Zhi Yao
MatterChat: A Multi-Modal LLM for Material Science
Feb 18, 2025


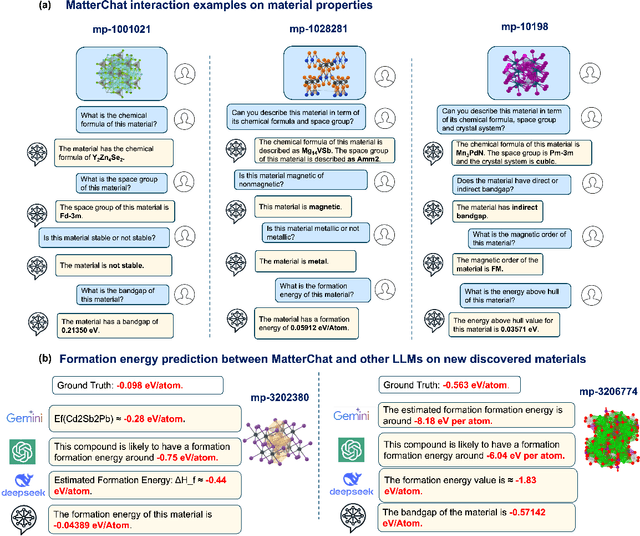
Abstract:Understanding and predicting the properties of inorganic materials is crucial for accelerating advancements in materials science and driving applications in energy, electronics, and beyond. Integrating material structure data with language-based information through multi-modal large language models (LLMs) offers great potential to support these efforts by enhancing human-AI interaction. However, a key challenge lies in integrating atomic structures at full resolution into LLMs. In this work, we introduce MatterChat, a versatile structure-aware multi-modal LLM that unifies material structural data and textual inputs into a single cohesive model. MatterChat employs a bridging module to effectively align a pretrained machine learning interatomic potential with a pretrained LLM, reducing training costs and enhancing flexibility. Our results demonstrate that MatterChat significantly improves performance in material property prediction and human-AI interaction, surpassing general-purpose LLMs such as GPT-4. We also demonstrate its usefulness in applications such as more advanced scientific reasoning and step-by-step material synthesis.
VELO: A Vector Database-Assisted Cloud-Edge Collaborative LLM QoS Optimization Framework
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:The Large Language Model (LLM) has gained significant popularity and is extensively utilized across various domains. Most LLM deployments occur within cloud data centers, where they encounter substantial response delays and incur high costs, thereby impacting the Quality of Services (QoS) at the network edge. Leveraging vector database caching to store LLM request results at the edge can substantially mitigate response delays and cost associated with similar requests, which has been overlooked by previous research. Addressing these gaps, this paper introduces a novel Vector database-assisted cloud-Edge collaborative LLM QoS Optimization (VELO) framework. Firstly, we propose the VELO framework, which ingeniously employs vector database to cache the results of some LLM requests at the edge to reduce the response time of subsequent similar requests. Diverging from direct optimization of the LLM, our VELO framework does not necessitate altering the internal structure of LLM and is broadly applicable to diverse LLMs. Subsequently, building upon the VELO framework, we formulate the QoS optimization problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and devise an algorithm grounded in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) to decide whether to request the LLM in the cloud or directly return the results from the vector database at the edge. Moreover, to enhance request feature extraction and expedite training, we refine the policy network of MARL and integrate expert demonstrations. Finally, we implement the proposed algorithm within a real edge system. Experimental findings confirm that our VELO framework substantially enhances user satisfaction by concurrently diminishing delay and resource consumption for edge users utilizing LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge