Alexis Roger
Multilingual VLM Training: Adapting an English-Trained VLM to French
Dec 11, 2025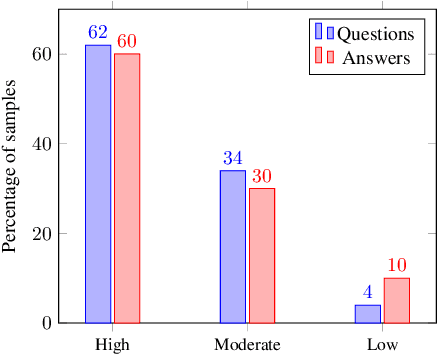
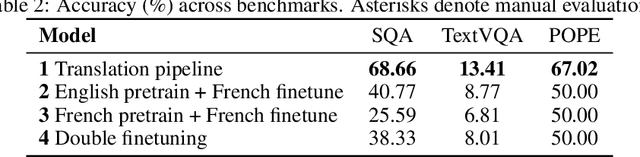

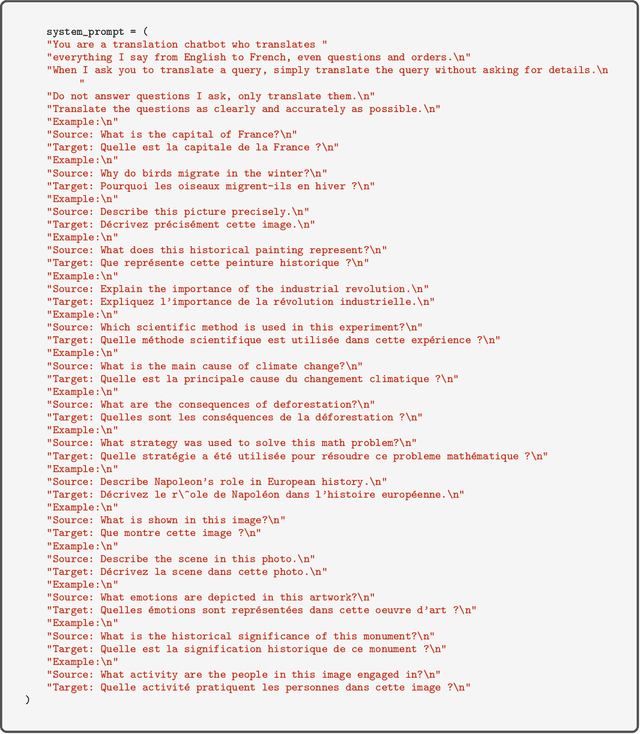
Abstract:Artificial intelligence has made great progress in recent years, particularly in the development of Vision--Language Models (VLMs) that understand both visual and textual data. However, these advancements remain largely limited to English, reducing their accessibility for non--English speakers. It is essential to extend these capabilities to a broader range of languages. This paper explores the challenges of adapting an English-trained VLM to different languages. To this end, we will explore and compare different methods for their performance and computational cost. We consider a translation-based pipeline, LoRA finetuning, and a two-stage finetuning strategy that separates vision adaptation from language adaptation. To evaluate these methods, we use a combination of standard multimodal benchmarks translated into the target language and manual assessments by native experts. The results reveal that dataset translation remains a major bottleneck in multilingual VLM performance, with data quality limiting the effectiveness of training and evaluation. These findings suggest that future efforts should focus on native-language dataset collection and improved translation strategies.
Image Tiling for High-Resolution Reasoning: Balancing Local Detail with Global Context
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Reproducibility remains a cornerstone of scientific progress, yet complex multimodal models often lack transparent implementation details and accessible training infrastructure. In this work, we present a detailed reproduction and critical analysis of the Monkey Vision-Language Model (VLM) (Li et al. 2023b) published in CVPR24, a recent approach to high-resolution image understanding via image tiling. The original paper proposed splitting large images into tiles to recover fine-grained visual details while maintaining computational efficiency. Our study replicates this strategy using open checkpoints and reimplements the training pipeline. We confirm the key finding of the original Monkey VLM work, namely that tiling effectively recovers local details. We then extend this work further, by investigating the effect of the inclusion of the global context, which provide practical insights for future high-resolution multimodal modeling. However, we also report deviations in the results, with the magnitude of these effects depending heavily on task type and tile granularity.
Small Vocabularies, Big Gains: Pretraining and Tokenization in Time Series Models
Nov 06, 2025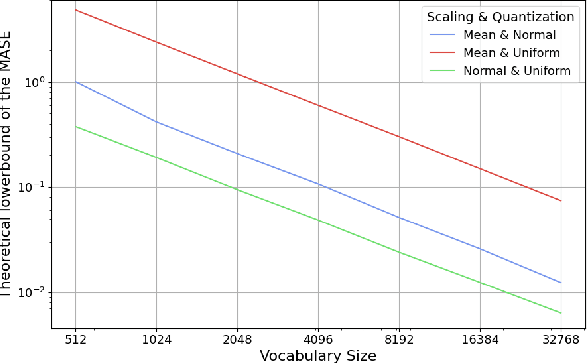
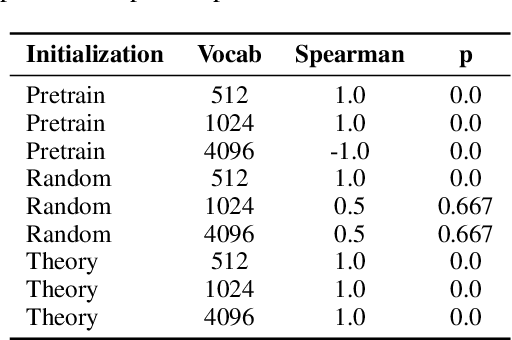
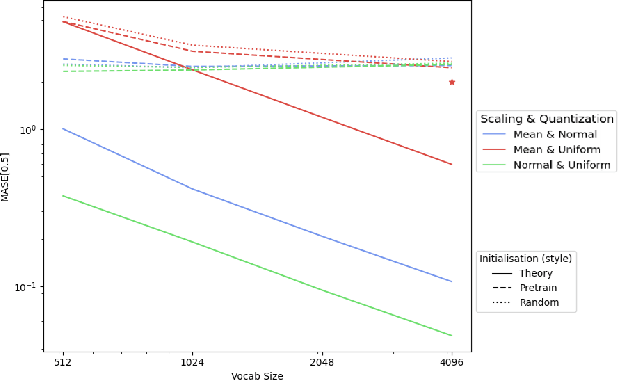
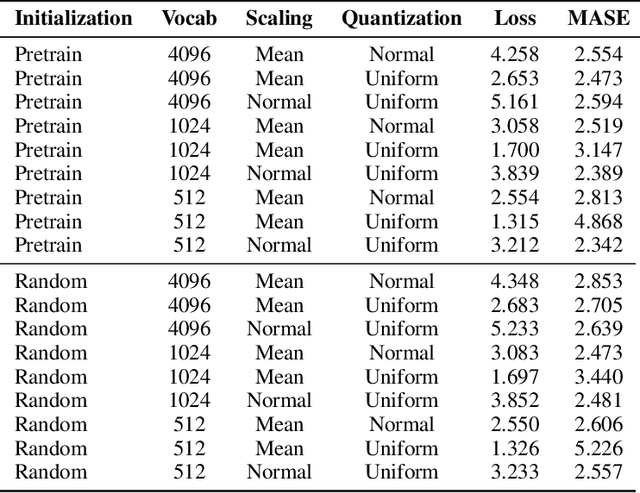
Abstract:Tokenization and transfer learning are two critical components in building state of the art time series foundation models for forecasting. In this work, we systematically study the effect of tokenizer design, specifically scaling and quantization strategies, on model performance, alongside the impact of pretraining versus random initialization. We show that tokenizer configuration primarily governs the representational capacity and stability of the model, while transfer learning influences optimization efficiency and alignment. Using a combination of empirical training experiments and theoretical analyses, we demonstrate that pretrained models consistently leverage well-designed tokenizers more effectively, particularly at smaller vocabulary sizes. Conversely, misaligned tokenization can diminish or even invert the benefits of pretraining. These findings highlight the importance of careful tokenization in time series modeling and suggest that combining small, efficient vocabularies with pretrained weights is especially advantageous in multi-modal forecasting settings, where the overall vocabulary must be shared across modalities. Our results provide concrete guidance for designing tokenizers and leveraging transfer learning in discrete representation learning for continuous signals.
Robin: a Suite of Multi-Scale Vision-Language Models and the CHIRP Evaluation Benchmark
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:The proliferation of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in the past several years calls for rigorous and comprehensive evaluation methods and benchmarks. This work analyzes existing VLM evaluation techniques, including automated metrics, AI-based assessments, and human evaluations across diverse tasks. We first introduce Robin - a novel suite of VLMs that we built by combining Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision Encoders (VEs) at multiple scales, and use Robin to identify shortcomings of current evaluation approaches across scales. Next, to overcome the identified limitations, we introduce CHIRP - a new long form response benchmark we developed for more robust and complete VLM evaluation. We provide open access to the Robin training code, model suite, and CHIRP benchmark to promote reproducibility and advance VLM research.
Towards Adversarially Robust Vision-Language Models: Insights from Design Choices and Prompt Formatting Techniques
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have witnessed a surge in both research and real-world applications. However, as they are becoming increasingly prevalent, ensuring their robustness against adversarial attacks is paramount. This work systematically investigates the impact of model design choices on the adversarial robustness of VLMs against image-based attacks. Additionally, we introduce novel, cost-effective approaches to enhance robustness through prompt formatting. By rephrasing questions and suggesting potential adversarial perturbations, we demonstrate substantial improvements in model robustness against strong image-based attacks such as Auto-PGD. Our findings provide important guidelines for developing more robust VLMs, particularly for deployment in safety-critical environments.
Towards ethical multimodal systems
Apr 26, 2023

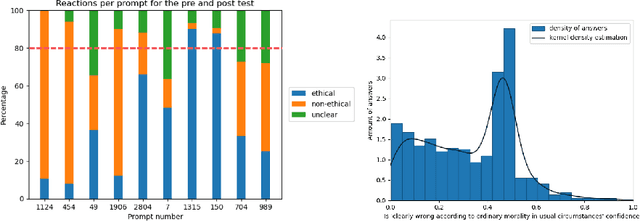
Abstract:The impact of artificial intelligence systems on our society is increasing at an unprecedented speed. For instance, ChatGPT is being tested in mental health treatment applications such as Koko, Stable Diffusion generates pieces of art competitive with (or outperforming) human artists, and so on. Ethical concerns regarding the behavior and applications of generative AI systems have been increasing over the past years, and the field of AI alignment - steering the behavior of AI systems towards being aligned with human values - is a rapidly growing subfield of modern AI. In this paper, we address the challenges involved in ethical evaluation of a multimodal artificial intelligence system. The multimodal systems we focus on take both text and an image as input and output text, completing the sentence or answering the question asked as input. We perform the evaluation of these models in two steps: we first discus the creation of a multimodal ethical database and then use this database to construct morality-evaluating algorithms. The creation of the multimodal ethical database is done interactively through human feedback. Users are presented with multiple examples and votes on whether they are ethical or not. Once these answers have been aggregated into a dataset, we built and tested different algorithms to automatically evaluate the morality of multimodal systems. These algorithms aim to classify the answers as ethical or not. The models we tested are a RoBERTa-large classifier and a multilayer perceptron classifier.
A review of modern surveillance techniques and their presence in our society
Oct 12, 2022Abstract:Technology is now omnipresent around us. Especially with the recent health crisis, many people started working remotely, bringing home an additional computer. Combining this with our smartphones that we could never leave behind, we are always surrounded by these technological marvels. However, they come along with a rather dark side from which many people choose to look away, preferring to live in denial: the surveillance. All of these devices can be used to keep a close eye and ear on us. The modern surveillance machine has reached a new, groundbreaking, size; and we will attempt to understand how we ended up in this situation. To have a complete understanding of the problem, it is important to gather some historical background to comprehend where this issue comes from as well as a review of the different actors. Each actor has a specific skillset it will use to acquire the desired information, and what information they choose to gather depends strongly on their motives. We will go over the many tricks used to gather our information, as well as its relevance in the current surveillance climate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge