Alejandra Sierra
USFetal: Tools for Fetal Brain Ultrasound Compounding
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Ultrasound offers a safe, cost-effective, and widely accessible technology for fetal brain imaging, making it especially suitable for routine clinical use. However, it suffers from view-dependent artifacts, operator variability, and a limited field of view, which make interpretation and quantitative evaluation challenging. Ultrasound compounding aims to overcome these limitations by integrating complementary information from multiple 3D acquisitions into a single, coherent volumetric representation. This work provides four main contributions: (1) We present the first systematic categorization of computational strategies for fetal brain ultrasound compounding, including both classical techniques and modern learning-based frameworks. (2) We implement and compare representative methods across four key categories - multi-scale, transformation-based, variational, and deep learning approaches - emphasizing their core principles and practical advantages. (3) Motivated by the lack of full-view, artifact-free ground truth required for supervised learning, we focus on unsupervised and self-supervised strategies and introduce two new deep learning based approaches: a self-supervised compounding framework and an adaptation of unsupervised deep plug-and-play priors for compounding. (4) We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on ten multi-view fetal brain ultrasound datasets, using both expert radiologist scoring and standard quantitative image-quality metrics. We also release the USFetal Compounding Toolbox, publicly available to support benchmarking and future research. Keywords: Ultrasound compounding, fetal brain, deep learning, self-supervised, unsupervised.
Scattering approach to diffusion quantifies axonal damage in brain injury
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Early diagnosis and noninvasive monitoring of neurological disorders require sensitivity to elusive cellular-level alterations that occur much earlier than volumetric changes observable with the millimeter-resolution of medical imaging modalities. Morphological changes in axons, such as axonal varicosities or beadings, are observed in neurological disorders, as well as in development and aging. Here, we reveal the sensitivity of time-dependent diffusion MRI (dMRI) to axonal morphology at the micrometer scale. Scattering theory uncovers the two parameters that determine the diffusive dynamics of water in axons: the average reciprocal cross-section and the variance of long-range cross-sectional fluctuations. This theoretical development allowed us to predict dMRI metrics sensitive to axonal alterations across tens of thousands of axons in seconds rather than months of simulations in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Our approach bridges the gap between micrometers and millimeters in resolution, offering quantitative, objective biomarkers applicable to a broad spectrum of neurological disorders.
Segment Anything for Dendrites from Electron Microscopy
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:Segmentation of cellular structures in electron microscopy (EM) images is fundamental to analyzing the morphology of neurons and glial cells in the healthy and diseased brain tissue. Current neuronal segmentation applications are based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and do not effectively capture global relationships within images. Here, we present DendriteSAM, a vision foundation model based on Segment Anything, for interactive and automatic segmentation of dendrites in EM images. The model is trained on high-resolution EM data from healthy rat hippocampus and is tested on diseased rat and human data. Our evaluation results demonstrate better mask quality compared to the original and other fine-tuned models, leveraging the features learned during training. This study introduces the first implementation of vision foundation models in dendrite segmentation, paving the path for computer-assisted diagnosis of neuronal anomalies.
No-Clean-Reference Image Super-Resolution: Application to Electron Microscopy
Jan 26, 2024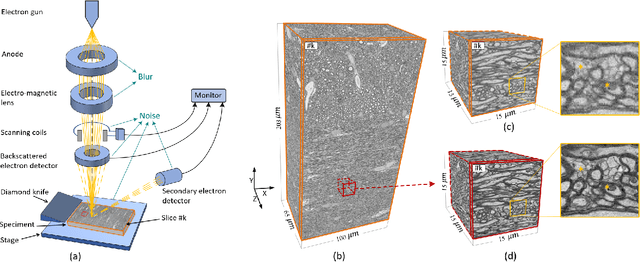
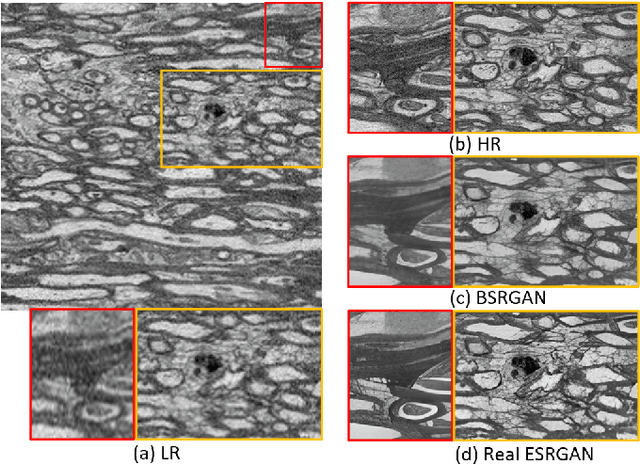



Abstract:The inability to acquire clean high-resolution (HR) electron microscopy (EM) images over a large brain tissue volume hampers many neuroscience studies. To address this challenge, we propose a deep-learning-based image super-resolution (SR) approach to computationally reconstruct clean HR 3D-EM with a large field of view (FoV) from noisy low-resolution (LR) acquisition. Our contributions are I) Investigating training with no-clean references for $\ell_2$ and $\ell_1$ loss functions; II) Introducing a novel network architecture, named EMSR, for enhancing the resolution of LR EM images while reducing inherent noise; and, III) Comparing different training strategies including using acquired LR and HR image pairs, i.e., real pairs with no-clean references contaminated with real corruptions, the pairs of synthetic LR and acquired HR, as well as acquired LR and denoised HR pairs. Experiments with nine brain datasets showed that training with real pairs can produce high-quality super-resolved results, demonstrating the feasibility of training with non-clean references for both loss functions. Additionally, comparable results were observed, both visually and numerically, when employing denoised and noisy references for training. Moreover, utilizing the network trained with synthetically generated LR images from HR counterparts proved effective in yielding satisfactory SR results, even in certain cases, outperforming training with real pairs. The proposed SR network was compared quantitatively and qualitatively with several established SR techniques, showcasing either the superiority or competitiveness of the proposed method in mitigating noise while recovering fine details.
Self-Supervised Super-Resolution Approach for Isotropic Reconstruction of 3D Electron Microscopy Images from Anisotropic Acquisition
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Three-dimensional electron microscopy (3DEM) is an essential technique to investigate volumetric tissue ultra-structure. Due to technical limitations and high imaging costs, samples are often imaged anisotropically, where resolution in the axial direction ($z$) is lower than in the lateral directions $(x,y)$. This anisotropy 3DEM can hamper subsequent analysis and visualization tasks. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel deep-learning (DL)-based self-supervised super-resolution approach that computationally reconstructs isotropic 3DEM from the anisotropic acquisition. The proposed DL-based framework is built upon the U-shape architecture incorporating vision-transformer (ViT) blocks, enabling high-capability learning of local and global multi-scale image dependencies. To train the tailored network, we employ a self-supervised approach. Specifically, we generate pairs of anisotropic and isotropic training datasets from the given anisotropic 3DEM data. By feeding the given anisotropic 3DEM dataset in the trained network through our proposed framework, the isotropic 3DEM is obtained. Importantly, this isotropic reconstruction approach relies solely on the given anisotropic 3DEM dataset and does not require pairs of co-registered anisotropic and isotropic 3DEM training datasets. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted experiments using three 3DEM datasets acquired from brain. The experimental results demonstrated that our proposed framework could successfully reconstruct isotropic 3DEM from the anisotropic acquisition.
Adversarial Distortion Learning for Medical Image Denoising
Apr 29, 2022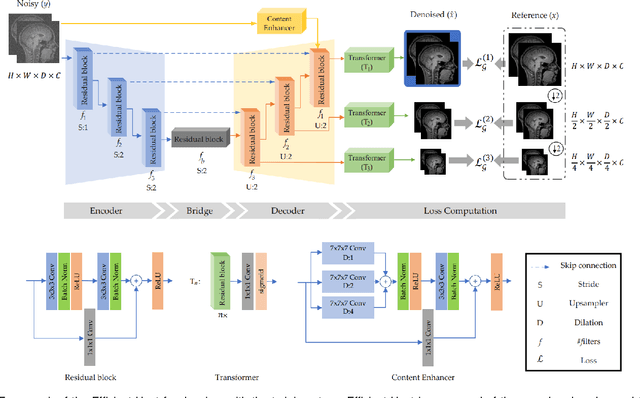
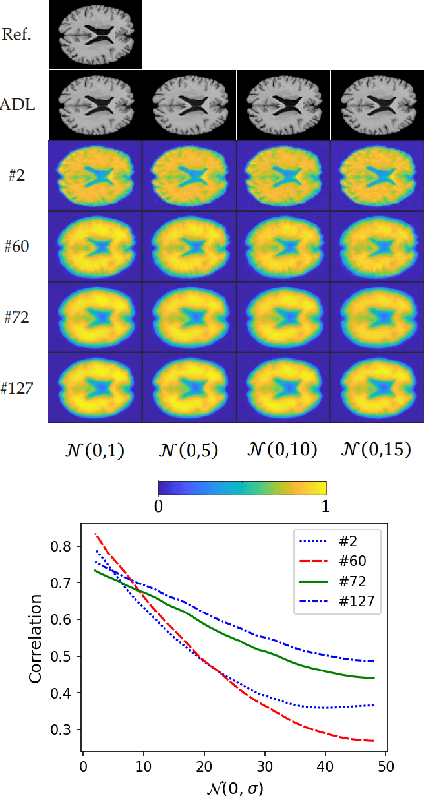
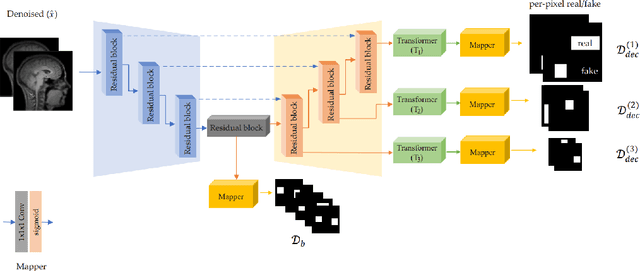
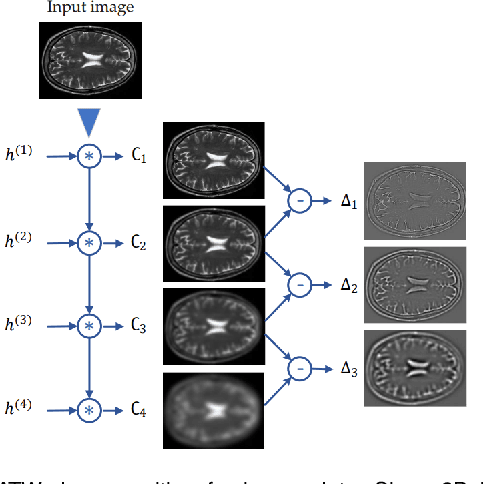
Abstract:We present a novel adversarial distortion learning (ADL) for denoising two- and three-dimensional (2D/3D) biomedical image data. The proposed ADL consists of two auto-encoders: a denoiser and a discriminator. The denoiser removes noise from input data and the discriminator compares the denoised result to its noise-free counterpart. This process is repeated until the discriminator cannot differentiate the denoised data from the reference. Both the denoiser and the discriminator are built upon a proposed auto-encoder called Efficient-Unet. Efficient-Unet has a light architecture that uses the residual blocks and a novel pyramidal approach in the backbone to efficiently extract and re-use feature maps. During training, the textural information and contrast are controlled by two novel loss functions. The architecture of Efficient-Unet allows generalizing the proposed method to any sort of biomedical data. The 2D version of our network was trained on ImageNet and tested on biomedical datasets whose distribution is completely different from ImageNet; so, there is no need for re-training. Experimental results carried out on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), dermatoscopy, electron microscopy and X-ray datasets show that the proposed method achieved the best on each benchmark. Our implementation and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/mogvision/ADL.
gACSON software for automated segmentation and morphology analyses of myelinated axons in 3D electron microscopy
Dec 13, 2021



Abstract:Background and Objective: Advances in electron microscopy (EM) now allow three-dimensional (3D) imaging of hundreds of micrometers of tissue with nanometer-scale resolution, providing new opportunities to study the ultrastructure of the brain. In this work, we introduce a freely available gACSON software for visualization, segmentation, assessment, and morphology analysis of myelinated axons in 3D-EM volumes of brain tissue samples. Methods: The gACSON software is equipped with a graphical user interface (GUI). It automatically segments the intra-axonal space of myelinated axons and their corresponding myelin sheaths and allows manual segmentation, proofreading, and interactive correction of the segmented components. gACSON analyzes the morphology of myelinated axons, such as axonal diameter, axonal eccentricity, myelin thickness, or g-ratio. Results: We illustrate the use of gACSON by segmenting and analyzing myelinated axons in six 3D-EM volumes of rat somatosensory cortex after sham surgery or traumatic brain injury (TBI). Our results suggest that the equivalent diameter of myelinated axons in somatisensory cortex was decreased in TBI animals five months after the injury. Conclusions: Our results indicate that gACSON is a valuable tool for visualization, segmentation, assessment, and morphology analysis of myelinated axons in 3D-EM volumes. gACSON is freely available at https://github.com/AndreaBehan/g-ACSON under the MIT license.
RatLesNetv2: A Fully Convolutional Network for Rodent Brain Lesion Segmentation
Jan 24, 2020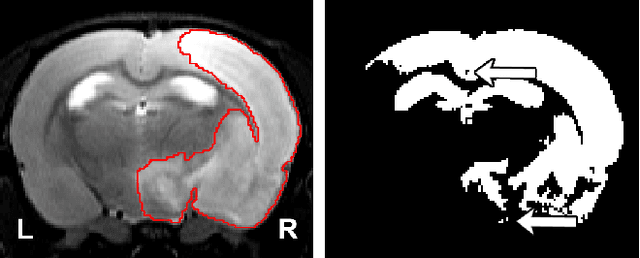
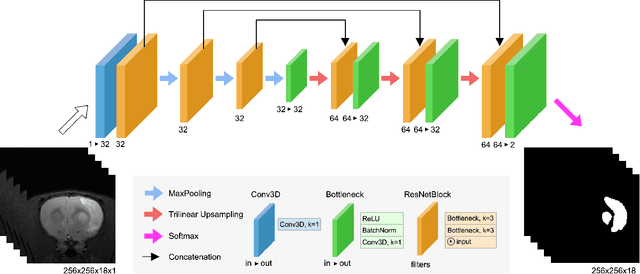

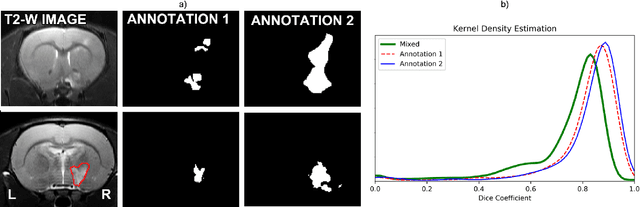
Abstract:Segmentation of rodent brain lesions on magnetic resonance images (MRIs) is a time-consuming task with high inter- and intra-operator variability due to its subjective nature. We present a three-dimensional fully convolutional neural network (ConvNet) named RatLesNetv2 for segmenting rodent brain lesions. We compare its performance with other ConvNets on an unusually large and heterogeneous data set composed by 916 T2-weighted rat brain scans at nine different lesion stages. RatLesNetv2 obtained similar to higher Dice coefficients than the other ConvNets and it produced much more realistic and compact segmentations with notably less holes and lower Hausdorff distance. RatLesNetv2-derived segmentations also exceeded inter-rater agreement Dice coefficients. Additionally, we show that training on disparate ground truths leads to significantly different segmentations, and we study RatLesNetv2 generalization capability when optimizing for training sets of different sizes. RatLesNetv2 is publicly available at https://github.com/jmlipman/RatLesNetv2.
Cylindrical Shape Decomposition Algorithm for 3D Segmentation
Nov 01, 2019



Abstract:Shape decomposition is a fundamental problem in geometry processing where an arbitrary object is regarded as an arrangement of simple primitives or semantic components. The application of 3D shape decomposition in the context of image segmentation, however, is not well-studied. In this paper, we develop a shape decomposition algorithm called cylindrical shape decomposition (CSD) to be applied for the segmentation of tubular structures in large-scale 3D images. CSD starts by partitioning the curve skeleton of a tubular object into maximal-length sub-skeletons, minimizing an orientation objective. Each sub-skeleton corresponds to a semantic component. To determine boundaries between the semantic components, CSD searches for critical points where the object cross-section substantially changes. CSD then cuts the object at critical points and assigns the same label to those object parts which are along the same sub-skeleton, defining a semantic tubular component. CSD further rectify/reconstructs these semantic components using generalized cylinders. We demonstrate the application of CSD in the segmentation of large-scale 3D electron microscopy image datasets of myelinated axons, the decomposition of vascular networks, and synthetic objects. We also compare CSD to other state-of-the-art decomposition techniques in these applications. These experiments indicate that CSD outperforms other decomposition techniques and achieves a promising performance.
Automatic Rodent Brain MRI Lesion Segmentation with Fully Convolutional Networks
Aug 23, 2019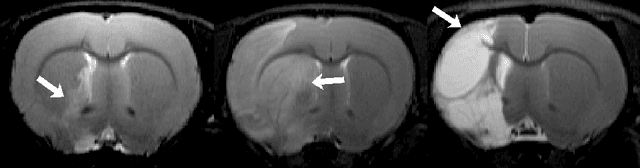
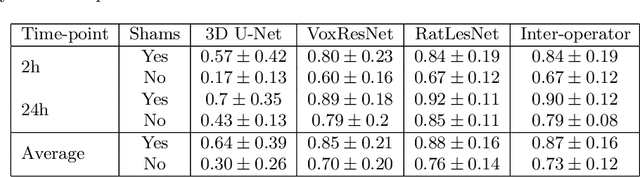
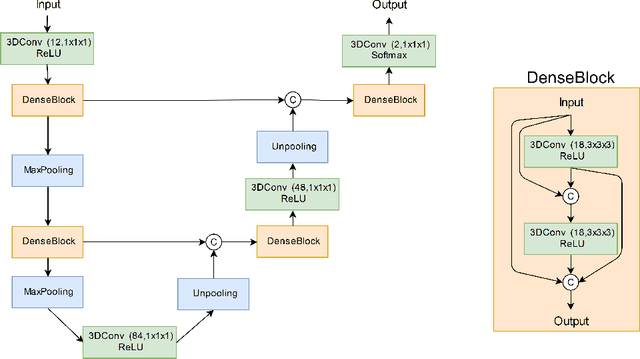
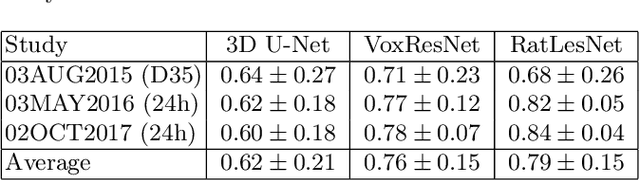
Abstract:Manual segmentation of rodent brain lesions from magnetic resonance images (MRIs) is an arduous, time-consuming and subjective task that is highly important in pre-clinical research. Several automatic methods have been developed for different human brain MRI segmentation, but little research has targeted automatic rodent lesion segmentation. The existing tools for performing automatic lesion segmentation in rodents are constrained by strict assumptions about the data. Deep learning has been successfully used for medical image segmentation. However, there has not been any deep learning approach specifically designed for tackling rodent brain lesion segmentation. In this work, we propose a novel Fully Convolutional Network (FCN), RatLesNet, for the aforementioned task. Our dataset consists of 131 T2-weighted rat brain scans from 4 different studies in which ischemic stroke was induced by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. We compare our method with two other 3D FCNs originally developed for anatomical segmentation (VoxResNet and 3D-U-Net) with 5-fold cross-validation on a single study and a generalization test, where the training was done on a single study and testing on three remaining studies. The labels generated by our method were quantitatively and qualitatively better than the predictions of the compared methods. The average Dice coefficient achieved in the 5-fold cross-validation experiment with the proposed approach was 0.88, between 3.7% and 38% higher than the compared architectures. The presented architecture also outperformed the other FCNs at generalizing on different studies, achieving the average Dice coefficient of 0.79.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge