Agnia Sergeyuk
Does In-IDE Calibration of Large Language Models work at Scale?
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:The introduction of large language models into integrated development environments (IDEs) is revolutionizing software engineering, yet it poses challenges to the usefulness and reliability of Artificial Intelligence-generated code. Post-hoc calibration of internal model confidences aims to align probabilities with an acceptability measure. Prior work suggests calibration can improve alignment, but at-scale evidence is limited. In this work, we investigate the feasibility of applying calibration of code models to an in-IDE context. We study two aspects of the problem: (1) the technical method for implementing confidence calibration and improving the reliability of code generation models, and (2) the human-centered design principles for effectively communicating reliability signal to developers. First, we develop a scalable and flexible calibration framework which can be used to obtain calibration weights for open-source models using any dataset, and evaluate whether calibrators improve the alignment between model confidence and developer acceptance behavior. Through a large-scale analysis of over 24 million real-world developer interactions across multiple programming languages, we find that a general, post-hoc calibration model based on Platt-scaling does not, on average, improve the reliability of model confidence signals. We also find that while dynamically personalizing calibration to individual users can be effective, its effectiveness is highly dependent on the volume of user interaction data. Second, we conduct a multi-phase design study with 3 expert designers and 153 professional developers, combining scenario-based design, semi-structured interviews, and survey validation, revealing a clear preference for presenting reliability signals via non-numerical, color-coded indicators within the in-editor code generation workflow.
Understanding Prompt Programming Tasks and Questions
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Prompting foundation models (FMs) like large language models (LLMs) have enabled new AI-powered software features (e.g., text summarization) that previously were only possible by fine-tuning FMs. Now, developers are embedding prompts in software, known as prompt programs. The process of prompt programming requires the developer to make many changes to their prompt. Yet, the questions developers ask to update their prompt is unknown, despite the answers to these questions affecting how developers plan their changes. With the growing number of research and commercial prompt programming tools, it is unclear whether prompt programmers' needs are being adequately addressed. We address these challenges by developing a taxonomy of 25 tasks prompt programmers do and 51 questions they ask, measuring the importance of each task and question. We interview 16 prompt programmers, observe 8 developers make prompt changes, and survey 50 developers. We then compare the taxonomy with 48 research and commercial tools. We find that prompt programming is not well-supported: all tasks are done manually, and 16 of the 51 questions -- including a majority of the most important ones -- remain unanswered. Based on this, we outline important opportunities for prompt programming tools.
Human-AI Experience in Integrated Development Environments: A Systematic Literature Review
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) is reshaping software development, fundamentally altering how developers interact with their tools. This shift marks the emergence of Human-AI Experience in Integrated Development Environment (in-IDE HAX), a field that explores the evolving dynamics of Human-Computer Interaction in AI-assisted coding environments. Despite rapid adoption, research on in-IDE HAX remains fragmented which highlights the need for a unified overview of current practices, challenges, and opportunities. To provide a structured overview of existing research, we conduct a systematic literature review of 89 studies, summarizing current findings and outlining areas for further investigation. Our findings reveal that AI-assisted coding enhances developer productivity but also introduces challenges, such as verification overhead, automation bias, and over-reliance, particularly among novice developers. Furthermore, concerns about code correctness, security, and maintainability highlight the urgent need for explainability, verification mechanisms, and adaptive user control. Although recent advances have driven the field forward, significant research gaps remain, including a lack of longitudinal studies, personalization strategies, and AI governance frameworks. This review provides a foundation for advancing in-IDE HAX research and offers guidance for responsibly integrating AI into software development.
Using AI-Based Coding Assistants in Practice: State of Affairs, Perceptions, and Ways Forward
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:The last several years saw the emergence of AI assistants for code -- multi-purpose AI-based helpers in software engineering. Their quick development makes it necessary to better understand how specifically developers are using them, why they are not using them in certain parts of their development workflow, and what needs to be improved. In this work, we carried out a large-scale survey aimed at how AI assistants are used, focusing on specific software development activities and stages. We collected opinions of 481 programmers on five broad activities: (a) implementing new features, (b) writing tests, (c) bug triaging, (d) refactoring, and (e) writing natural-language artifacts, as well as their individual stages. Our results show that usage of AI assistants varies depending on activity and stage. For instance, developers find writing tests and natural-language artifacts to be the least enjoyable activities and want to delegate them the most, currently using AI assistants to generate tests and test data, as well as generating comments and docstrings most of all. This can be a good focus for features aimed to help developers right now. As for why developers do not use assistants, in addition to general things like trust and company policies, there are fixable issues that can serve as a guide for further research, e.g., the lack of project-size context, and lack of awareness about assistants. We believe that our comprehensive and specific results are especially needed now to steer active research toward where users actually need AI assistants.
A Design Space for Intelligent and Interactive Writing Assistants
Mar 26, 2024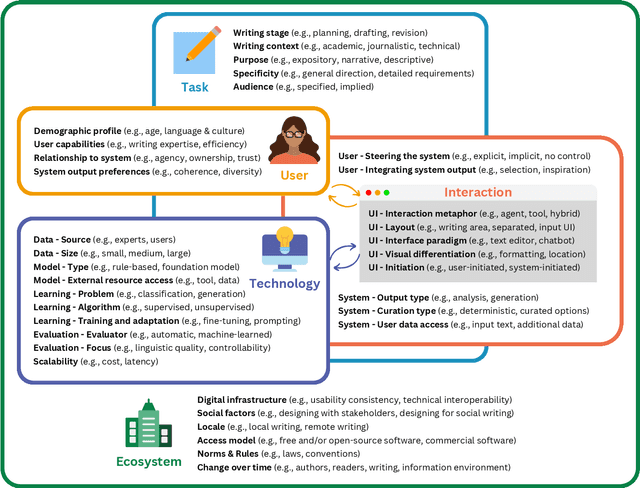
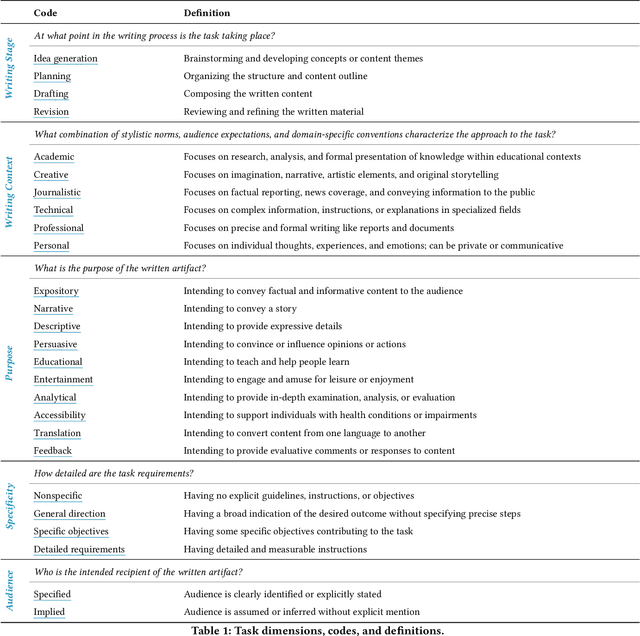
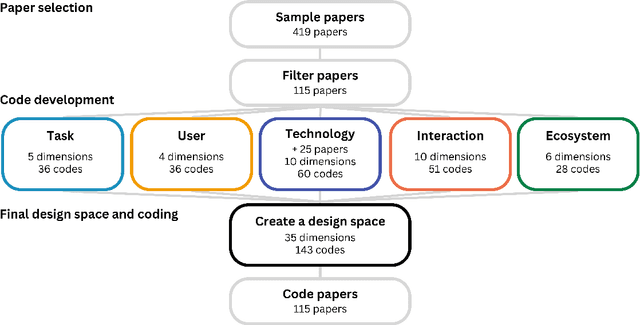
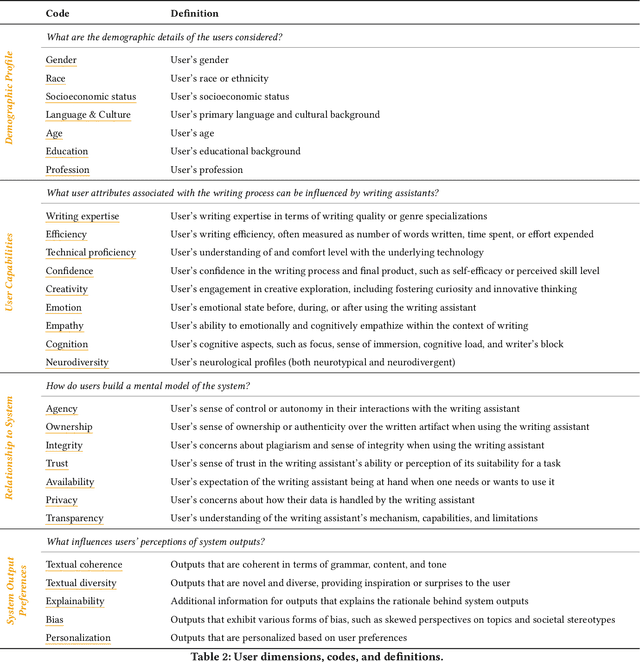
Abstract:In our era of rapid technological advancement, the research landscape for writing assistants has become increasingly fragmented across various research communities. We seek to address this challenge by proposing a design space as a structured way to examine and explore the multidimensional space of intelligent and interactive writing assistants. Through a large community collaboration, we explore five aspects of writing assistants: task, user, technology, interaction, and ecosystem. Within each aspect, we define dimensions (i.e., fundamental components of an aspect) and codes (i.e., potential options for each dimension) by systematically reviewing 115 papers. Our design space aims to offer researchers and designers a practical tool to navigate, comprehend, and compare the various possibilities of writing assistants, and aid in the envisioning and design of new writing assistants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge