Alexander von Rohr
Fine-Tuning of Neural Network Approximate MPC without Retraining via Bayesian Optimization
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Approximate model-predictive control (AMPC) aims to imitate an MPC's behavior with a neural network, removing the need to solve an expensive optimization problem at runtime. However, during deployment, the parameters of the underlying MPC must usually be fine-tuned. This often renders AMPC impractical as it requires repeatedly generating a new dataset and retraining the neural network. Recent work addresses this problem by adapting AMPC without retraining using approximated sensitivities of the MPC's optimization problem. Currently, this adaption must be done by hand, which is labor-intensive and can be unintuitive for high-dimensional systems. To solve this issue, we propose using Bayesian optimization to tune the parameters of AMPC policies based on experimental data. By combining model-based control with direct and local learning, our approach achieves superior performance to nominal AMPC on hardware, with minimal experimentation. This allows automatic and data-efficient adaptation of AMPC to new system instances and fine-tuning to cost functions that are difficult to directly implement in MPC. We demonstrate the proposed method in hardware experiments for the swing-up maneuver on an inverted cartpole and yaw control of an under-actuated balancing unicycle robot, a challenging control problem.
Viability of Future Actions: Robust Safety in Reinforcement Learning via Entropy Regularization
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Despite the many recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL), the question of learning policies that robustly satisfy state constraints under unknown disturbances remains open. In this paper, we offer a new perspective on achieving robust safety by analyzing the interplay between two well-established techniques in model-free RL: entropy regularization, and constraints penalization. We reveal empirically that entropy regularization in constrained RL inherently biases learning toward maximizing the number of future viable actions, thereby promoting constraints satisfaction robust to action noise. Furthermore, we show that by relaxing strict safety constraints through penalties, the constrained RL problem can be approximated arbitrarily closely by an unconstrained one and thus solved using standard model-free RL. This reformulation preserves both safety and optimality while empirically improving resilience to disturbances. Our results indicate that the connection between entropy regularization and robustness is a promising avenue for further empirical and theoretical investigation, as it enables robust safety in RL through simple reward shaping.
Diffusion Predictive Control with Constraints
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have recently gained popularity for policy learning in robotics due to their ability to capture high-dimensional and multimodal distributions. However, diffusion policies are inherently stochastic and typically trained offline, limiting their ability to handle unseen and dynamic conditions where novel constraints not represented in the training data must be satisfied. To overcome this limitation, we propose diffusion predictive control with constraints (DPCC), an algorithm for diffusion-based control with explicit state and action constraints that can deviate from those in the training data. DPCC uses constraint tightening and incorporates model-based projections into the denoising process of a trained trajectory diffusion model. This allows us to generate constraint-satisfying, dynamically feasible, and goal-reaching trajectories for predictive control. We show through simulations of a robot manipulator that DPCC outperforms existing methods in satisfying novel test-time constraints while maintaining performance on the learned control task.
Local Bayesian Optimization for Controller Tuning with Crash Constraints
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Controller tuning is crucial for closed-loop performance but often involves manual adjustments. Although Bayesian optimization (BO) has been established as a data-efficient method for automated tuning, applying it to large and high-dimensional search spaces remains challenging. We extend a recently proposed local variant of BO to include crash constraints, where the controller can only be successfully evaluated in an a-priori unknown feasible region. We demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method through simulations and hardware experiments. Our findings showcase the potential of local BO to enhance controller performance and reduce the time and resources necessary for tuning.
* Published in at-Automatisierungstechnik
Simulation-Aided Policy Tuning for Black-Box Robot Learning
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:How can robots learn and adapt to new tasks and situations with little data? Systematic exploration and simulation are crucial tools for efficient robot learning. We present a novel black-box policy search algorithm focused on data-efficient policy improvements. The algorithm learns directly on the robot and treats simulation as an additional information source to speed up the learning process. At the core of the algorithm, a probabilistic model learns the dependence of the policy parameters and the robot learning objective not only by performing experiments on the robot, but also by leveraging data from a simulator. This substantially reduces interaction time with the robot. Using this model, we can guarantee improvements with high probability for each policy update, thereby facilitating fast, goal-oriented learning. We evaluate our algorithm on simulated fine-tuning tasks and demonstrate the data-efficiency of the proposed dual-information source optimization algorithm. In a real robot learning experiment, we show fast and successful task learning on a robot manipulator with the aid of an imperfect simulator.
Latent Action Priors From a Single Gait Cycle Demonstration for Online Imitation Learning
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) in simulation often results in brittle and unrealistic learning outcomes. To push the agent towards more desirable solutions, prior information can be injected in the learning process through, for instance, reward shaping, expert data, or motion primitives. We propose an additional inductive bias for robot learning: latent actions learned from expert demonstration as priors in the action space. We show that these action priors can be learned from only a single open-loop gait cycle using a simple autoencoder. Using these latent action priors combined with established style rewards for imitation in DRL achieves above expert demonstration level of performance and leads to more desirable gaits. Further, action priors substantially improve the performance on transfer tasks, even leading to gait transitions for higher target speeds. Videos and code are available at https://sites.google.com/view/latent-action-priors.
Experience Transfer for Robust Direct Data-Driven Control
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Learning-based control uses data to design efficient controllers for specific systems. When multiple systems are involved, experience transfer usually focuses on data availability and controller performance yet neglects robustness to variations between systems. In contrast, this letter explores experience transfer from a robustness perspective. We leverage the transfer to design controllers that are robust not only to the uncertainty regarding an individual agent's model but also to the choice of agent in a fleet. Experience transfer enables the design of safe and robust controllers that work out of the box for all systems in a heterogeneous fleet. Our approach combines scenario optimization and recent formulations for direct data-driven control without the need to estimate a model of the system or determine uncertainty bounds for its parameters. We demonstrate the benefits of our data-driven robustification method through a numerical case study and obtain learned controllers that generalize well from a small number of open-loop trajectories in a quadcopter simulation.
Multi-Arm Bin-Picking in Real-Time: A Combined Task and Motion Planning Approach
Nov 20, 2022



Abstract:Automated bin-picking is a prerequisite for fully automated manufacturing and warehouses. To successfully pick an item from an unstructured bin the robot needs to first detect possible grasps for the objects, decide on the object to remove and consequently plan and execute a feasible trajectory to retrieve the chosen object. Over the last years significant progress has been made towards solving these problems. However, when multiple robot arms are cooperating the decision and planning problems become exponentially harder. We propose an integrated multi-arm bin-picking pipeline (IMAPIP), and demonstrate that it is able to reliably pick objects from a bin in real-time using multiple robot arms. IMAPIP solves the multi-arm bin-picking task first at high-level using a geometry-aware policy integrated in a combined task and motion planning framework. We then plan motions consistent with this policy using the BIT* algorithm on the motion planning level. We show that this integrated solution enables robot arm cooperation. In our experiments, we show the proposed geometry-aware policy outperforms a baseline by increasing bin-picking time by 28\% using two robot arms. The policy is robust to changes in the position of the bin and number of objects. We also show that IMAPIP to successfully scale up to four robot arms working in close proximity.
Event-Triggered Time-Varying Bayesian Optimization
Aug 23, 2022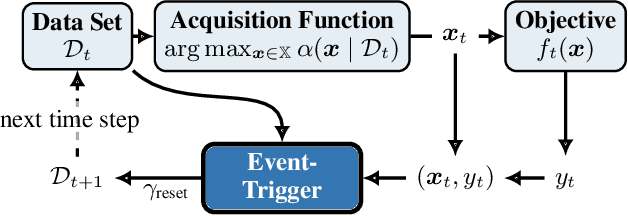

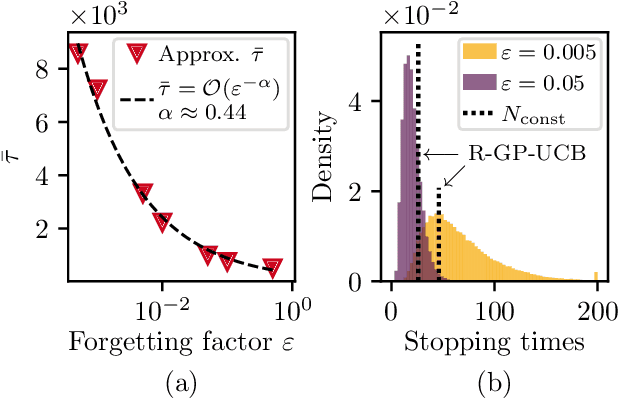
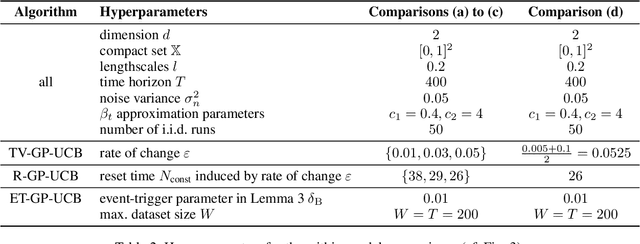
Abstract:We consider the problem of sequentially optimizing a time-varying objective function using time-varying Bayesian optimization (TVBO). Here, the key challenge is to cope with old data. Current approaches to TVBO require prior knowledge of a constant rate of change. However, the rate of change is usually neither known nor constant. We propose an event-triggered algorithm, ET-GP-UCB, that detects changes in the objective function online. The event-trigger is based on probabilistic uniform error bounds used in Gaussian process regression. The trigger automatically detects when significant change in the objective functions occurs. The algorithm then adapts to the temporal change by resetting the accumulated dataset. We provide regret bounds for ET-GP-UCB and show in numerical experiments that it is competitive with state-of-the-art algorithms even though it requires no knowledge about the temporal changes. Further, ET-GP-UCB outperforms these competitive baselines if the rate of change is misspecified and we demonstrate that it is readily applicable to various settings without tuning hyperparameters.
Improving the Performance of Robust Control through Event-Triggered Learning
Jul 28, 2022



Abstract:Robust controllers ensure stability in feedback loops designed under uncertainty but at the cost of performance. Model uncertainty in time-invariant systems can be reduced by recently proposed learning-based methods, thus improving the performance of robust controllers using data. However, in practice, many systems also exhibit uncertainty in the form of changes over time, e.g., due to weight shifts or wear and tear, leading to decreased performance or instability of the learning-based controller. We propose an event-triggered learning algorithm that decides when to learn in the face of uncertainty in the LQR problem with rare or slow changes. Our key idea is to switch between robust and learned controllers. For learning, we first approximate the optimal length of the learning phase via Monte-Carlo estimations using a probabilistic model. We then design a statistical test for uncertain systems based on the moment-generating function of the LQR cost. The test detects changes in the system under control and triggers re-learning when control performance deteriorates due to system changes. We demonstrate improved performance over a robust controller baseline in a numerical example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge