Zhipeng Lu
Convolutional optimization with convex kernel and power lift
Mar 28, 2025

Abstract:We focus on establishing the foundational paradigm of a novel optimization theory based on convolution with convex kernels. Our goal is to devise a morally deterministic model of locating the global optima of an arbitrary function, which is distinguished from most commonly used statistical models. Limited preliminary numerical results are provided to test the efficiency of some specific algorithms derived from our paradigm, which we hope to stimulate further practical interest.
Residual Hyperbolic Graph Convolution Networks
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Hyperbolic graph convolutional networks (HGCNs) have demonstrated representational capabilities of modeling hierarchical-structured graphs. However, as in general GCNs, over-smoothing may occur as the number of model layers increases, limiting the representation capabilities of most current HGCN models. In this paper, we propose residual hyperbolic graph convolutional networks (R-HGCNs) to address the over-smoothing problem. We introduce a hyperbolic residual connection function to overcome the over-smoothing problem, and also theoretically prove the effectiveness of the hyperbolic residual function. Moreover, we use product manifolds and HyperDrop to facilitate the R-HGCNs. The distinctive features of the R-HGCNs are as follows: (1) The hyperbolic residual connection preserves the initial node information in each layer and adds a hyperbolic identity mapping to prevent node features from being indistinguishable. (2) Product manifolds in R-HGCNs have been set up with different origin points in different components to facilitate the extraction of feature information from a wider range of perspectives, which enhances the representing capability of R-HGCNs. (3) HyperDrop adds multiplicative Gaussian noise into hyperbolic representations, such that perturbations can be added to alleviate the over-fitting problem without deconstructing the hyperbolic geometry. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of R-HGCNs under various graph convolution layers and different structures of product manifolds.
Spatio-temporal-spectral-angular observation model that integrates observations from UAV and mobile mapping vehicle for better urban mapping
Sep 05, 2021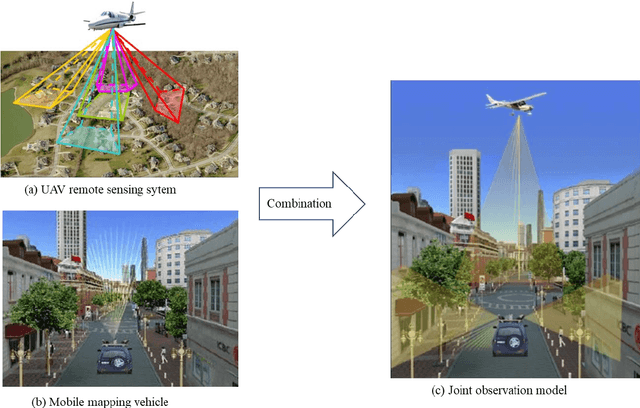
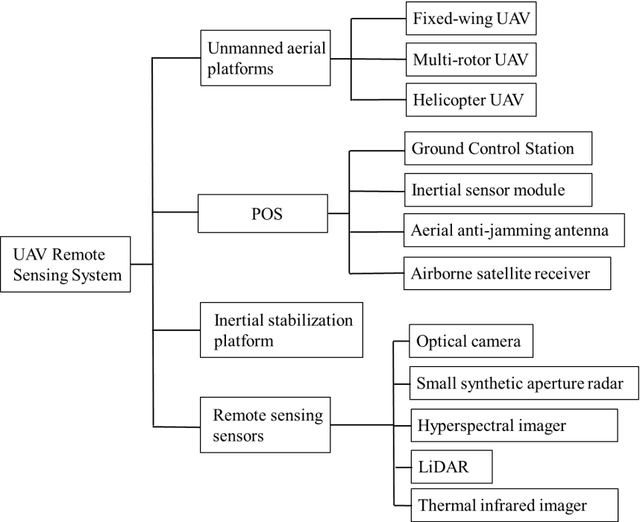

Abstract:In a complex urban scene, observation from a single sensor unavoidably leads to voids in observations, failing to describe urban objects in a comprehensive manner. In this paper, we propose a spatio-temporal-spectral-angular observation model to integrate observations from UAV and mobile mapping vehicle platform, realizing a joint, coordinated observation operation from both air and ground. We develop a multi-source remote sensing data acquisition system to effectively acquire multi-angle data of complex urban scenes. Multi-source data fusion solves the missing data problem caused by occlusion and achieves accurate, rapid, and complete collection of holographic spatial and temporal information in complex urban scenes. We carried out an experiment on Baisha Town, Chongqing, China and obtained multi-sensor, multi-angle data from UAV and mobile mapping vehicle. We first extracted the point cloud from UAV and then integrated the UAV and mobile mapping vehicle point cloud. The integrated results combined both the characteristic of UAV and mobile mapping vehicle point cloud, confirming the practicability of the proposed joint data acquisition platform and the effectiveness of spatio-temporal-spectral-angular observation model. Compared with the observation from UAV or mobile mapping vehicle alone, the integrated system provides an effective data acquisition solution towards comprehensive urban monitoring.
A Memetic Algorithm for the Linear Ordering Problem with Cumulative Costs
May 18, 2014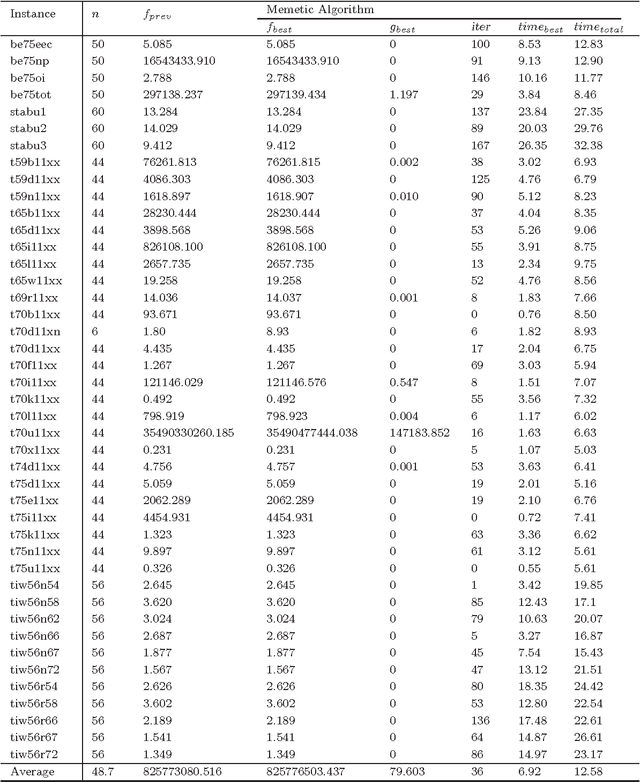
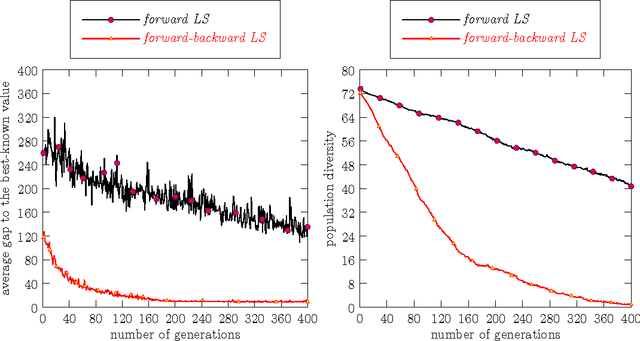
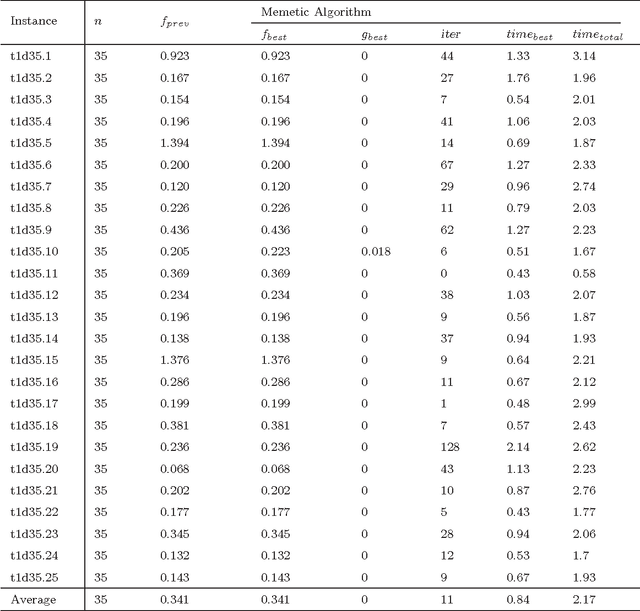
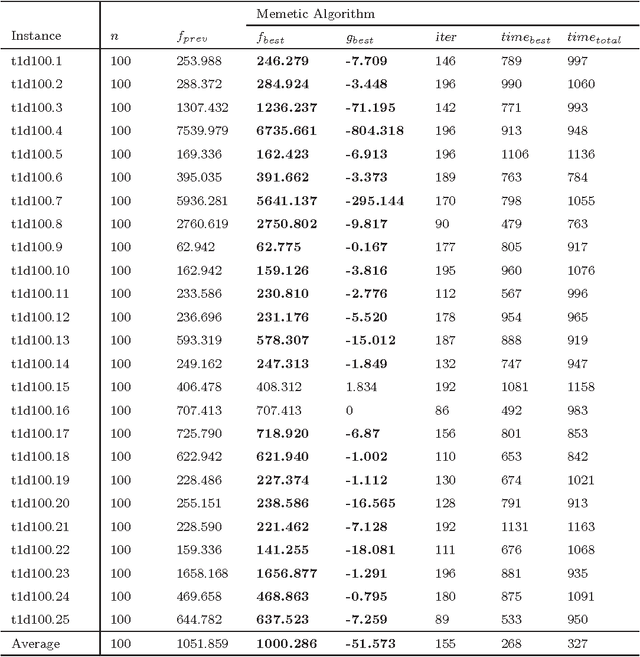
Abstract:This paper introduces an effective memetic algorithm for the linear ordering problem with cumulative costs. The proposed algorithm combines an order-based recombination operator with an improved forward-backward local search procedure and employs a solution quality based replacement criterion for pool updating. Extensive experiments on 118 well-known benchmark instances show that the proposed algorithm achieves competitive results by identifying 46 new upper bounds. Furthermore, some critical ingredients of our algorithm are analyzed to understand the source of its performance.
A Multi-parent Memetic Algorithm for the Linear Ordering Problem
May 18, 2014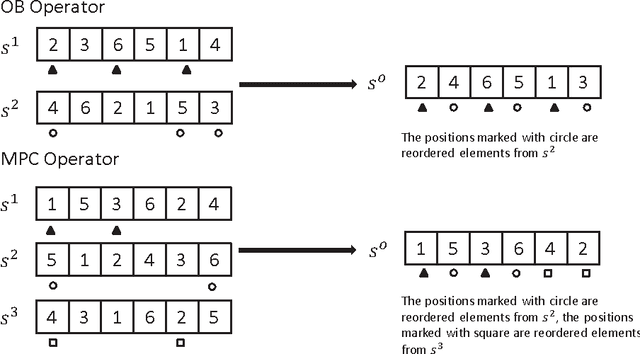
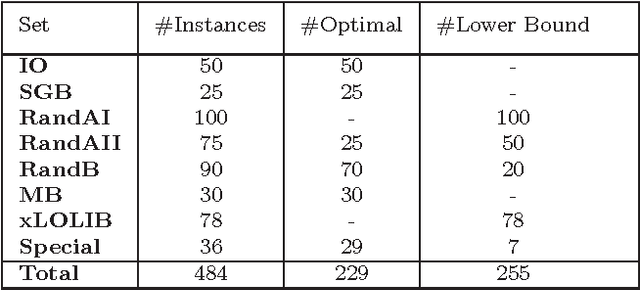
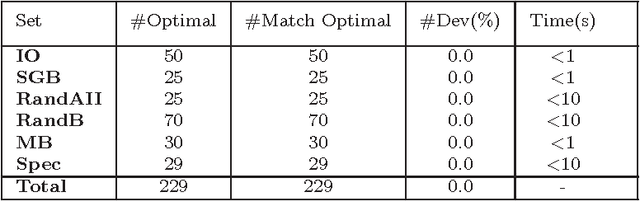
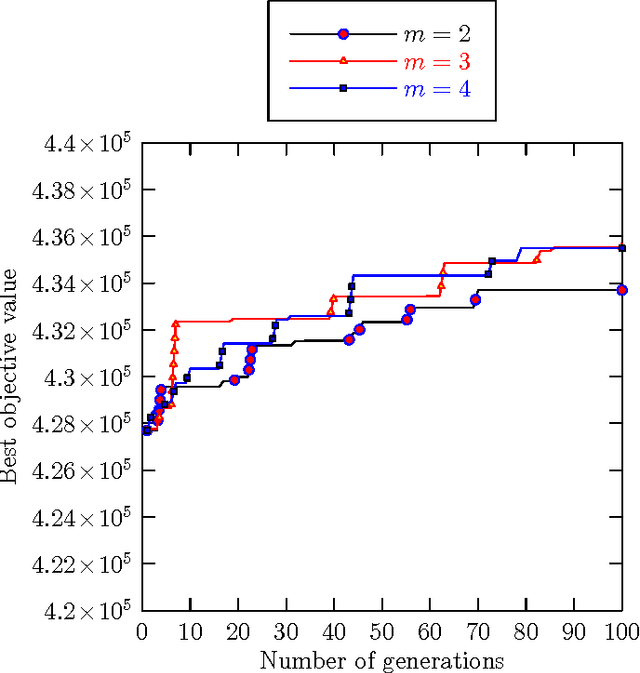
Abstract:In this paper, we present a multi-parent memetic algorithm (denoted by MPM) for solving the classic Linear Ordering Problem (LOP). The MPM algorithm integrates in particular a multi-parent recombination operator for generating offspring solutions and a distance-and-quality based criterion for pool updating. Our MPM algorithm is assessed on 8 sets of 484 widely used LOP instances and compared with several state-of-the-art algorithms in the literature, showing the efficacy of the MPM algorithm. Specifically, for the 255 instances whose optimal solutions are unknown, the MPM is able to detect better solutions than the previous best-known ones for 66 instances, while matching the previous best-known results for 163 instances. Furthermore, some additional experiments are carried out to analyze the key elements and important parameters of MPM.
Iterated Tabu Search Algorithm for Packing Unequal Circles in a Circle
Jun 04, 2013
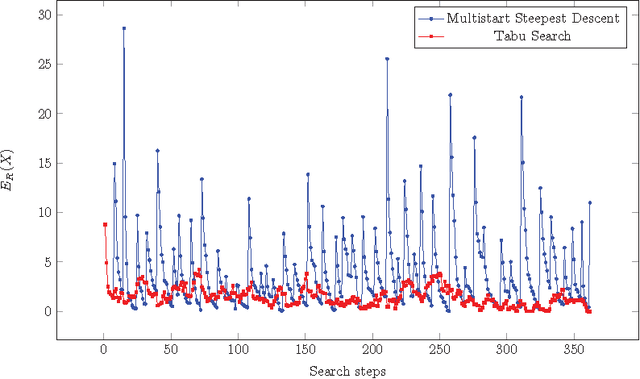
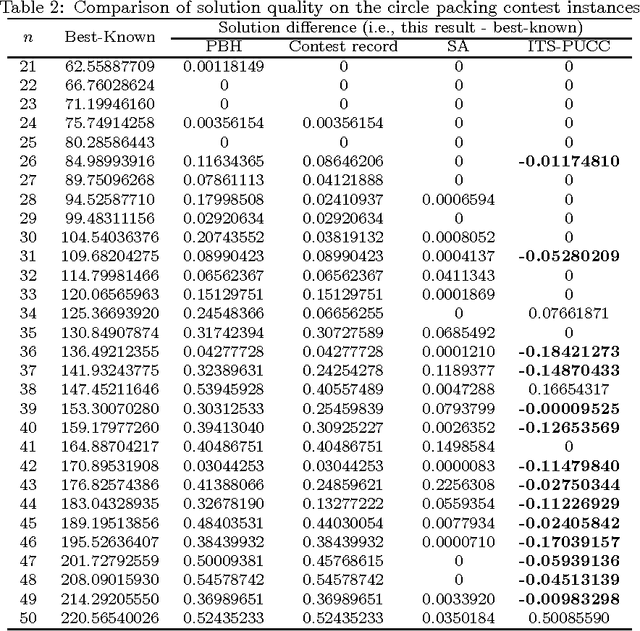
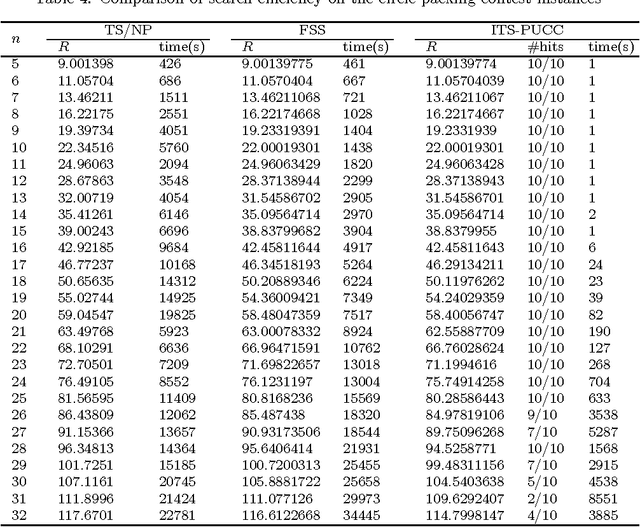
Abstract:This paper presents an Iterated Tabu Search algorithm (denoted by ITS-PUCC) for solving the problem of Packing Unequal Circles in a Circle. The algorithm exploits the continuous and combinatorial nature of the unequal circles packing problem. It uses a continuous local optimization method to generate locally optimal packings. Meanwhile, it builds a neighborhood structure on the set of local minimum via two appropriate perturbation moves and integrates two combinatorial optimization methods, Tabu Search and Iterated Local Search, to systematically search for good local minima. Computational experiments on two sets of widely-used test instances prove its effectiveness and efficiency. For the first set of 46 instances coming from the famous circle packing contest and the second set of 24 instances widely used in the literature, the algorithm is able to discover respectively 14 and 16 better solutions than the previous best-known records.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge