Amir Atapour Abarghouei
Disentangling Racial Phenotypes: Fine-Grained Control of Race-related Facial Phenotype Characteristics
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Achieving an effective fine-grained appearance variation over 2D facial images, whilst preserving facial identity, is a challenging task due to the high complexity and entanglement of common 2D facial feature encoding spaces. Despite these challenges, such fine-grained control, by way of disentanglement is a crucial enabler for data-driven racial bias mitigation strategies across multiple automated facial analysis tasks, as it allows to analyse, characterise and synthesise human facial diversity. In this paper, we propose a novel GAN framework to enable fine-grained control over individual race-related phenotype attributes of the facial images. Our framework factors the latent (feature) space into elements that correspond to race-related facial phenotype representations, thereby separating phenotype aspects (e.g. skin, hair colour, nose, eye, mouth shapes), which are notoriously difficult to annotate robustly in real-world facial data. Concurrently, we also introduce a high quality augmented, diverse 2D face image dataset drawn from CelebA-HQ for GAN training. Unlike prior work, our framework only relies upon 2D imagery and related parameters to achieve state-of-the-art individual control over race-related phenotype attributes with improved photo-realistic output.
Eliminating the Blind Spot: Adapting 3D Object Detection and Monocular Depth Estimation to 360° Panoramic Imagery
Aug 19, 2018



Abstract:Recent automotive vision work has focused almost exclusively on processing forward-facing cameras. However, future autonomous vehicles will not be viable without a more comprehensive surround sensing, akin to a human driver, as can be provided by 360{\deg} panoramic cameras. We present an approach to adapt contemporary deep network architectures developed on conventional rectilinear imagery to work on equirectangular 360{\deg} panoramic imagery. To address the lack of annotated panoramic automotive datasets availability, we adapt a contemporary automotive dataset, via style and projection transformations, to facilitate the cross-domain retraining of contemporary algorithms for panoramic imagery. Following this approach we retrain and adapt existing architectures to recover scene depth and 3D pose of vehicles from monocular panoramic imagery without any panoramic training labels or calibration parameters. Our approach is evaluated qualitatively on crowd-sourced panoramic images and quantitatively using an automotive environment simulator to provide the first benchmark for such techniques within panoramic imagery.
Inspiring Computer Vision System Solutions
Jul 22, 2017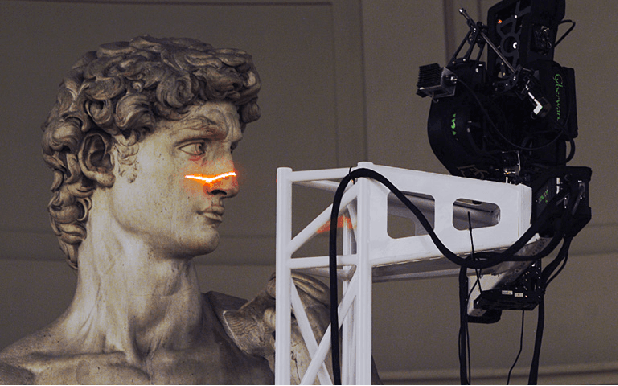


Abstract:The "digital Michelangelo project" was a seminal computer vision project in the early 2000's that pushed the capabilities of acquisition systems and involved multiple people from diverse fields, many of whom are now leaders in industry and academia. Reviewing this project with modern eyes provides us with the opportunity to reflect on several issues, relevant now as then to the field of computer vision and research in general, that go beyond the technical aspects of the work. This article was written in the context of a reading group competition at the week-long International Computer Vision Summer School 2017 (ICVSS) on Sicily, Italy. To deepen the participants understanding of computer vision and to foster a sense of community, various reading groups were tasked to highlight important lessons which may be learned from provided literature, going beyond the contents of the paper. This report is the winning entry of this guided discourse (Fig. 1). The authors closely examined the origins, fruits and most importantly lessons about research in general which may be distilled from the "digital Michelangelo project". Discussions leading to this report were held within the group as well as with Hao Li, the group mentor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge