Allard Oelen
TIB AIssistant: a Platform for AI-Supported Research Across Research Life Cycles
Dec 18, 2025

Abstract:The rapidly growing popularity of adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI), and specifically Large Language Models (LLMs), is having a widespread impact throughout society, including the academic domain. AI-supported research has the potential to support researchers with tasks across the entire research life cycle. In this work, we demonstrate the TIB AIssistant, an AI-supported research platform providing support throughout the research life cycle. The AIssistant consists of a collection of assistants, each responsible for a specific research task. In addition, tools are provided to give access to external scholarly services. Generated data is stored in the assets and can be exported as an RO-Crate bundle to provide transparency and enhance reproducibility of the research project. We demonstrate the AIssistant's main functionalities by means of a sequential walk-through of assistants, interacting with each other to generate sections for a draft research paper. In the end, with the AIssistant, we lay the foundation for a larger agenda of providing a community-maintained platform for AI-supported research.
Introducing ORKG ASK: an AI-driven Scholarly Literature Search and Exploration System Taking a Neuro-Symbolic Approach
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:As the volume of published scholarly literature continues to grow, finding relevant literature becomes increasingly difficult. With the rise of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), and particularly Large Language Models (LLMs), new possibilities emerge to find and explore literature. We introduce ASK (Assistant for Scientific Knowledge), an AI-driven scholarly literature search and exploration system that follows a neuro-symbolic approach. ASK aims to provide active support to researchers in finding relevant scholarly literature by leveraging vector search, LLMs, and knowledge graphs. The system allows users to input research questions in natural language and retrieve relevant articles. ASK automatically extracts key information and generates answers to research questions using a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach. We present an evaluation of ASK, assessing the system's usability and usefulness. Findings indicate that the system is user-friendly and users are generally satisfied while using the system.
Towards AI-Supported Research: a Vision of the TIB AIssistant
Dec 18, 2025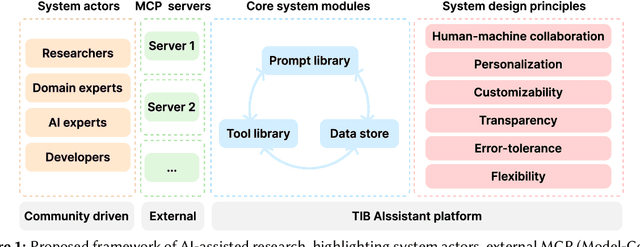
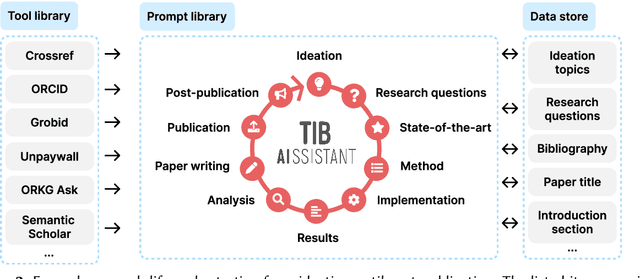
Abstract:The rapid advancements in Generative AI and Large Language Models promise to transform the way research is conducted, potentially offering unprecedented opportunities to augment scholarly workflows. However, effectively integrating AI into research remains a challenge due to varying domain requirements, limited AI literacy, the complexity of coordinating tools and agents, and the unclear accuracy of Generative AI in research. We present the vision of the TIB AIssistant, a domain-agnostic human-machine collaborative platform designed to support researchers across disciplines in scientific discovery, with AI assistants supporting tasks across the research life cycle. The platform offers modular components - including prompt and tool libraries, a shared data store, and a flexible orchestration framework - that collectively facilitate ideation, literature analysis, methodology development, data analysis, and scholarly writing. We describe the conceptual framework, system architecture, and implementation of an early prototype that demonstrates the feasibility and potential impact of our approach.
Fine-tuning and Prompt Engineering with Cognitive Knowledge Graphs for Scholarly Knowledge Organization
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:The increasing amount of published scholarly articles, exceeding 2.5 million yearly, raises the challenge for researchers in following scientific progress. Integrating the contributions from scholarly articles into a novel type of cognitive knowledge graph (CKG) will be a crucial element for accessing and organizing scholarly knowledge, surpassing the insights provided by titles and abstracts. This research focuses on effectively conveying structured scholarly knowledge by utilizing large language models (LLMs) to categorize scholarly articles and describe their contributions in a structured and comparable manner. While previous studies explored language models within specific research domains, the extensive domain-independent knowledge captured by LLMs offers a substantial opportunity for generating structured contribution descriptions as CKGs. Additionally, LLMs offer customizable pathways through prompt engineering or fine-tuning, thus facilitating to leveraging of smaller LLMs known for their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental considerations. Our methodology involves harnessing LLM knowledge, and complementing it with domain expert-verified scholarly data sourced from a CKG. This strategic fusion significantly enhances LLM performance, especially in tasks like scholarly article categorization and predicate recommendation. Our method involves fine-tuning LLMs with CKG knowledge and additionally injecting knowledge from a CKG with a novel prompting technique significantly increasing the accuracy of scholarly knowledge extraction. We integrated our approach in the Open Research Knowledge Graph (ORKG), thus enabling precise access to organized scholarly knowledge, crucially benefiting domain-independent scholarly knowledge exchange and dissemination among policymakers, industrial practitioners, and the general public.
Toward FAIR Semantic Publishing of Research Dataset Metadata in the Open Research Knowledge Graph
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:Search engines these days can serve datasets as search results. Datasets get picked up by search technologies based on structured descriptions on their official web pages, informed by metadata ontologies such as the Dataset content type of schema.org. Despite this promotion of the content type dataset as a first-class citizen of search results, a vast proportion of datasets, particularly research datasets, still need to be made discoverable and, therefore, largely remain unused. This is due to the sheer volume of datasets released every day and the inability of metadata to reflect a dataset's content and context accurately. This work seeks to improve this situation for a specific class of datasets, namely research datasets, which are the result of research endeavors and are accompanied by a scholarly publication. We propose the ORKG-Dataset content type, a specialized branch of the Open Research Knowledge Graoh (ORKG) platform, which provides descriptive information and a semantic model for research datasets, integrating them with their accompanying scholarly publications. This work aims to establish a standardized framework for recording and reporting research datasets within the ORKG-Dataset content type. This, in turn, increases research dataset transparency on the web for their improved discoverability and applied use. In this paper, we present a proposal -- the minimum FAIR, comparable, semantic description of research datasets in terms of salient properties of their supporting publication. We design a specific application of the ORKG-Dataset semantic model based on 40 diverse research datasets on scientific information extraction.
* 8 pages, 1 figure, published in the Joint Proceedings of the Onto4FAIR 2023 Workshops
Knowledge Graphs Evolution and Preservation -- A Technical Report from ISWS 2019
Dec 22, 2020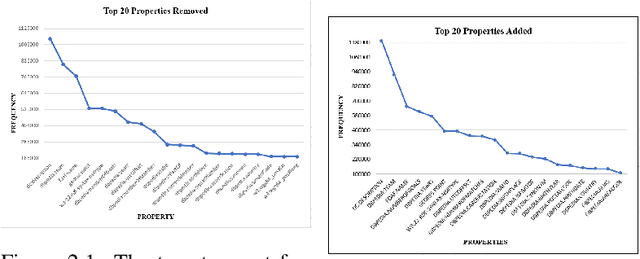
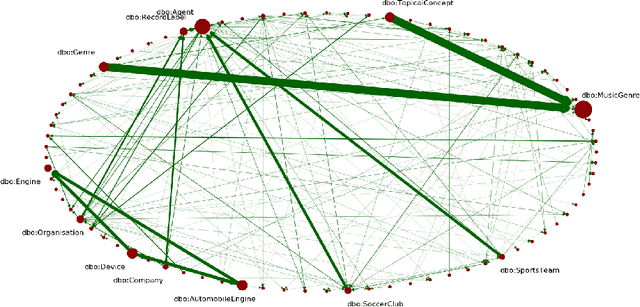

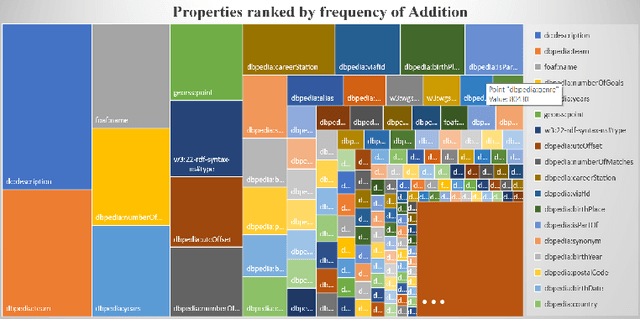
Abstract:One of the grand challenges discussed during the Dagstuhl Seminar "Knowledge Graphs: New Directions for Knowledge Representation on the Semantic Web" and described in its report is that of a: "Public FAIR Knowledge Graph of Everything: We increasingly see the creation of knowledge graphs that capture information about the entirety of a class of entities. [...] This grand challenge extends this further by asking if we can create a knowledge graph of "everything" ranging from common sense concepts to location based entities. This knowledge graph should be "open to the public" in a FAIR manner democratizing this mass amount of knowledge." Although linked open data (LOD) is one knowledge graph, it is the closest realisation (and probably the only one) to a public FAIR Knowledge Graph (KG) of everything. Surely, LOD provides a unique testbed for experimenting and evaluating research hypotheses on open and FAIR KG. One of the most neglected FAIR issues about KGs is their ongoing evolution and long term preservation. We want to investigate this problem, that is to understand what preserving and supporting the evolution of KGs means and how these problems can be addressed. Clearly, the problem can be approached from different perspectives and may require the development of different approaches, including new theories, ontologies, metrics, strategies, procedures, etc. This document reports a collaborative effort performed by 9 teams of students, each guided by a senior researcher as their mentor, attending the International Semantic Web Research School (ISWS 2019). Each team provides a different perspective to the problem of knowledge graph evolution substantiated by a set of research questions as the main subject of their investigation. In addition, they provide their working definition for KG preservation and evolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge