Modelling Stance Detection as Textual Entailment Recognition and Leveraging Measurement Knowledge from Social Sciences
Paper and Code
Dec 13, 2022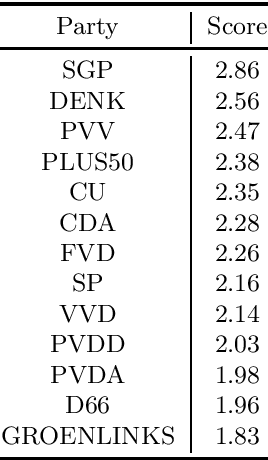
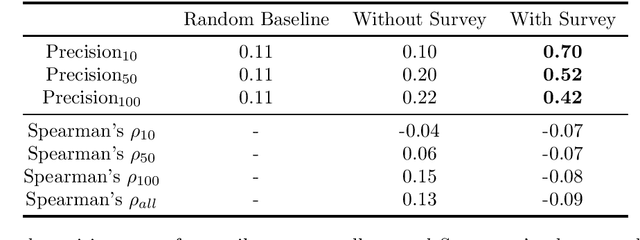
Stance detection (SD) can be considered a special case of textual entailment recognition (TER), a generic natural language task. Modelling SD as TER may offer benefits like more training data and a more general learning scheme. In this paper, we present an initial empirical analysis of this approach. We apply it to a difficult but relevant test case where no existing labelled SD dataset is available, because this is where modelling SD as TER may be especially helpful. We also leverage measurement knowledge from social sciences to improve model performance. We discuss our findings and suggest future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge