Zhihui Miao
Reconstruct Face from Features Using GAN Generator as a Distribution Constraint
Jun 09, 2022
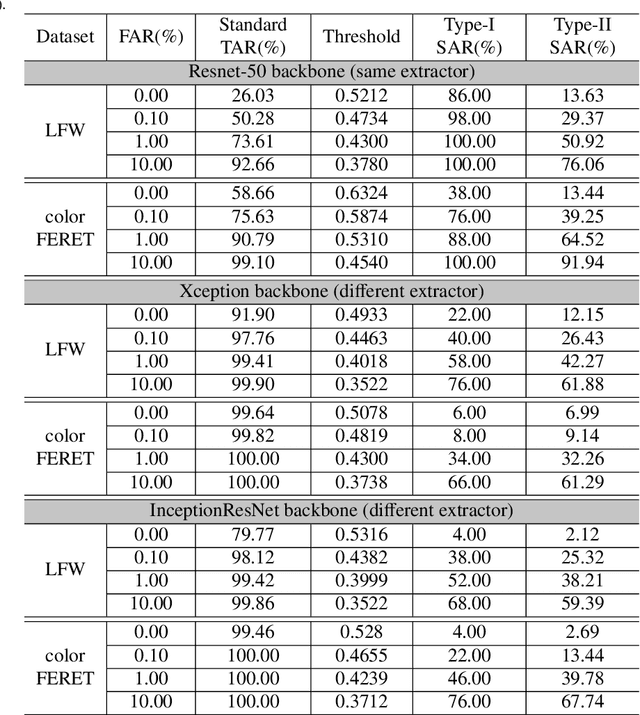
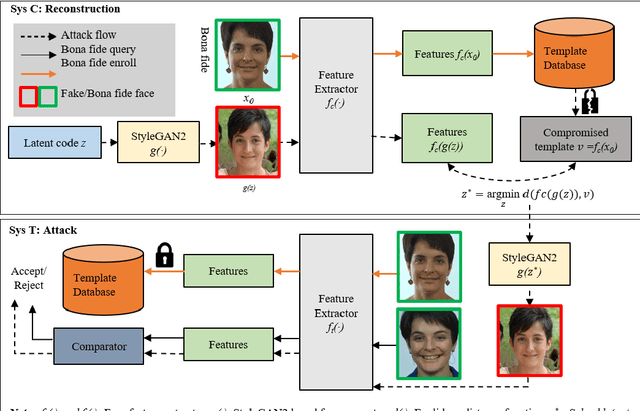
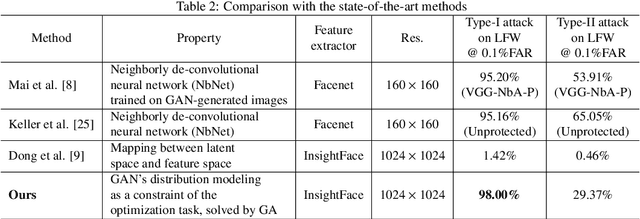
Abstract:Face recognition based on the deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) shows superior accuracy performance attributed to the high discriminative features extracted. Yet, the security and privacy of the extracted features from deep learning models (deep features) have been often overlooked. This paper proposes the reconstruction of face images from deep features without accessing the CNN network configurations as a constrained optimization problem. Such optimization minimizes the distance between the features extracted from the original face image and the reconstructed face image. Instead of directly solving the optimization problem in the image space, we innovatively reformulate the problem by looking for a latent vector of a GAN generator, then use it to generate the face image. The GAN generator serves as a dual role in this novel framework, i.e., face distribution constraint of the optimization goal and a face generator. On top of the novel optimization task, we also propose an attack pipeline to impersonate the target user based on the generated face image. Our results show that the generated face images can achieve a state-of-the-art successful attack rate of 98.0\% on LFW under type-I attack @ FAR of 0.1\%. Our work sheds light on the biometric deployment to meet the privacy-preserving and security policies.
Abandoning the Bayer-Filter to See in the Dark
Mar 22, 2022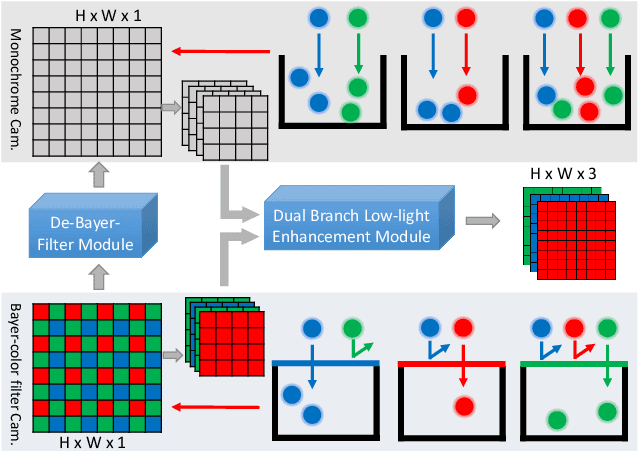
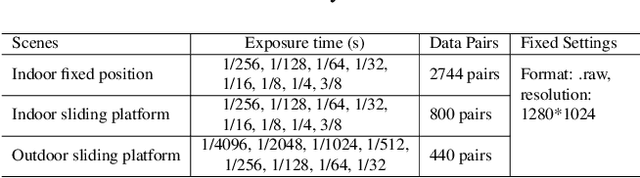
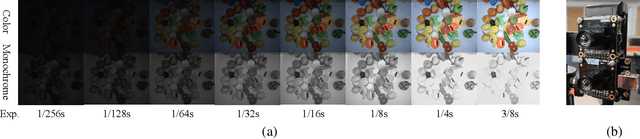
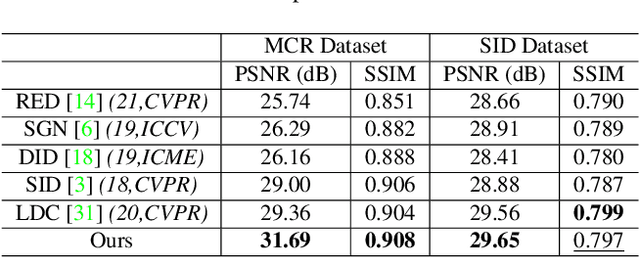
Abstract:Low-light image enhancement - a pervasive but challenging problem, plays a central role in enhancing the visibility of an image captured in a poor illumination environment. Due to the fact that not all photons can pass the Bayer-Filter on the sensor of the color camera, in this work, we first present a De-Bayer-Filter simulator based on deep neural networks to generate a monochrome raw image from the colored raw image. Next, a fully convolutional network is proposed to achieve the low-light image enhancement by fusing colored raw data with synthesized monochrome raw data. Channel-wise attention is also introduced to the fusion process to establish a complementary interaction between features from colored and monochrome raw images. To train the convolutional networks, we propose a dataset with monochrome and color raw pairs named Mono-Colored Raw paired dataset (MCR) collected by using a monochrome camera without Bayer-Filter and a color camera with Bayer-Filter. The proposed pipeline take advantages of the fusion of the virtual monochrome and the color raw images and our extensive experiments indicate that significant improvement can be achieved by leveraging raw sensor data and data-driven learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge