Ana Cismaru
Command A: An Enterprise-Ready Large Language Model
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:In this report we describe the development of Command A, a powerful large language model purpose-built to excel at real-world enterprise use cases. Command A is an agent-optimised and multilingual-capable model, with support for 23 languages of global business, and a novel hybrid architecture balancing efficiency with top of the range performance. It offers best-in-class Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities with grounding and tool use to automate sophisticated business processes. These abilities are achieved through a decentralised training approach, including self-refinement algorithms and model merging techniques. We also include results for Command R7B which shares capability and architectural similarities to Command A. Weights for both models have been released for research purposes. This technical report details our original training pipeline and presents an extensive evaluation of our models across a suite of enterprise-relevant tasks and public benchmarks, demonstrating excellent performance and efficiency.
Generating Probabilistic Scenario Programs from Natural Language
May 03, 2024
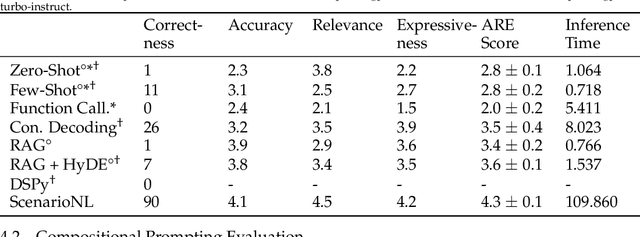

Abstract:For cyber-physical systems (CPS), including robotics and autonomous vehicles, mass deployment has been hindered by fatal errors that occur when operating in rare events. To replicate rare events such as vehicle crashes, many companies have created logging systems and employed crash reconstruction experts to meticulously recreate these valuable events in simulation. However, in these methods, "what if" questions are not easily formulated and answered. We present ScenarioNL, an AI System for creating scenario programs from natural language. Specifically, we generate these programs from police crash reports. Reports normally contain uncertainty about the exact details of the incidents which we represent through a Probabilistic Programming Language (PPL), Scenic. By using Scenic, we can clearly and concisely represent uncertainty and variation over CPS behaviors, properties, and interactions. We demonstrate how commonplace prompting techniques with the best Large Language Models (LLM) are incapable of reasoning about probabilistic scenario programs and generating code for low-resource languages such as Scenic. Our system is comprised of several LLMs chained together with several kinds of prompting strategies, a compiler, and a simulator. We evaluate our system on publicly available autonomous vehicle crash reports in California from the last five years and share insights into how we generate code that is both semantically meaningful and syntactically correct.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge