Alexa R. Tartaglini
Beyond the Doors of Perception: Vision Transformers Represent Relations Between Objects
Jun 22, 2024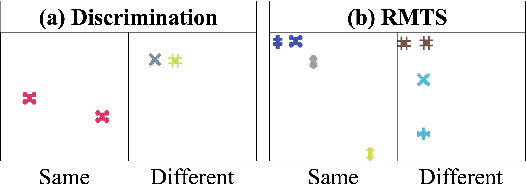
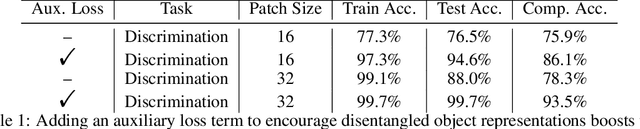
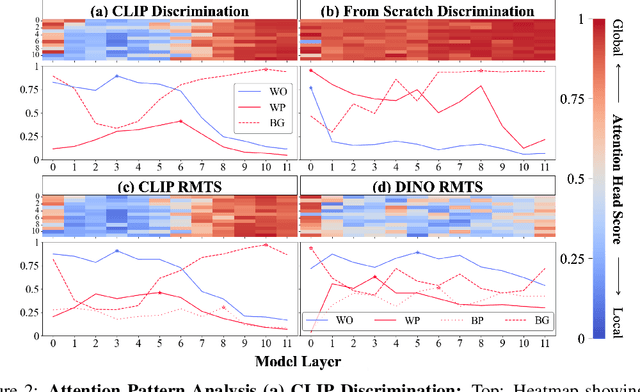
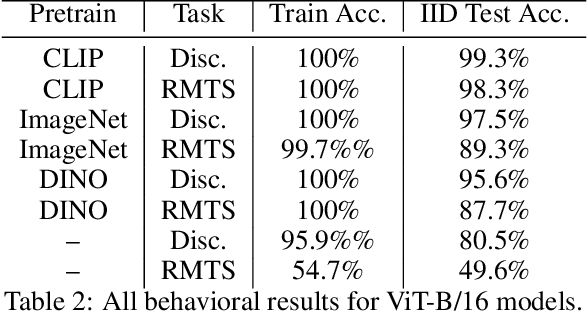
Abstract:Though vision transformers (ViTs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance in a variety of settings, they exhibit surprising failures when performing tasks involving visual relations. This begs the question: how do ViTs attempt to perform tasks that require computing visual relations between objects? Prior efforts to interpret ViTs tend to focus on characterizing relevant low-level visual features. In contrast, we adopt methods from mechanistic interpretability to study the higher-level visual algorithms that ViTs use to perform abstract visual reasoning. We present a case study of a fundamental, yet surprisingly difficult, relational reasoning task: judging whether two visual entities are the same or different. We find that pretrained ViTs fine-tuned on this task often exhibit two qualitatively different stages of processing despite having no obvious inductive biases to do so: 1) a perceptual stage wherein local object features are extracted and stored in a disentangled representation, and 2) a relational stage wherein object representations are compared. In the second stage, we find evidence that ViTs can learn to represent somewhat abstract visual relations, a capability that has long been considered out of reach for artificial neural networks. Finally, we demonstrate that failure points at either stage can prevent a model from learning a generalizable solution to our fairly simple tasks. By understanding ViTs in terms of discrete processing stages, one can more precisely diagnose and rectify shortcomings of existing and future models.
Deep Neural Networks Can Learn Generalizable Same-Different Visual Relations
Oct 14, 2023



Abstract:Although deep neural networks can achieve human-level performance on many object recognition benchmarks, prior work suggests that these same models fail to learn simple abstract relations, such as determining whether two objects are the same or different. Much of this prior work focuses on training convolutional neural networks to classify images of two same or two different abstract shapes, testing generalization on within-distribution stimuli. In this article, we comprehensively study whether deep neural networks can acquire and generalize same-different relations both within and out-of-distribution using a variety of architectures, forms of pretraining, and fine-tuning datasets. We find that certain pretrained transformers can learn a same-different relation that generalizes with near perfect accuracy to out-of-distribution stimuli. Furthermore, we find that fine-tuning on abstract shapes that lack texture or color provides the strongest out-of-distribution generalization. Our results suggest that, with the right approach, deep neural networks can learn generalizable same-different visual relations.
A Developmentally-Inspired Examination of Shape versus Texture Bias in Machines
Feb 16, 2022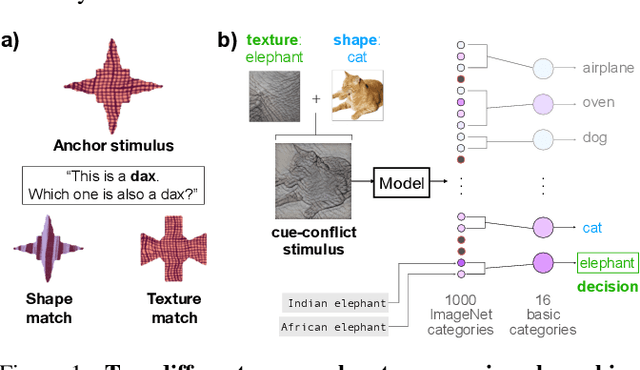
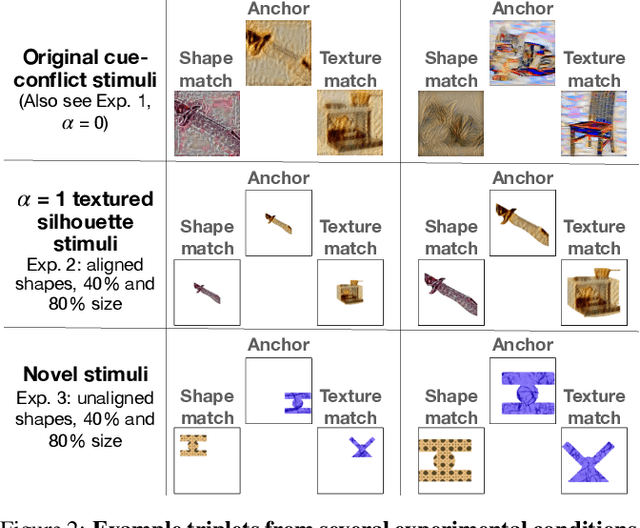
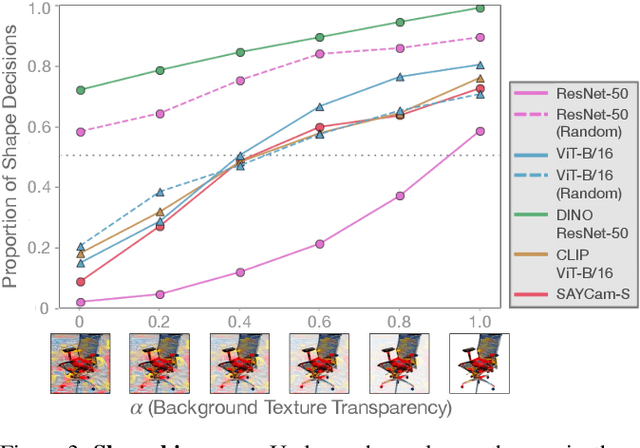
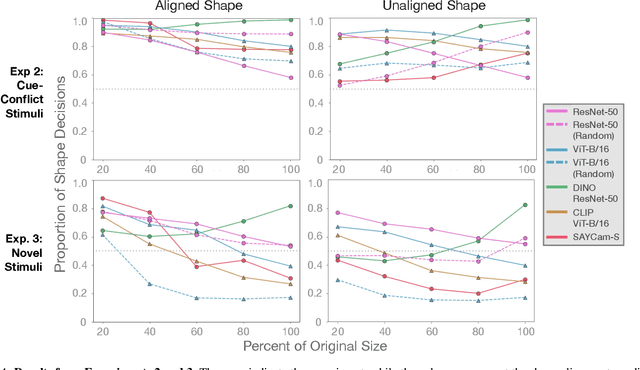
Abstract:Early in development, children learn to extend novel category labels to objects with the same shape, a phenomenon known as the shape bias. Inspired by these findings, Geirhos et al. (2019) examined whether deep neural networks show a shape or texture bias by constructing images with conflicting shape and texture cues. They found that convolutional neural networks strongly preferred to classify familiar objects based on texture as opposed to shape, suggesting a texture bias. However, there are a number of differences between how the networks were tested in this study versus how children are typically tested. In this work, we re-examine the inductive biases of neural networks by adapting the stimuli and procedure from Geirhos et al. (2019) to more closely follow the developmental paradigm and test on a wide range of pre-trained neural networks. Across three experiments, we find that deep neural networks exhibit a preference for shape rather than texture when tested under conditions that more closely replicate the developmental procedure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge