Alex Kirilin
Taxonomy of multimodal self-supervised representation learning
Dec 29, 2020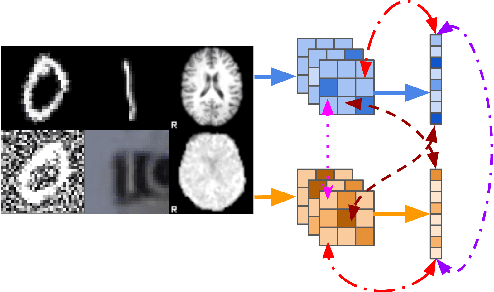
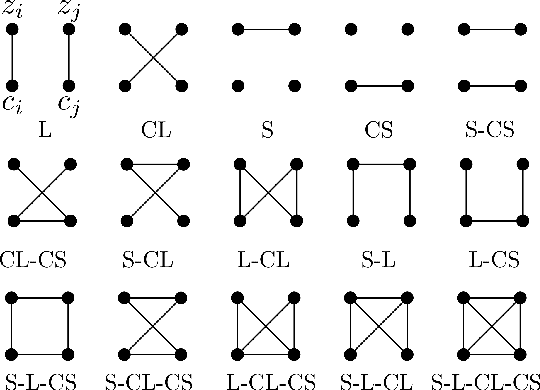
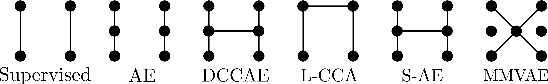
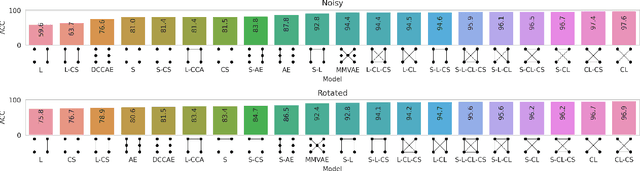
Abstract:Sensory input from multiple sources is crucial for robust and coherent human perception. Different sources contribute complementary explanatory factors and get combined based on factors they share. This system motivated the design of powerful unsupervised representation-learning algorithms. In this paper, we unify recent work on multimodal self-supervised learning under a single framework. Observing that most self-supervised methods optimize similarity metrics between a set of model components, we propose a taxonomy of all reasonable ways to organize this process. We empirically show on two versions of multimodal MNIST and a multimodal brain imaging dataset that (1) multimodal contrastive learning has significant benefits over its unimodal counterpart, (2) the specific composition of multiple contrastive objectives is critical to performance on a downstream task, (3) maximization of the similarity between representations has a regularizing effect on a neural network, which sometimes can lead to reduced downstream performance but still can reveal multimodal relations. Consequently, we outperform previous unsupervised encoder-decoder methods based on CCA or variational mixtures MMVAE on various datasets on linear evaluation protocol.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge