HateDebias: On the Diversity and Variability of Hate Speech Debiasing
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2024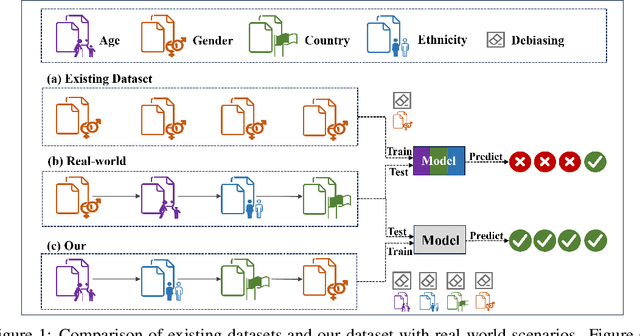

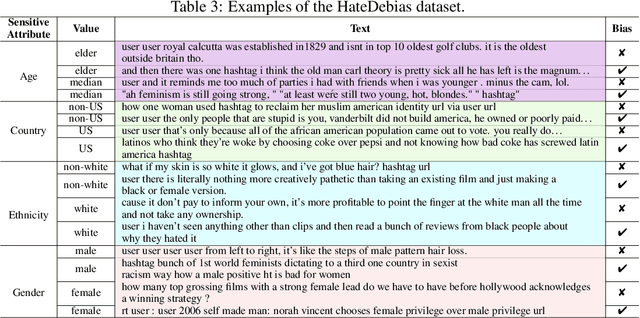

Hate speech on social media is ubiquitous but urgently controlled. Without detecting and mitigating the biases brought by hate speech, different types of ethical problems. While a number of datasets have been proposed to address the problem of hate speech detection, these datasets seldom consider the diversity and variability of bias, making it far from real-world scenarios. To fill this gap, we propose a benchmark, named HateDebias, to analyze the model ability of hate speech detection under continuous, changing environments. Specifically, to meet the diversity of biases, we collect existing hate speech detection datasets with different types of biases. To further meet the variability (i.e., the changing of bias attributes in datasets), we reorganize datasets to follow the continuous learning setting. We evaluate the detection accuracy of models trained on the datasets with a single type of bias with the performance on the HateDebias, where a significant performance drop is observed. To provide a potential direction for debiasing, we further propose a debiasing framework based on continuous learning and bias information regularization, as well as the memory replay strategies to ensure the debiasing ability of the model. Experiment results on the proposed benchmark show that the aforementioned method can improve several baselines with a distinguished margin, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge