Ademir Ferreira da Silva
Fine-tuning of Geospatial Foundation Models for Aboveground Biomass Estimation
Jun 28, 2024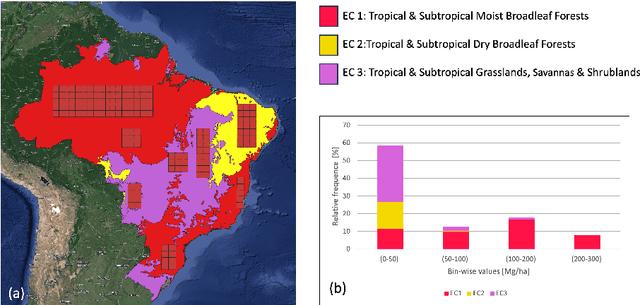

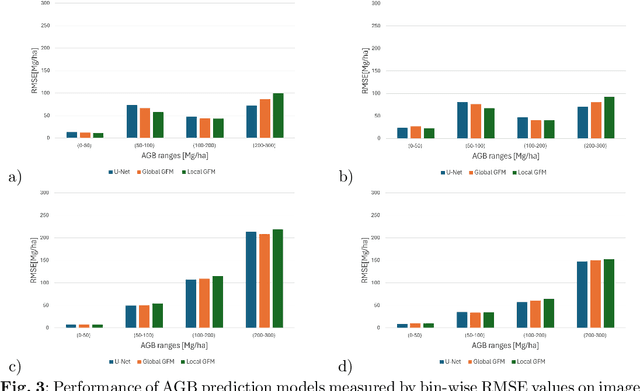
Abstract:Global vegetation structure mapping is critical for understanding the global carbon cycle and maximizing the efficacy of nature-based carbon sequestration initiatives. Moreover, vegetation structure mapping can help reduce the impacts of climate change by, for example, guiding actions to improve water security, increase biodiversity and reduce flood risk. Global satellite measurements provide an important set of observations for monitoring and managing deforestation and degradation of existing forests, natural forest regeneration, reforestation, biodiversity restoration, and the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices. In this paper, we explore the effectiveness of fine-tuning of a geospatial foundation model to estimate above-ground biomass (AGB) using space-borne data collected across different eco-regions in Brazil. The fine-tuned model architecture consisted of a Swin-B transformer as the encoder (i.e., backbone) and a single convolutional layer for the decoder head. All results were compared to a U-Net which was trained as the baseline model Experimental results of this sparse-label prediction task demonstrate that the fine-tuned geospatial foundation model with a frozen encoder has comparable performance to a U-Net trained from scratch. This is despite the fine-tuned model having 13 times less parameters requiring optimization, which saves both time and compute resources. Further, we explore the transfer-learning capabilities of the geospatial foundation models by fine-tuning on satellite imagery with sparse labels from different eco-regions in Brazil.
Image-Based Soil Organic Carbon Remote Sensing from Satellite Images with Fourier Neural Operator and Structural Similarity
Nov 21, 2023

Abstract:Soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration is the transfer and storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide in soils, which plays an important role in climate change mitigation. SOC concentration can be improved by proper land use, thus it is beneficial if SOC can be estimated at a regional or global scale. As multispectral satellite data can provide SOC-related information such as vegetation and soil properties at a global scale, estimation of SOC through satellite data has been explored as an alternative to manual soil sampling. Although existing studies show promising results, they are mainly based on pixel-based approaches with traditional machine learning methods, and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are uncommon. To study the use of CNNs on SOC remote sensing, here we propose the FNO-DenseNet based on the Fourier neural operator (FNO). By combining the advantages of the FNO and DenseNet, the FNO-DenseNet outperformed the FNO in our experiments with hundreds of times fewer parameters. The FNO-DenseNet also outperformed a pixel-based random forest by 18% in the mean absolute percentage error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge