Zixiang Kuai
Progressive Dual Priori Network for Generalized Breast Tumor Segmentation
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:To promote the generalization ability of breast tumor segmentation models, as well as to improve the segmentation performance for breast tumors with smaller size, low-contrast amd irregular shape, we propose a progressive dual priori network (PDPNet) to segment breast tumors from dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance images (DCE-MRI) acquired at different sites. The PDPNet first cropped tumor regions with a coarse-segmentation based localization module, then the breast tumor mask was progressively refined by using the weak semantic priori and cross-scale correlation prior knowledge. To validate the effectiveness of PDPNet, we compared it with several state-of-the-art methods on multi-center datasets. The results showed that, comparing against the suboptimal method, the DSC, SEN, KAPPA and HD95 of PDPNet were improved 3.63\%, 8.19\%, 5.52\%, and 3.66\% respectively. In addition, through ablations, we demonstrated that the proposed localization module can decrease the influence of normal tissues and therefore improve the generalization ability of the model. The weak semantic priors allow focusing on tumor regions to avoid missing small tumors and low-contrast tumors. The cross-scale correlation priors are beneficial for promoting the shape-aware ability for irregual tumors. Thus integrating them in a unified framework improved the multi-center breast tumor segmentation performance.
CNN-Based Invertible Wavelet Scattering for the Investigation of Diffusion Properties of the In Vivo Human Heart in Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Dec 17, 2019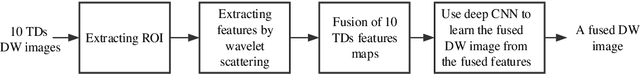
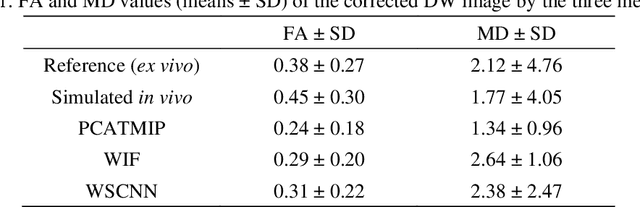
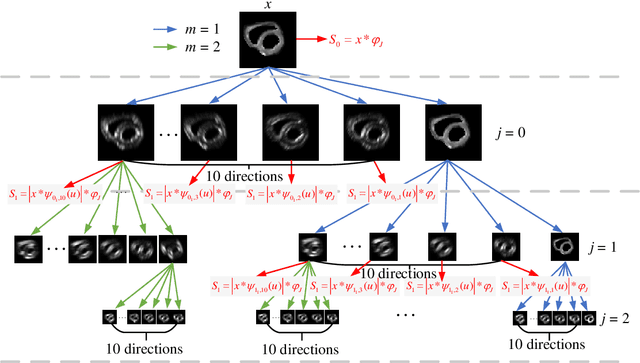
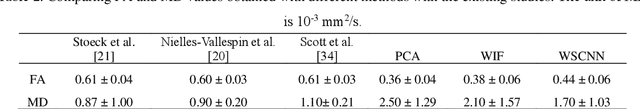
Abstract:In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a promising technique to investigate noninvasively the fiber structures of the in vivo human heart. However, signal loss due to motions remains a persistent problem in in vivo cardiac DTI. We propose a novel motion-compensation method for investigating in vivo myocardium structures in DTI with free-breathing acquisitions. The method is based on an invertible Wavelet Scattering achieved by means of Convolutional Neural Network (WSCNN). It consists of first extracting translation-invariant wavelet scattering features from DW images acquired at different trigger delays and then mapping the fused scattering features into motion-compensated spatial DW images by performing an inverse wavelet scattering transform achieved using CNN. The results on both simulated and acquired in vivo cardiac DW images showed that the proposed WSCNN method effectively compensates for motion-induced signal loss and produces in vivo cardiac DW images with better quality and more coherent fiber structures with respect to existing methods, which makes it an interesting method for measuring correctly the diffusion properties of the in vivo human heart in DTI under free breathing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge