ViR:the Vision Reservoir
Paper and Code
Dec 29, 2021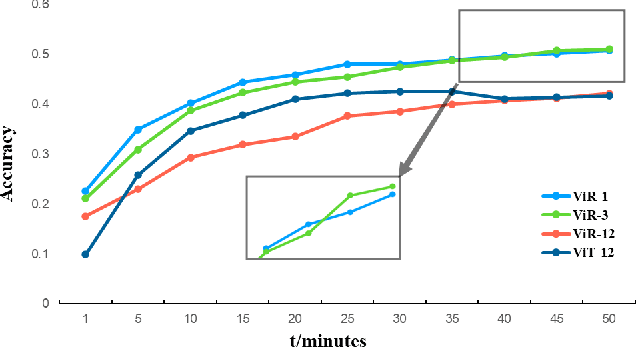
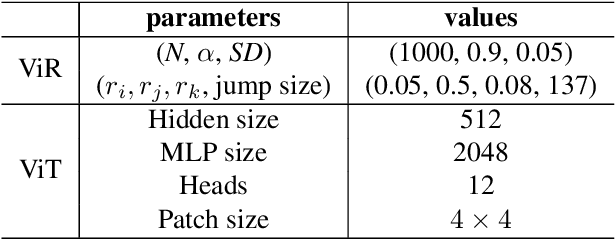
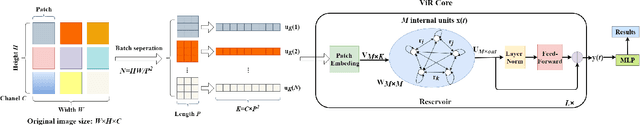
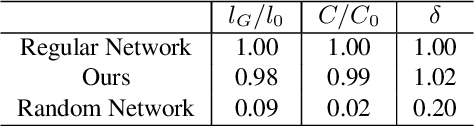
The most recent year has witnessed the success of applying the Vision Transformer (ViT) for image classification. However, there are still evidences indicating that ViT often suffers following two aspects, i) the high computation and the memory burden from applying the multiple Transformer layers for pre-training on a large-scale dataset, ii) the over-fitting when training on small datasets from scratch. To address these problems, a novel method, namely, Vision Reservoir computing (ViR), is proposed here for image classification, as a parallel to ViT. By splitting each image into a sequence of tokens with fixed length, the ViR constructs a pure reservoir with a nearly fully connected topology to replace the Transformer module in ViT. Two kinds of deep ViR models are subsequently proposed to enhance the network performance. Comparative experiments between the ViR and the ViT are carried out on several image classification benchmarks. Without any pre-training process, the ViR outperforms the ViT in terms of both model and computational complexity. Specifically, the number of parameters of the ViR is about 15% even 5% of the ViT, and the memory footprint is about 20% to 40% of the ViT. The superiority of the ViR performance is explained by Small-World characteristics, Lyapunov exponents, and memory capacity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge