Amit K. Sanyal
Breaking Symmetries Leads to Diverse Quadrupedal Gaits
Mar 08, 2023Abstract:Symmetry manifests itself in legged locomotion in a variety of ways. No matter where a legged system begins to move periodically, the torso and limbs coordinate with each other's movements in a similar manner. Also, in many gaits observed in nature, the legs on both sides of the torso move in exactly the same way, sometimes they are just half a period out of phase. Furthermore, when some animals move forward and backward, their movements are strikingly similar as if the time had been reversed. This work aims to generalize these phenomena and propose formal definitions of symmetries in legged locomotion using group theory terminology. Symmetries in some common quadrupedal gaits such as pronking, bounding, half-bounding, and galloping have been discussed. Moreover, a spring-mass model has been used to demonstrate how breaking symmetries can alter gaits in a legged system. Studying the symmetries may provide insight into which gaits may be suitable for a particular robotic design, or may enable roboticists to design more agile and efficient robot controllers by using certain gaits.
Practice Makes Perfect: an iterative approach to achieve precise tracking for legged robots
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Precise trajectory tracking for legged robots can be challenging due to their high degrees of freedom, unmodeled nonlinear dynamics, or random disturbances from the environment. A commonly adopted solution to overcome these challenges is to use optimization-based algorithms and approximate the system with a simplified, reduced-order model. Additionally, deep neural networks are becoming a more promising option for achieving agile and robust legged locomotion. These approaches, however, either require large amounts of onboard calculations or the collection of millions of data points from a single robot. To address these problems and improve tracking performance, this paper proposes a method based on iterative learning control. This method lets a robot learn from its own mistakes by exploiting the repetitive nature of legged locomotion within only a few trials. Then, a torque library is created as a lookup table so that the robot does not need to repeat calculations or learn the same skill over and over again. This process resembles how animals learn their muscle memories in nature. The proposed method is tested on the A1 robot in a simulated environment, and it allows the robot to pronk at different speeds while precisely following the reference trajectories without heavy calculations.
Input Influence Matrix Design for MIMO Discrete-Time Ultra-Local Model
Mar 16, 2022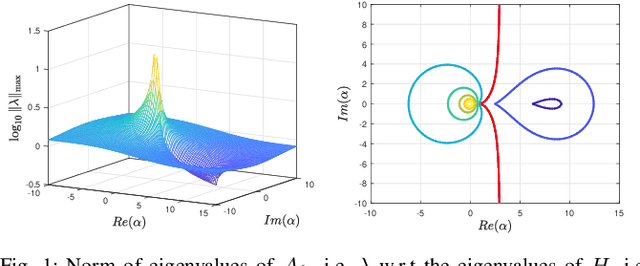
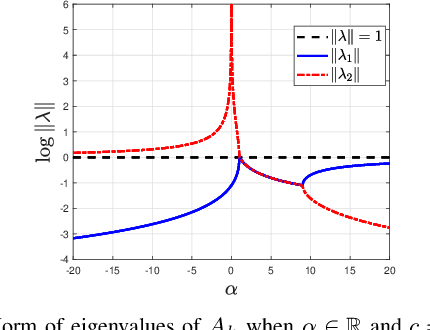
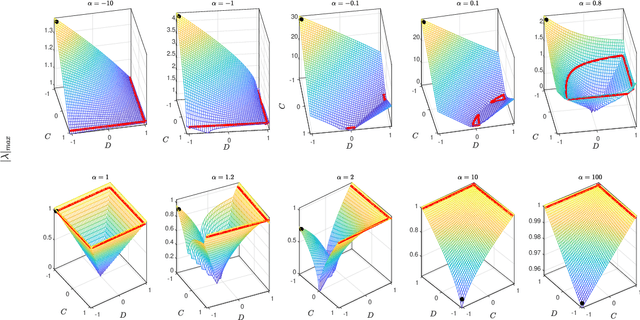
Abstract:Ultra-Local Models (ULM) have been applied to perform model-free control of nonlinear systems with unknown or partially known dynamics. Unfortunately, extending these methods to MIMO systems requires designing a dense input influence matrix which is challenging. This paper presents guidelines for designing an input influence matrix for discrete-time, control-affine MIMO systems using an ULM-based controller. This paper analyzes the case that uses ULM and a model-free control scheme: the H\"older-continuous Finite-Time Stable (FTS) control. By comparing the ULM with the actual system dynamics, the paper describes how to extract the input-dependent part from the lumped ULM dynamics and finds that the tracking and state estimation error are coupled. The stability of the ULM-FTS error dynamics is affected by the eigenvalues of the difference (defined by matrix multiplication) between the actual and designed input influence matrix. Finally, the paper shows that a wide range of input influence matrix designs can keep the ULM-FTS error dynamics (at least locally) asymptotically stable. A numerical simulation is included to verify the result. The analysis can also be extended to other ULM-based controllers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge