Diff-PIC: Revolutionizing Particle-In-Cell Simulation for Advancing Nuclear Fusion with Diffusion Models
Paper and Code
Aug 03, 2024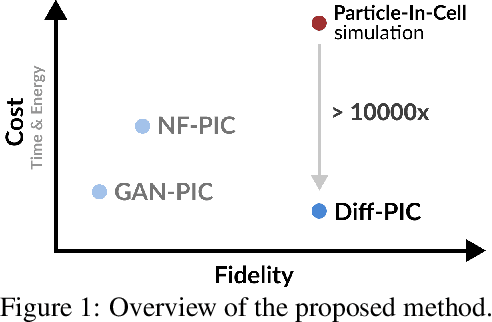
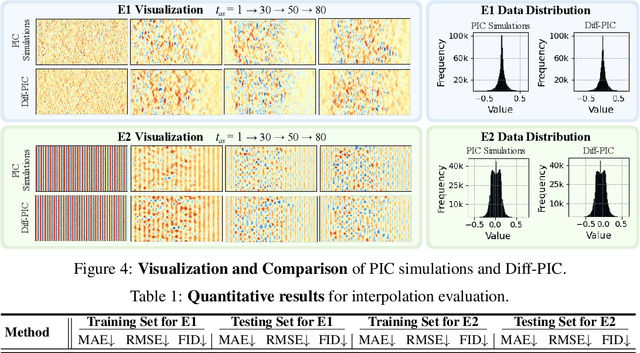
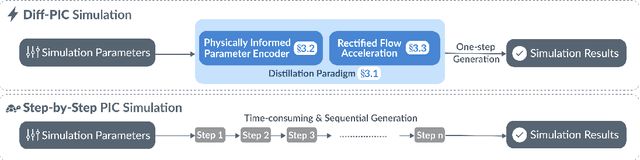
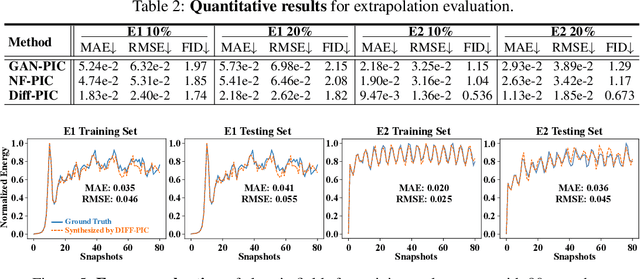
Sustainable energy is a crucial global challenge, and recent breakthroughs in nuclear fusion ignition underscore the potential of harnessing energy extracted from nuclear fusion in everyday life, thereby drawing significant attention to fusion ignition research, especially Laser-Plasma Interaction (LPI). Unfortunately, the complexity of LPI at ignition scale renders theory-based analysis nearly impossible -- instead, it has to rely heavily on Particle-in-Cell (PIC) simulations, which is extremely computationally intensive, making it a major bottleneck in advancing fusion ignition. In response, this work introduces Diff-PIC, a novel paradigm that leverages conditional diffusion models as a computationally efficient alternative to PIC simulations for generating high-fidelity scientific data. Specifically, we design a distillation paradigm to distill the physical patterns captured by PIC simulations into diffusion models, demonstrating both theoretical and practical feasibility. Moreover, to ensure practical effectiveness, we provide solutions for two critical challenges: (1) We develop a physically-informed conditional diffusion model that can learn and generate meaningful embeddings for mathematically continuous physical conditions. This model offers algorithmic generalization and adaptable transferability, effectively capturing the complex relationships between physical conditions and simulation outcomes; and (2) We employ the rectified flow technique to make our model a one-step conditional diffusion model, enhancing its efficiency further while maintaining high fidelity and physical validity. Diff-PIC establishes a new paradigm for using diffusion models to overcome the computational barriers in nuclear fusion research, setting a benchmark for future innovations and advancements in this field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge