ATOMIC: An Atlas of Machine Commonsense for If-Then Reasoning
Paper and Code
Oct 31, 2018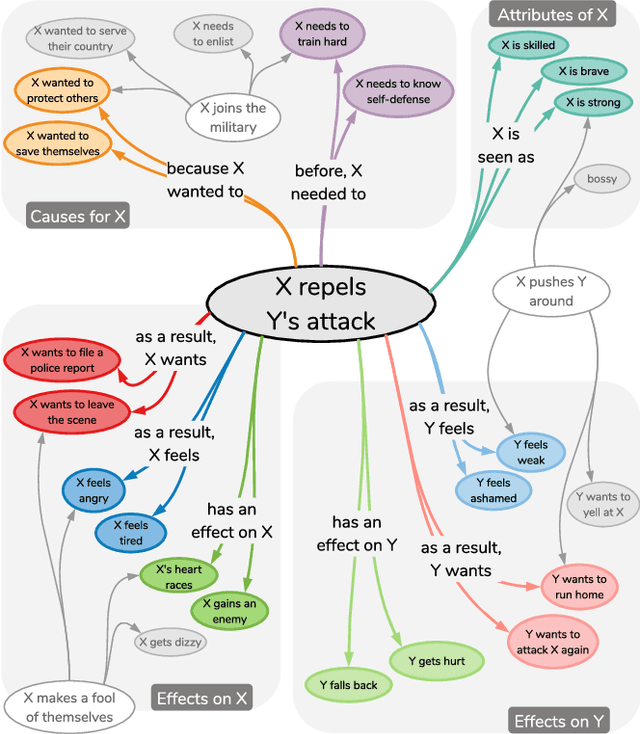
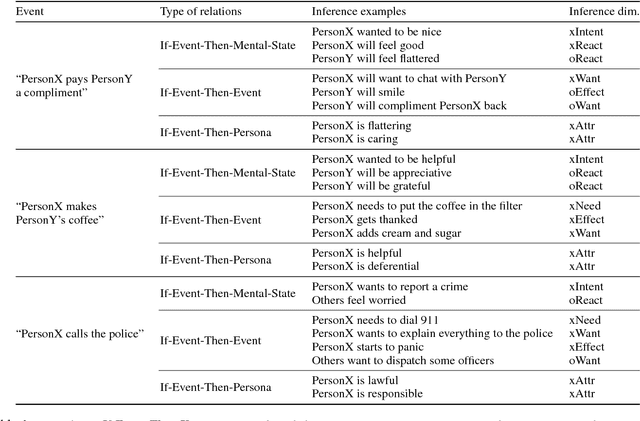
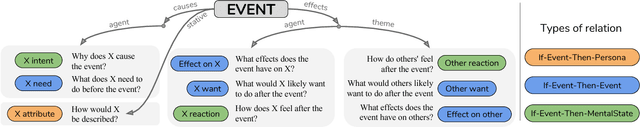
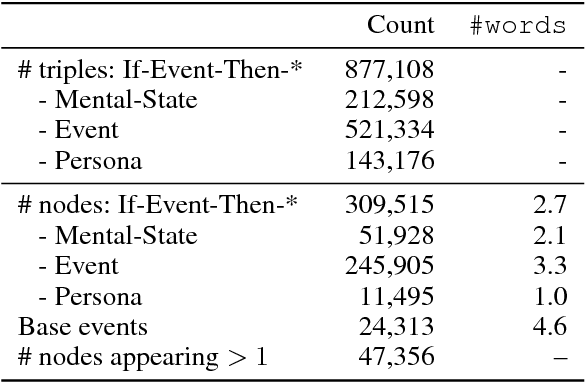
We present ATOMIC, an atlas of everyday commonsense reasoning, organized through 300k textual descriptions. Compared to existing resources that center around taxonomic knowledge, ATOMIC focuses on inferential knowledge organized as typed if-then relations with variables (e.g., "if X pays Y a compliment, then Y will likely return the compliment"). We propose nine if-then relation types to distinguish causes v.s. effects, agents v.s. themes, voluntary v.s. involuntary events, and actions v.s. mental states. By generatively training on the rich inferential knowledge described in ATOMIC, we show that neural models can acquire simple commonsense capabilities and reason about previously unseen events. Experimental results demonstrate that multitask models that incorporate the hierarchical structure of if-then relation types lead to more accurate inference compared to models trained in isolation, as measured by both automatic and human evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge