Abdelkader El Mahdaouy
M-DAIGT: A Shared Task on Multi-Domain Detection of AI-Generated Text
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The generation of highly fluent text by Large Language Models (LLMs) poses a significant challenge to information integrity and academic research. In this paper, we introduce the Multi-Domain Detection of AI-Generated Text (M-DAIGT) shared task, which focuses on detecting AI-generated text across multiple domains, particularly in news articles and academic writing. M-DAIGT comprises two binary classification subtasks: News Article Detection (NAD) (Subtask 1) and Academic Writing Detection (AWD) (Subtask 2). To support this task, we developed and released a new large-scale benchmark dataset of 30,000 samples, balanced between human-written and AI-generated texts. The AI-generated content was produced using a variety of modern LLMs (e.g., GPT-4, Claude) and diverse prompting strategies. A total of 46 unique teams registered for the shared task, of which four teams submitted final results. All four teams participated in both Subtask 1 and Subtask 2. We describe the methods employed by these participating teams and briefly discuss future directions for M-DAIGT.
DomURLs_BERT: Pre-trained BERT-based Model for Malicious Domains and URLs Detection and Classification
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Detecting and classifying suspicious or malicious domain names and URLs is fundamental task in cybersecurity. To leverage such indicators of compromise, cybersecurity vendors and practitioners often maintain and update blacklists of known malicious domains and URLs. However, blacklists frequently fail to identify emerging and obfuscated threats. Over the past few decades, there has been significant interest in developing machine learning models that automatically detect malicious domains and URLs, addressing the limitations of blacklists maintenance and updates. In this paper, we introduce DomURLs_BERT, a pre-trained BERT-based encoder adapted for detecting and classifying suspicious/malicious domains and URLs. DomURLs_BERT is pre-trained using the Masked Language Modeling (MLM) objective on a large multilingual corpus of URLs, domain names, and Domain Generation Algorithms (DGA) dataset. In order to assess the performance of DomURLs_BERT, we have conducted experiments on several binary and multi-class classification tasks involving domain names and URLs, covering phishing, malware, DGA, and DNS tunneling. The evaluations results show that the proposed encoder outperforms state-of-the-art character-based deep learning models and cybersecurity-focused BERT models across multiple tasks and datasets. The pre-training dataset, the pre-trained DomURLs_BERT encoder, and the experiments source code are publicly available.
CS-UM6P at SemEval-2022 Task 6: Transformer-based Models for Intended Sarcasm Detection in English and Arabic
Jun 16, 2022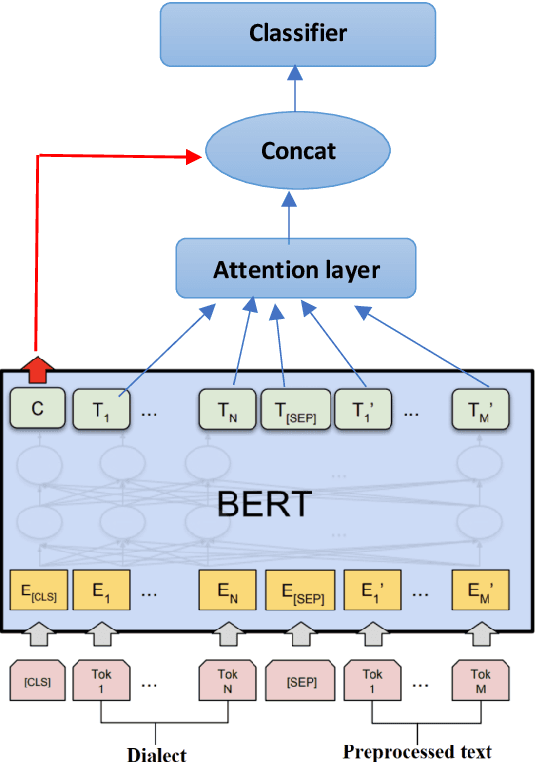
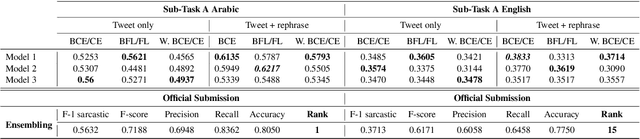
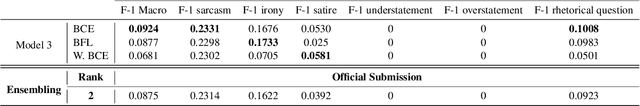
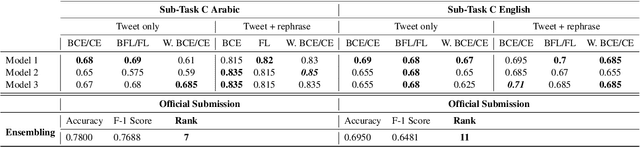
Abstract:Sarcasm is a form of figurative language where the intended meaning of a sentence differs from its literal meaning. This poses a serious challenge to several Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications such as Sentiment Analysis, Opinion Mining, and Author Profiling. In this paper, we present our participating system to the intended sarcasm detection task in English and Arabic languages. Our system\footnote{The source code of our system is available at \url{https://github.com/AbdelkaderMH/iSarcasmEval}} consists of three deep learning-based models leveraging two existing pre-trained language models for Arabic and English. We have participated in all sub-tasks. Our official submissions achieve the best performance on sub-task A for Arabic language and rank second in sub-task B. For sub-task C, our system is ranked 7th and 11th on Arabic and English datasets, respectively.
Deep Multi-Task Models for Misogyny Identification and Categorization on Arabic Social Media
Jun 16, 2022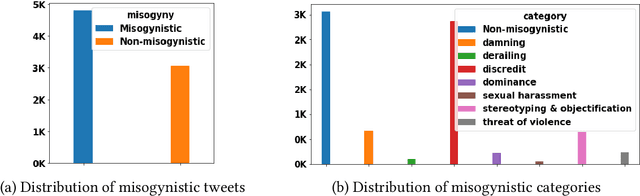
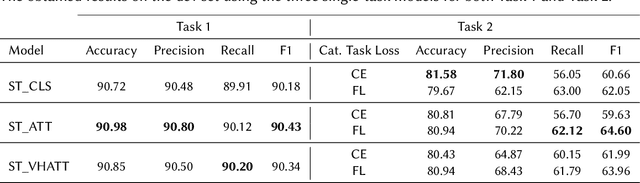
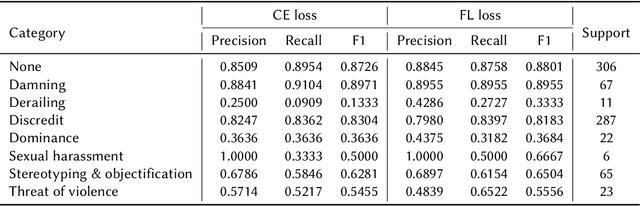
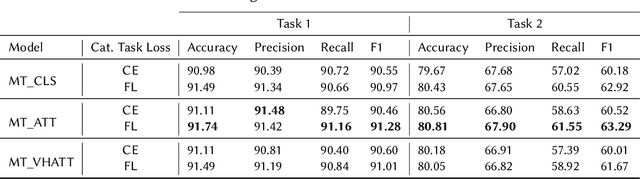
Abstract:The prevalence of toxic content on social media platforms, such as hate speech, offensive language, and misogyny, presents serious challenges to our interconnected society. These challenging issues have attracted widespread attention in Natural Language Processing (NLP) community. In this paper, we present the submitted systems to the first Arabic Misogyny Identification shared task. We investigate three multi-task learning models as well as their single-task counterparts. In order to encode the input text, our models rely on the pre-trained MARBERT language model. The overall obtained results show that all our submitted models have achieved the best performances (top three ranked submissions) in both misogyny identification and categorization tasks.
UM6P-CS at SemEval-2022 Task 11: Enhancing Multilingual and Code-Mixed Complex Named Entity Recognition via Pseudo Labels using Multilingual Transformer
Apr 28, 2022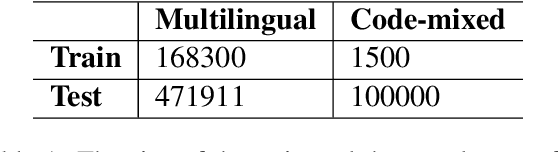
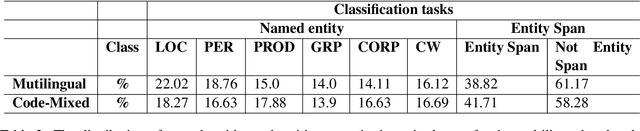
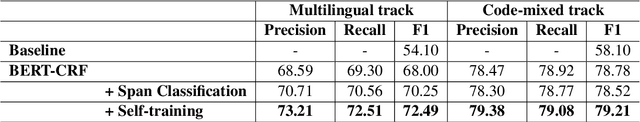
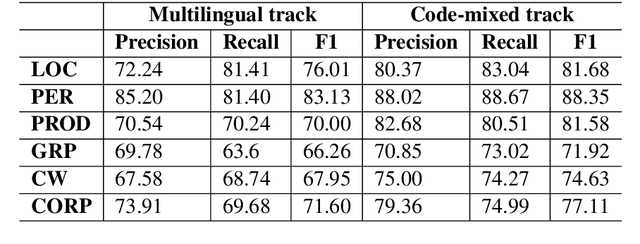
Abstract:Building real-world complex Named Entity Recognition (NER) systems is a challenging task. This is due to the complexity and ambiguity of named entities that appear in various contexts such as short input sentences, emerging entities, and complex entities. Besides, real-world queries are mostly malformed, as they can be code-mixed or multilingual, among other scenarios. In this paper, we introduce our submitted system to the Multilingual Complex Named Entity Recognition (MultiCoNER) shared task. We approach the complex NER for multilingual and code-mixed queries, by relying on the contextualized representation provided by the multilingual Transformer XLM-RoBERTa. In addition to the CRF-based token classification layer, we incorporate a span classification loss to recognize named entities spans. Furthermore, we use a self-training mechanism to generate weakly-annotated data from a large unlabeled dataset. Our proposed system is ranked 6th and 8th in the multilingual and code-mixed MultiCoNER's tracks respectively.
BERT-based Multi-Task Model for Country and Province Level Modern Standard Arabic and Dialectal Arabic Identification
Jun 23, 2021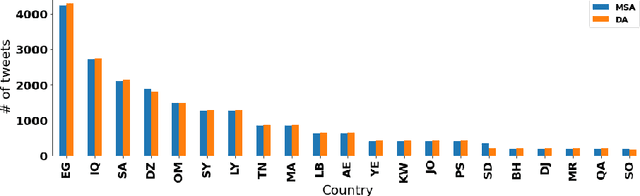
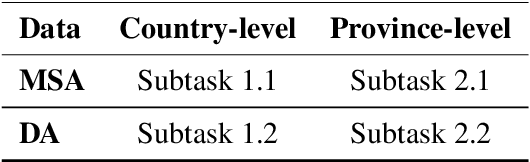
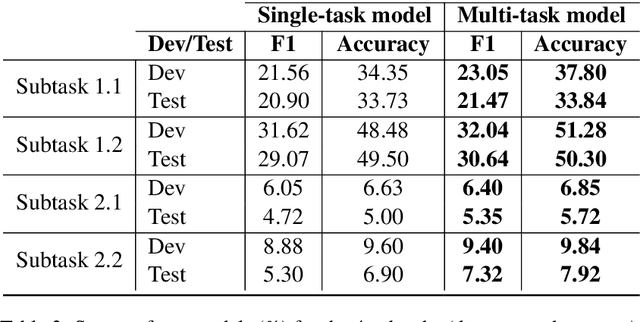
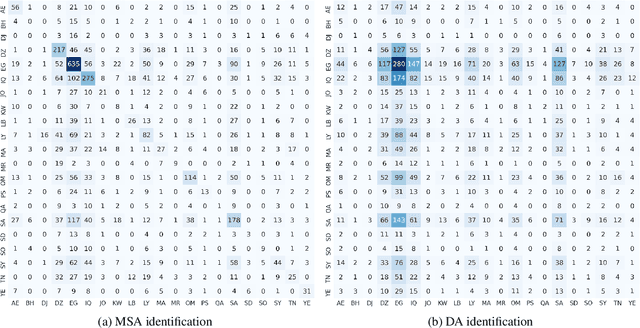
Abstract:Dialect and standard language identification are crucial tasks for many Arabic natural language processing applications. In this paper, we present our deep learning-based system, submitted to the second NADI shared task for country-level and province-level identification of Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) and Dialectal Arabic (DA). The system is based on an end-to-end deep Multi-Task Learning (MTL) model to tackle both country-level and province-level MSA/DA identification. The latter MTL model consists of a shared Bidirectional Encoder Representation Transformers (BERT) encoder, two task-specific attention layers, and two classifiers. Our key idea is to leverage both the task-discriminative and the inter-task shared features for country and province MSA/DA identification. The obtained results show that our MTL model outperforms single-task models on most subtasks.
Deep Multi-Task Model for Sarcasm Detection and Sentiment Analysis in Arabic Language
Jun 23, 2021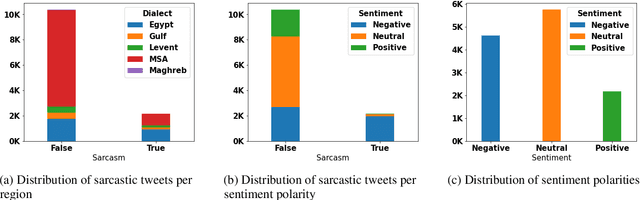



Abstract:The prominence of figurative language devices, such as sarcasm and irony, poses serious challenges for Arabic Sentiment Analysis (SA). While previous research works tackle SA and sarcasm detection separately, this paper introduces an end-to-end deep Multi-Task Learning (MTL) model, allowing knowledge interaction between the two tasks. Our MTL model's architecture consists of a Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers (BERT) model, a multi-task attention interaction module, and two task classifiers. The overall obtained results show that our proposed model outperforms its single-task counterparts on both SA and sarcasm detection sub-tasks.
A Study of Association Measures and their Combination for Arabic MWT Extraction
Sep 10, 2014



Abstract:Automatic Multi-Word Term (MWT) extraction is a very important issue to many applications, such as information retrieval, question answering, and text categorization. Although many methods have been used for MWT extraction in English and other European languages, few studies have been applied to Arabic. In this paper, we propose a novel, hybrid method which combines linguistic and statistical approaches for Arabic Multi-Word Term extraction. The main contribution of our method is to consider contextual information and both termhood and unithood for association measures at the statistical filtering step. In addition, our technique takes into account the problem of MWT variation in the linguistic filtering step. The performance of the proposed statistical measure (NLC-value) is evaluated using an Arabic environment corpus by comparing it with some existing competitors. Experimental results show that our NLC-value measure outperforms the other ones in term of precision for both bi-grams and tri-grams.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge