Alireza Abedin
Guided-GAN: Adversarial Representation Learning for Activity Recognition with Wearables
Oct 12, 2021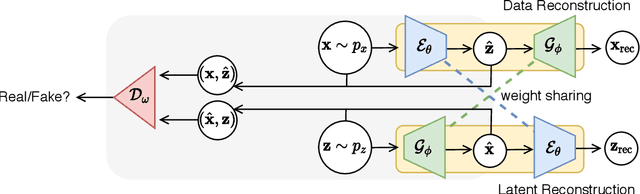
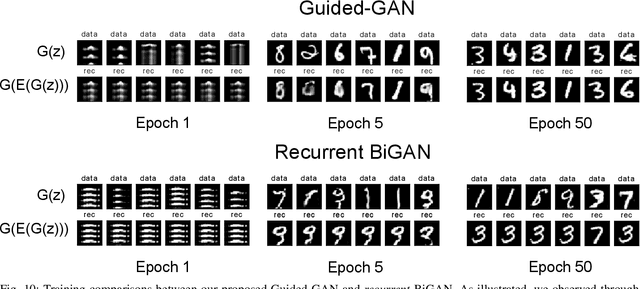
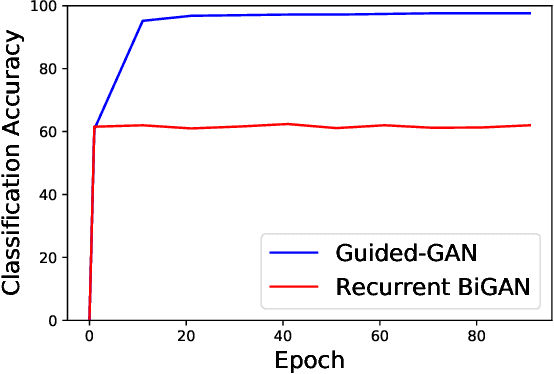
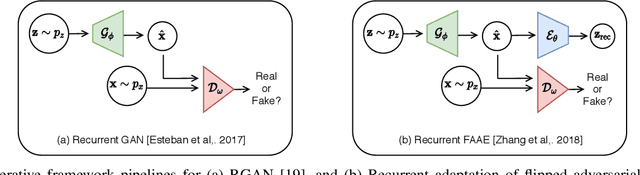
Abstract:Human activity recognition (HAR) is an important research field in ubiquitous computing where the acquisition of large-scale labeled sensor data is tedious, labor-intensive and time consuming. State-of-the-art unsupervised remedies investigated to alleviate the burdens of data annotations in HAR mainly explore training autoencoder frameworks. In this paper: we explore generative adversarial network (GAN) paradigms to learn unsupervised feature representations from wearable sensor data; and design a new GAN framework-Geometrically-Guided GAN or Guided-GAN-for the task. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our formulation, we evaluate the features learned by Guided-GAN in an unsupervised manner on three downstream classification benchmarks. Our results demonstrate Guided-GAN to outperform existing unsupervised approaches whilst closely approaching the performance with fully supervised learned representations. The proposed approach paves the way to bridge the gap between unsupervised and supervised human activity recognition whilst helping to reduce the cost of human data annotation tasks.
Towards Deep Clustering of Human Activities from Wearables
Aug 19, 2020

Abstract:Our ability to exploit low-cost wearable sensing modalities for critical human behaviour and activity monitoring applications in health and wellness is reliant on supervised learning regimes; here, deep learning paradigms have proven extremely successful in learning activity representations from annotated data. However, the costly work of gathering and annotating sensory activity datasets is labor-intensive, time consuming and not scalable to large volumes of data. While existing unsupervised remedies of deep clustering leverage network architectures and optimization objectives that are tailored for static image datasets, deep architectures to uncover cluster structures from raw sequence data captured by on-body sensors remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we develop an unsupervised end-to-end learning strategy for the fundamental problem of human activity recognition (HAR) from wearables. Through extensive experiments, including comparisons with existing methods, we show the effectiveness of our approach to jointly learn unsupervised representations for sensory data and generate cluster assignments with strong semantic correspondence to distinct human activities.
Attend And Discriminate: Beyond the State-of-the-Art for Human Activity Recognition using Wearable Sensors
Jul 14, 2020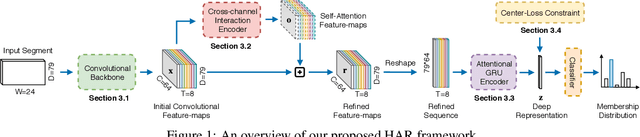

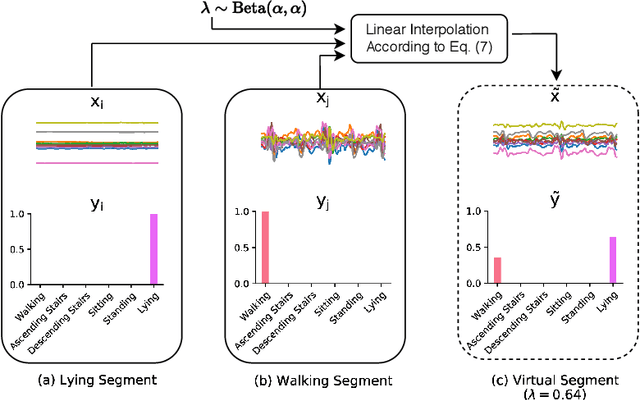
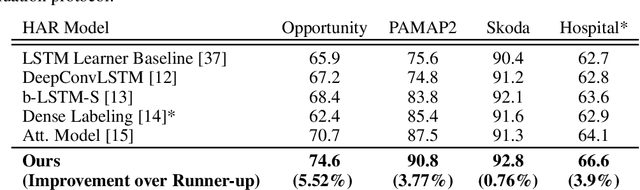
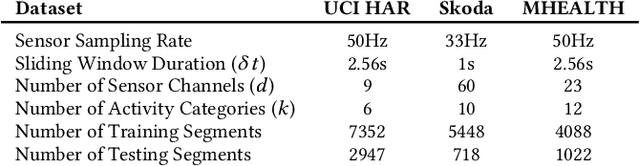
Abstract:Wearables are fundamental to improving our understanding of human activities, especially for an increasing number of healthcare applications from rehabilitation to fine-grained gait analysis. Although our collective know-how to solve Human Activity Recognition (HAR) problems with wearables has progressed immensely with end-to-end deep learning paradigms, several fundamental opportunities remain overlooked. We rigorously explore these new opportunities to learn enriched and highly discriminating activity representations. We propose: i) learning to exploit the latent relationships between multi-channel sensor modalities and specific activities; ii) investigating the effectiveness of data-agnostic augmentation for multi-modal sensor data streams to regularize deep HAR models; and iii) incorporating a classification loss criterion to encourage minimal intra-class representation differences whilst maximising inter-class differences to achieve more discriminative features. Our contributions achieves new state-of-the-art performance on four diverse activity recognition problem benchmarks with large margins -- with up to 6% relative margin improvement. We extensively validate the contributions from our design concepts through extensive experiments, including activity misalignment measures, ablation studies and insights shared through both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Joint learning of Social Groups, Individuals Action and Sub-group Activities in Videos
Jul 06, 2020
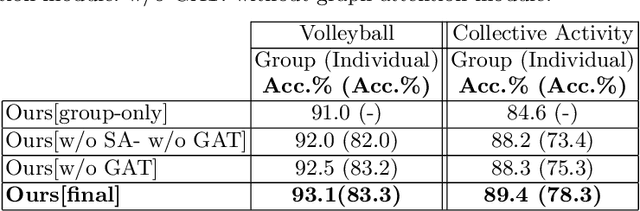
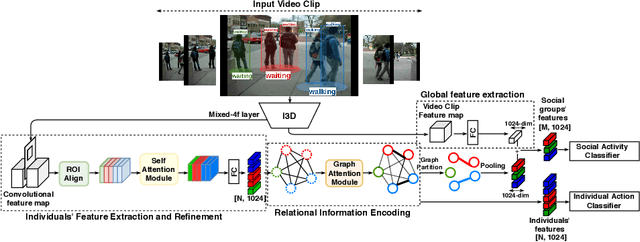
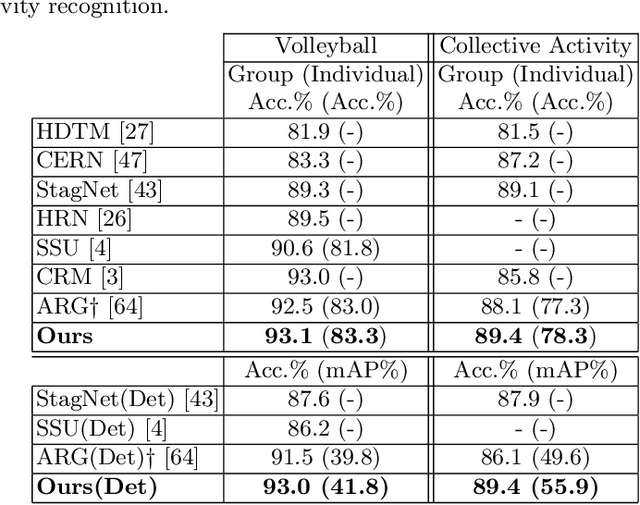
Abstract:The state-of-the art solutions for human activity understanding from a video stream formulate the task as a spatio-temporal problem which requires joint localization of all individuals in the scene and classification of their actions or group activity over time. Who is interacting with whom, e.g. not everyone in a queue is interacting with each other, is often not predicted. There are scenarios where people are best to be split into sub-groups, which we call social groups, and each social group may be engaged in a different social activity. In this paper, we solve the problem of simultaneously grouping people by their social interactions, predicting their individual actions and the social activity of each social group, which we call the social task. Our main contributions are: i) we propose an end-to-end trainable framework for the social task; ii) our proposed method also sets the state-of-the-art results on two widely adopted benchmarks for the traditional group activity recognition task (assuming individuals of the scene form a single group and predicting a single group activity label for the scene); iii) we introduce new annotations on an existing group activity dataset, re-purposing it for the social task.
SparseSense: Human Activity Recognition from Highly Sparse Sensor Data-streams Using Set-based Neural Networks
Jun 06, 2019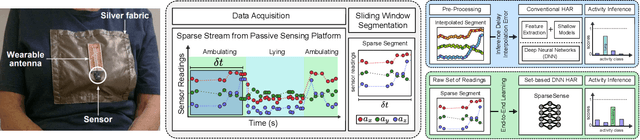
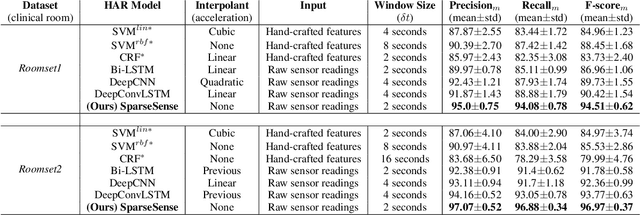
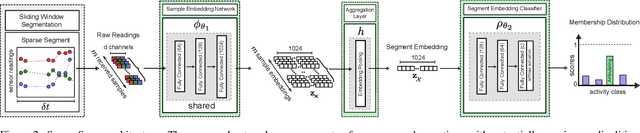
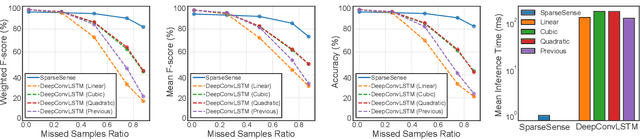
Abstract:Batteryless or so called passive wearables are providing new and innovative methods for human activity recognition (HAR), especially in healthcare applications for older people. Passive sensors are low cost, lightweight, unobtrusive and desirably disposable; attractive attributes for healthcare applications in hospitals and nursing homes. Despite the compelling propositions for sensing applications, the data streams from these sensors are characterised by high sparsity---the time intervals between sensor readings are irregular while the number of readings per unit time are often limited. In this paper, we rigorously explore the problem of learning activity recognition models from temporally sparse data. We describe how to learn directly from sparse data using a deep learning paradigm in an end-to-end manner. We demonstrate significant classification performance improvements on real-world passive sensor datasets from older people over the state-of-the-art deep learning human activity recognition models. Further, we provide insights into the model's behaviour through complementary experiments on a benchmark dataset and visualisation of the learned activity feature spaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge