Zhoutao Wang
MODNet: Multi-offset Point Cloud Denoising Network Customized for Multi-scale Patches
Sep 01, 2022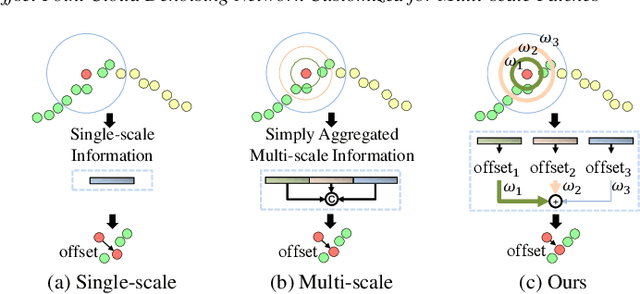
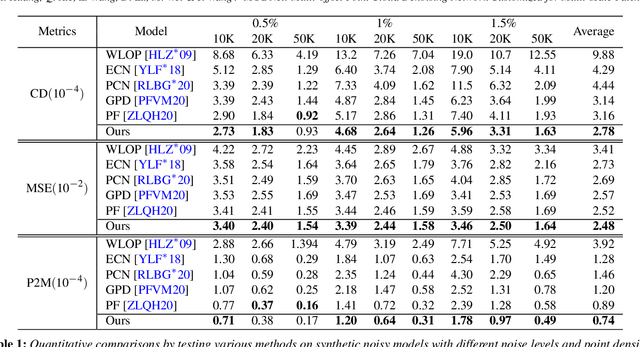
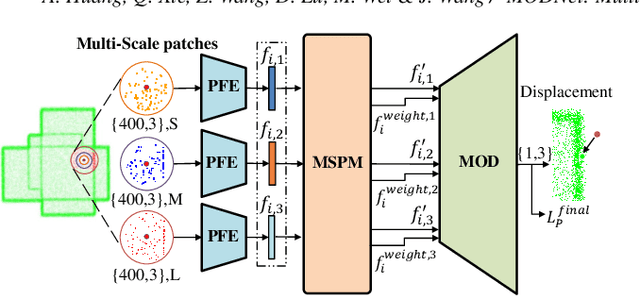
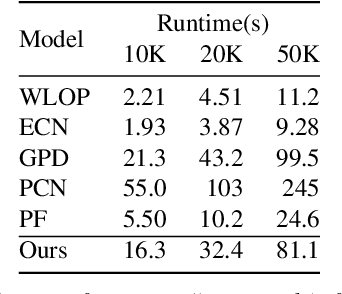
Abstract:The intricacy of 3D surfaces often results cutting-edge point cloud denoising (PCD) models in surface degradation including remnant noise, wrongly-removed geometric details. Although using multi-scale patches to encode the geometry of a point has become the common wisdom in PCD, we find that simple aggregation of extracted multi-scale features can not adaptively utilize the appropriate scale information according to the geometric information around noisy points. It leads to surface degradation, especially for points close to edges and points on complex curved surfaces. We raise an intriguing question -- if employing multi-scale geometric perception information to guide the network to utilize multi-scale information, can eliminate the severe surface degradation problem? To answer it, we propose a Multi-offset Denoising Network (MODNet) customized for multi-scale patches. First, we extract the low-level feature of three scales patches by patch feature encoders. Second, a multi-scale perception module is designed to embed multi-scale geometric information for each scale feature and regress multi-scale weights to guide a multi-offset denoising displacement. Third, a multi-offset decoder regresses three scale offsets, which are guided by the multi-scale weights to predict the final displacement by weighting them adaptively. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-scanned datasets.
MLCVNet: Multi-Level Context VoteNet for 3D Object Detection
Apr 12, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we address the 3D object detection task by capturing multi-level contextual information with the self-attention mechanism and multi-scale feature fusion. Most existing 3D object detection methods recognize objects individually, without giving any consideration on contextual information between these objects. Comparatively, we propose Multi-Level Context VoteNet (MLCVNet) to recognize 3D objects correlatively, building on the state-of-the-art VoteNet. We introduce three context modules into the voting and classifying stages of VoteNet to encode contextual information at different levels. Specifically, a Patch-to-Patch Context (PPC) module is employed to capture contextual information between the point patches, before voting for their corresponding object centroid points. Subsequently, an Object-to-Object Context (OOC) module is incorporated before the proposal and classification stage, to capture the contextual information between object candidates. Finally, a Global Scene Context (GSC) module is designed to learn the global scene context. We demonstrate these by capturing contextual information at patch, object and scene levels. Our method is an effective way to promote detection accuracy, achieving new state-of-the-art detection performance on challenging 3D object detection datasets, i.e., SUN RGBD and ScanNet. We also release our code at https://github.com/NUAAXQ/MLCVNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge