language task. Modelling SD as TER may offer benefits like more training data and a more general learning scheme. In this paper, we present an initial empirical analysis of this approach. We apply it to a difficult but relevant test case where no existing labelled SD dataset is available, because this is where modelling SD as TER may be especially helpful. We also leverage measurement knowledge from social sciences to improve model performance. We discuss our findings and suggest future research directions.
Surveying the Research on Fake News in Social Media: a Tale of Networks and Language
Sep 13, 2021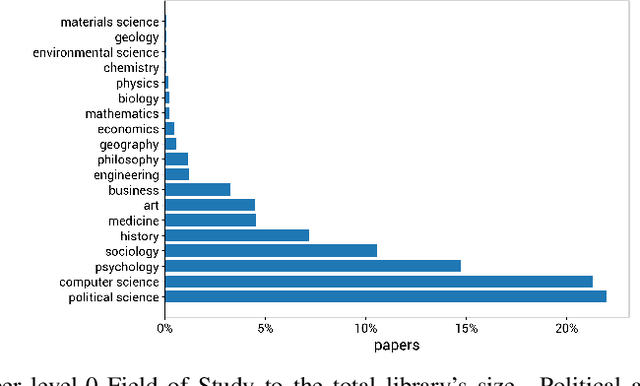
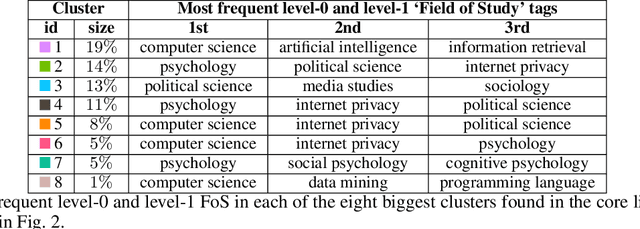
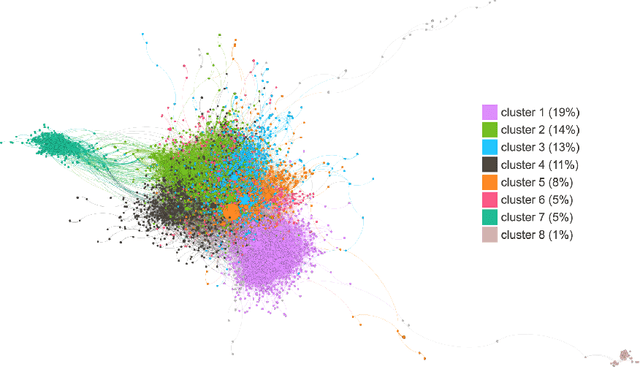
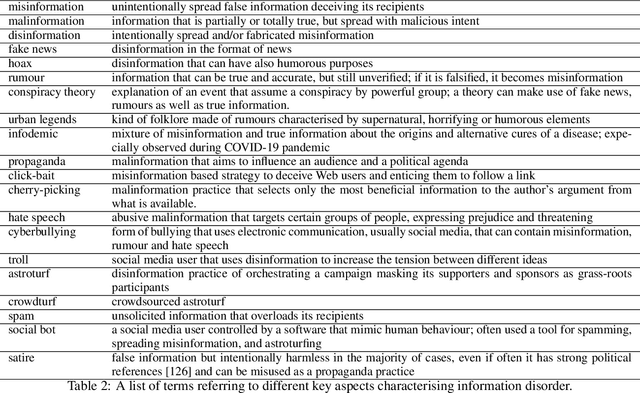
Abstract:The history of journalism and news diffusion is tightly coupled with the effort to dispel hoaxes, misinformation, propaganda, unverified rumours, poor reporting, and messages containing hate and divisions. With the explosive growth of online social media and billions of individuals engaged with consuming, creating, and sharing news, this ancient problem has surfaced with a renewed intensity threatening our democracies, public health, and news outlets credibility. This has triggered many researchers to develop new methods for studying, understanding, detecting, and preventing fake-news diffusion; as a consequence, thousands of scientific papers have been published in a relatively short period, making researchers of different disciplines to struggle in search of open problems and most relevant trends. The aim of this survey is threefold: first, we want to provide the researchers interested in this multidisciplinary and challenging area with a network-based analysis of the existing literature to assist them with a visual exploration of papers that can be of interest; second, we present a selection of the main results achieved so far adopting the network as an unifying framework to represent and make sense of data, to model diffusion processes, and to evaluate different debunking strategies. Finally, we present an outline of the most relevant research trends focusing on the moving target of fake-news, bots, and trolls identification by means of data mining and text technologies; despite scholars working on computational linguistics and networks traditionally belong to different scientific communities, we expect that forthcoming computational approaches to prevent fake news from polluting the social media must be developed using hybrid and up-to-date methodologies.
Comparative Opinion Mining: A Review
Dec 24, 2017Abstract:Opinion mining refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in textual material. Opinion mining, also known as sentiment analysis, has received a lot of attention in recent times, as it provides a number of tools to analyse the public opinion on a number of different topics. Comparative opinion mining is a subfield of opinion mining that deals with identifying and extracting information that is expressed in a comparative form (e.g.~"paper X is better than the Y"). Comparative opinion mining plays a very important role when ones tries to evaluate something, as it provides a reference point for the comparison. This paper provides a review of the area of comparative opinion mining. It is the first review that cover specifically this topic as all previous reviews dealt mostly with general opinion mining. This survey covers comparative opinion mining from two different angles. One from perspective of techniques and the other from perspective of comparative opinion elements. It also incorporates preprocessing tools as well as dataset that were used by the past researchers that can be useful to the future researchers in the field of comparative opinion mining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge