Alexandre See
Source-free Domain Adaptation Requires Penalized Diversity
Apr 12, 2023



Abstract:While neural networks are capable of achieving human-like performance in many tasks such as image classification, the impressive performance of each model is limited to its own dataset. Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) was introduced to address knowledge transfer between different domains in the absence of source data, thus, increasing data privacy. Diversity in representation space can be vital to a model`s adaptability in varied and difficult domains. In unsupervised SFDA, the diversity is limited to learning a single hypothesis on the source or learning multiple hypotheses with a shared feature extractor. Motivated by the improved predictive performance of ensembles, we propose a novel unsupervised SFDA algorithm that promotes representational diversity through the use of separate feature extractors with Distinct Backbone Architectures (DBA). Although diversity in feature space is increased, the unconstrained mutual information (MI) maximization may potentially introduce amplification of weak hypotheses. Thus we introduce the Weak Hypothesis Penalization (WHP) regularizer as a mitigation strategy. Our work proposes Penalized Diversity (PD) where the synergy of DBA and WHP is applied to unsupervised source-free domain adaptation for covariate shift. In addition, PD is augmented with a weighted MI maximization objective for label distribution shift. Empirical results on natural, synthetic, and medical domains demonstrate the effectiveness of PD under different distributional shifts.
Application of Homomorphic Encryption in Medical Imaging
Oct 12, 2021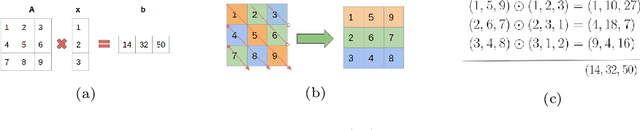
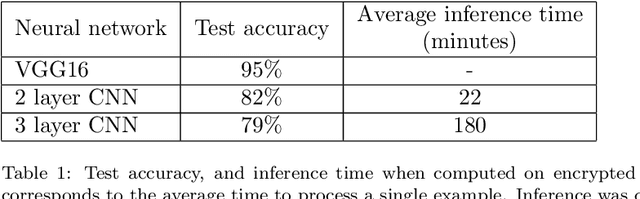
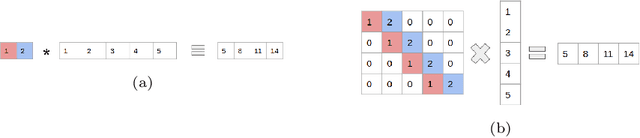
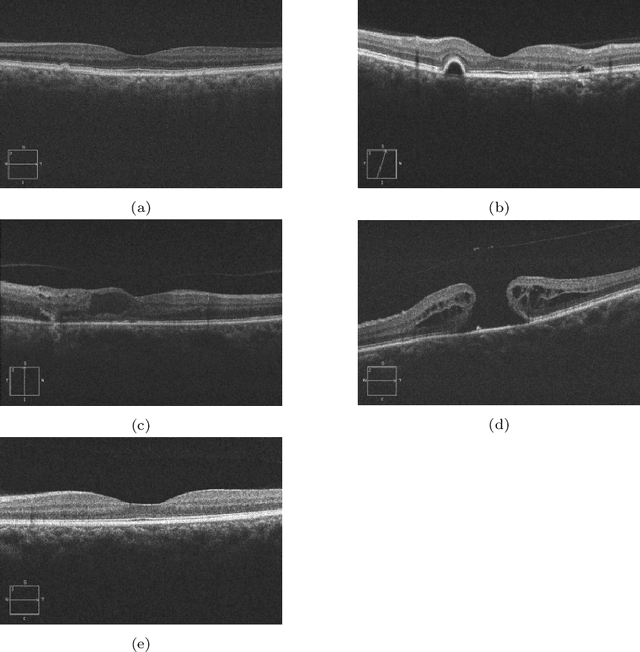
Abstract:In this technical report, we explore the use of homomorphic encryption (HE) in the context of training and predicting with deep learning (DL) models to deliver strict \textit{Privacy by Design} services, and to enforce a zero-trust model of data governance. First, we show how HE can be used to make predictions over medical images while preventing unauthorized secondary use of data, and detail our results on a disease classification task with OCT images. Then, we demonstrate that HE can be used to secure the training of DL models through federated learning, and report some experiments using 3D chest CT-Scans for a nodule detection task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge