GasHis-Transformer: A Multi-scale Visual Transformer Approach for Gastric Histopathology Image Classification
Paper and Code
May 25, 2021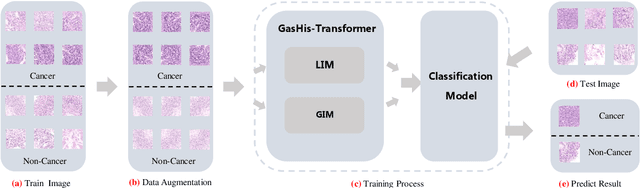
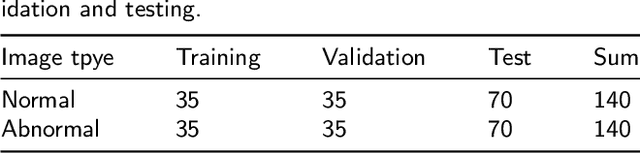
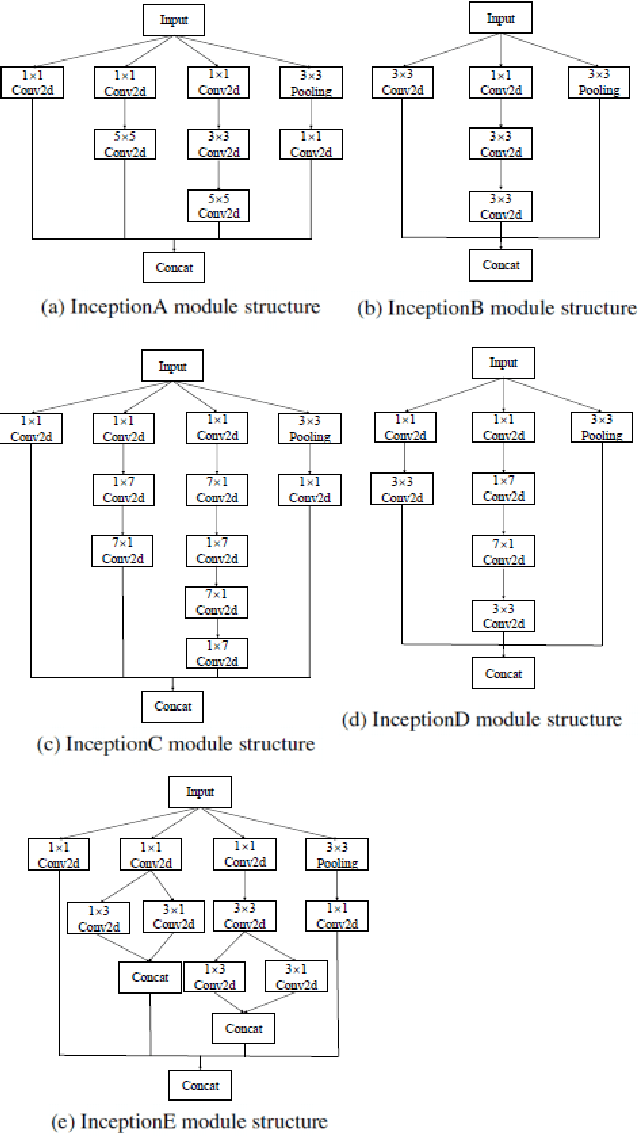
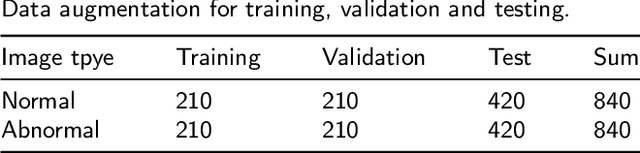
Existing deep learning methods for diagnosis of gastric cancer commonly use convolutional neural networks (CNN). Recently, the Visual Transformer (VT) has attracted a major attention because of its performance and efficiency, but its applications are mostly in the field of computer vision. In this paper, a multi-scale visual transformer model, referred to as GasHis-Transformer, is proposed for gastric histopathology image classification (GHIC), which enables the automatic classification of microscopic gastric images into abnormal and normal cases. The GasHis-Transformer model consists of two key modules: a global information module (GIM) and a local information module (LIM) to extract pathological features effectively. In our experiments, a public hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained gastric histopathology dataset with 280 abnormal or normal images using the GasHis-Transformer model is applied to estimate precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy on the testing set as 98.0%, 100.0%, 96.0% and 98.0% respectively. Furthermore, a critical study is conducted to evaluate the robustness of GasHis-Transformer according to add ten different noises including adversarial attack and traditional image noise. In addition, a clinically meaningful study is executed to test the gastric cancer identification of GasHis-Transformerwith 420 abnormal images and achieves 96.2% accuracy. Finally, a comparative study is performed to test the generalizability with both H&E and Immunohistochemical (IHC) stained images on a lymphoma image dataset, a breast cancer dataset and a cervical cancer dataset, producing comparable F1-scores (85.6%, 82.8% and 65.7%, respectively) and accuracy (83.9%, 89.4% and 65.7%, respectively) respectively. In conclusion, GasHis-Transformerdemonstrates a high classification performance and shows its significant potential in histopathology image analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge