Anand Kumar M
Towards Unsupervised Question Answering System with Multi-level Summarization for Legal Text
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:This paper summarizes Team SCaLAR's work on SemEval-2024 Task 5: Legal Argument Reasoning in Civil Procedure. To address this Binary Classification task, which was daunting due to the complexity of the Legal Texts involved, we propose a simple yet novel similarity and distance-based unsupervised approach to generate labels. Further, we explore the Multi-level fusion of Legal-Bert embeddings using ensemble features, including CNN, GRU, and LSTM. To address the lengthy nature of Legal explanation in the dataset, we introduce T5-based segment-wise summarization, which successfully retained crucial information, enhancing the model's performance. Our unsupervised system witnessed a 20-point increase in macro F1-score on the development set and a 10-point increase on the test set, which is promising given its uncomplicated architecture.
Signed Link Representation in Continuous-Time Dynamic Signed Networks
Jul 07, 2022
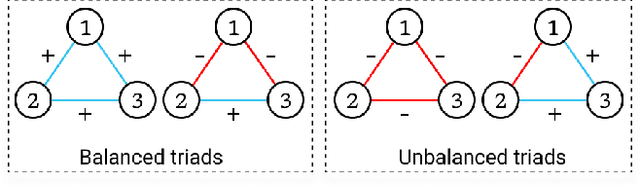
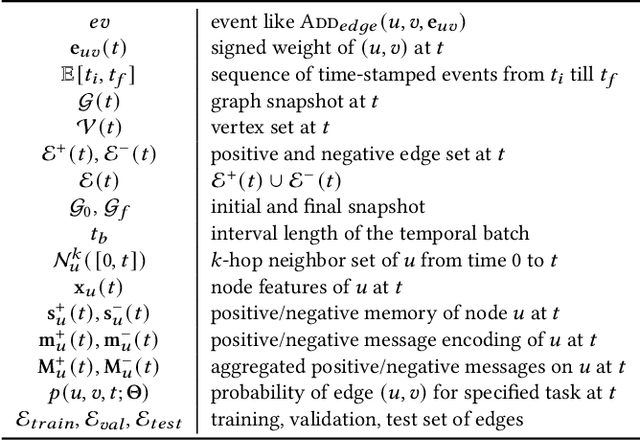
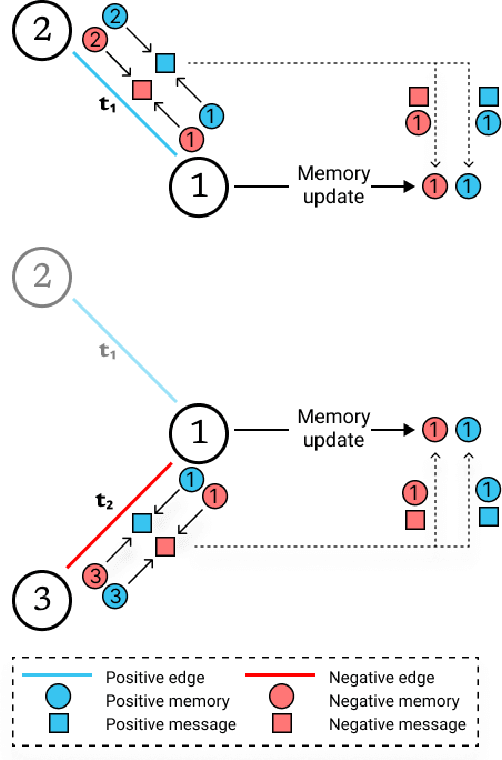
Abstract:Signed networks allow us to model bi-faceted relationships and interactions, such as friend/enemy, support/oppose, etc. These interactions are often temporal in real datasets, where nodes and edges appear over time. Learning the dynamics of signed networks is thus crucial to effectively predict the sign and strength of future links. Existing works model either signed networks or dynamic networks but not both together. In this work, we study dynamic signed networks where links are both signed and evolving with time. Our model learns a Signed link's Evolution using Memory modules and Balanced Aggregation (hence, the name SEMBA). Each node maintains two separate memory encodings for positive and negative interactions. On the arrival of a new edge, each interacting node aggregates this signed information with its memories while exploiting balance theory. Node embeddings are generated using updated memories, which are then used to train for multiple downstream tasks, including link sign prediction and link weight prediction. Our results show that SEMBA outperforms all the baselines on the task of sign prediction by achieving up to an 8% increase in the AUC and up to a 50% reduction in FPR. Results on the task of predicting signed weights show that SEMBA reduces the mean squared error by 9% while achieving up to 69% reduction in the KL-divergence on the distribution of predicted signed weights.
Leveraging Multimodal Behavioral Analytics for Automated Job Interview Performance Assessment and Feedback
Jun 16, 2020
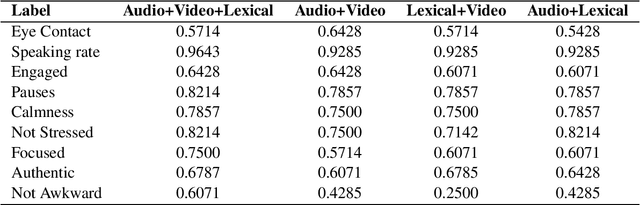
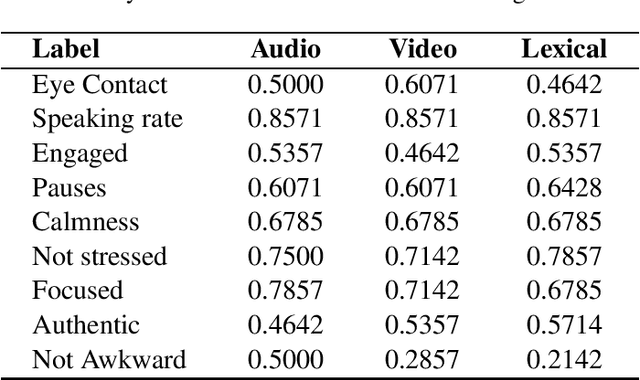
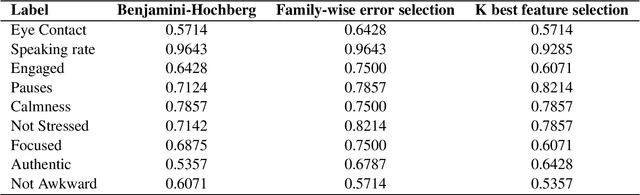
Abstract:Behavioral cues play a significant part in human communication and cognitive perception. In most professional domains, employee recruitment policies are framed such that both professional skills and personality traits are adequately assessed. Hiring interviews are structured to evaluate expansively a potential employee's suitability for the position - their professional qualifications, interpersonal skills, ability to perform in critical and stressful situations, in the presence of time and resource constraints, etc. Therefore, candidates need to be aware of their positive and negative attributes and be mindful of behavioral cues that might have adverse effects on their success. We propose a multimodal analytical framework that analyzes the candidate in an interview scenario and provides feedback for predefined labels such as engagement, speaking rate, eye contact, etc. We perform a comprehensive analysis that includes the interviewee's facial expressions, speech, and prosodic information, using the video, audio, and text transcripts obtained from the recorded interview. We use these multimodal data sources to construct a composite representation, which is used for training machine learning classifiers to predict the class labels. Such analysis is then used to provide constructive feedback to the interviewee for their behavioral cues and body language. Experimental validation showed that the proposed methodology achieved promising results.
Deep-Net: Deep Neural Network for Cyber Security Use Cases
Dec 09, 2018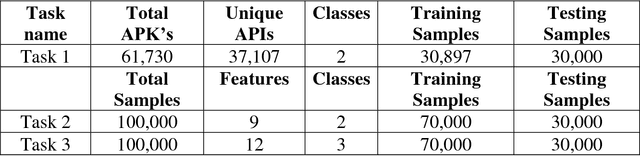
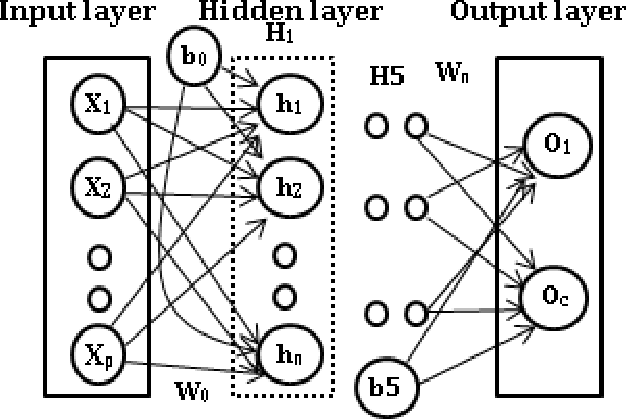
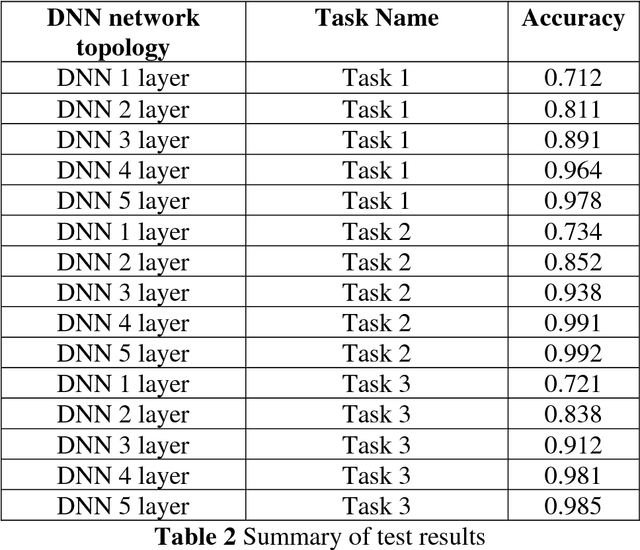
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have witnessed as a powerful approach in this year by solving long-standing Artificial intelligence (AI) supervised and unsupervised tasks exists in natural language processing, speech processing, computer vision and others. In this paper, we attempt to apply DNNs on three different cyber security use cases: Android malware classification, incident detection and fraud detection. The data set of each use case contains real known benign and malicious activities samples. The efficient network architecture for DNN is chosen by conducting various trails of experiments for network parameters and network structures. The experiments of such chosen efficient configurations of DNNs are run up to 1000 epochs with learning rate set in the range [0.01-0.5]. Experiments of DNN performed well in comparison to the classical machine learning algorithms in all cases of experiments of cyber security use cases. This is due to the fact that DNNs implicitly extract and build better features, identifies the characteristics of the data that lead to better accuracy. The best accuracy obtained by DNN and XGBoost on Android malware classification 0.940 and 0.741, incident detection 1.00 and 0.997 fraud detection 0.972 and 0.916 respectively.
Deep Health Care Text Classification
Oct 23, 2017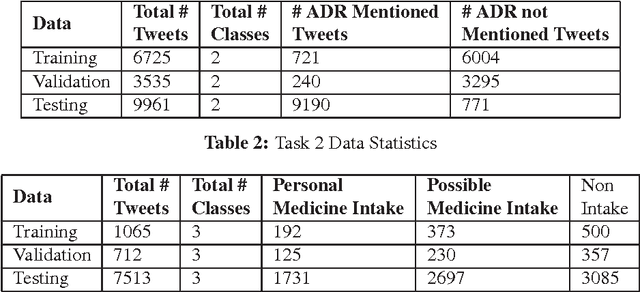

Abstract:Health related social media mining is a valuable apparatus for the early recognition of the diverse antagonistic medicinal conditions. Mostly, the existing methods are based on machine learning with knowledge-based learning. This working note presents the Recurrent neural network (RNN) and Long short-term memory (LSTM) based embedding for automatic health text classification in the social media mining. For each task, two systems are built and that classify the tweet at the tweet level. RNN and LSTM are used for extracting features and non-linear activation function at the last layer facilitates to distinguish the tweets of different categories. The experiments are conducted on 2nd Social Media Mining for Health Applications Shared Task at AMIA 2017. The experiment results are considerable; however the proposed method is appropriate for the health text classification. This is primarily due to the reason that, it doesn't rely on any feature engineering mechanisms.
Vector Space Model as Cognitive Space for Text Classification
Aug 21, 2017
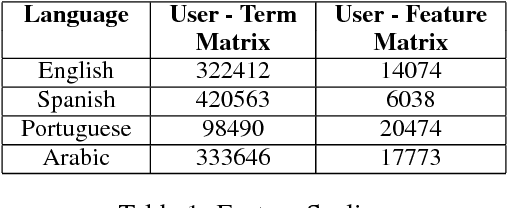
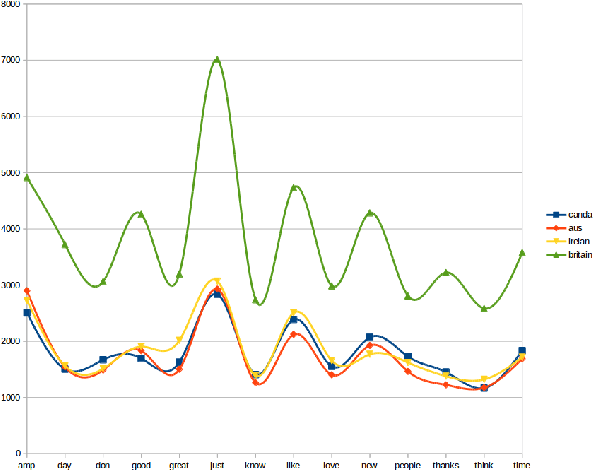
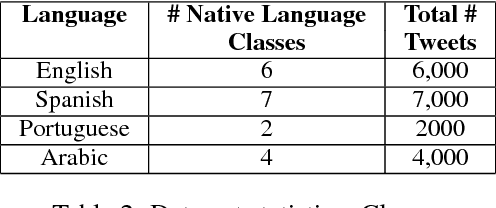
Abstract:In this era of digitization, knowing the user's sociolect aspects have become essential features to build the user specific recommendation systems. These sociolect aspects could be found by mining the user's language sharing in the form of text in social media and reviews. This paper describes about the experiment that was performed in PAN Author Profiling 2017 shared task. The objective of the task is to find the sociolect aspects of the users from their tweets. The sociolect aspects considered in this experiment are user's gender and native language information. Here user's tweets written in a different language from their native language are represented as Document - Term Matrix with document frequency as the constraint. Further classification is done using the Support Vector Machine by taking gender and native language as target classes. This experiment attains the average accuracy of 73.42% in gender prediction and 76.26% in the native language identification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge