Adversarial Texture Optimization from RGB-D Scans
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2020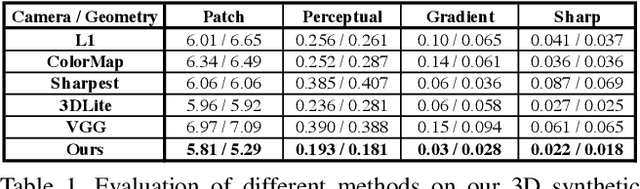
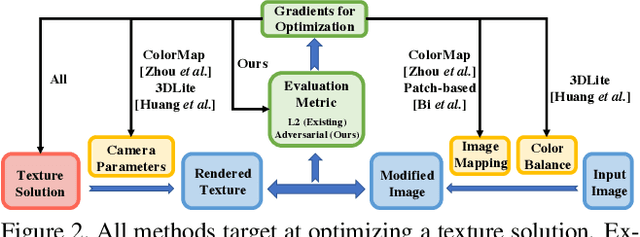
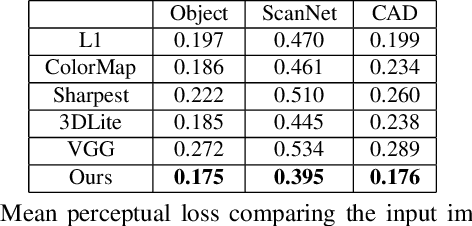
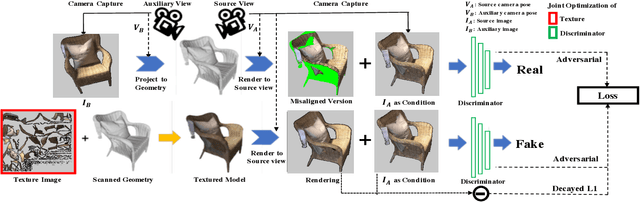
Realistic color texture generation is an important step in RGB-D surface reconstruction, but remains challenging in practice due to inaccuracies in reconstructed geometry, misaligned camera poses, and view-dependent imaging artifacts. In this work, we present a novel approach for color texture generation using a conditional adversarial loss obtained from weakly-supervised views. Specifically, we propose an approach to produce photorealistic textures for approximate surfaces, even from misaligned images, by learning an objective function that is robust to these errors. The key idea of our approach is to learn a patch-based conditional discriminator which guides the texture optimization to be tolerant to misalignments. Our discriminator takes a synthesized view and a real image, and evaluates whether the synthesized one is realistic, under a broadened definition of realism. We train the discriminator by providing as `real' examples pairs of input views and their misaligned versions -- so that the learned adversarial loss will tolerate errors from the scans. Experiments on synthetic and real data under quantitative or qualitative evaluation demonstrate the advantage of our approach in comparison to state of the art. Our code is publicly available with video demonstration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge