Zhenning Niu
GeneAnnotator: A Semi-automatic Annotation Tool for Visual Scene Graph
Sep 06, 2021
Abstract:In this manuscript, we introduce a semi-automatic scene graph annotation tool for images, the GeneAnnotator. This software allows human annotators to describe the existing relationships between participators in the visual scene in the form of directed graphs, hence enabling the learning and reasoning on visual relationships, e.g., image captioning, VQA and scene graph generation, etc. The annotations for certain image datasets could either be merged in a single VG150 data-format file to support most existing models for scene graph learning or transformed into a separated annotation file for each single image to build customized datasets. Moreover, GeneAnnotator provides a rule-based relationship recommending algorithm to reduce the heavy annotation workload. With GeneAnnotator, we propose Traffic Genome, a comprehensive scene graph dataset with 1000 diverse traffic images, which in return validates the effectiveness of the proposed software for scene graph annotation. The project source code, with usage examples and sample data is available at https://github.com/Milomilo0320/A-Semi-automatic-Annotation-Software-for-Scene-Graph, under the Apache open-source license.
Spatio-Temporal Road Scene Reconstruction using Superpixel MRF
Nov 27, 2018
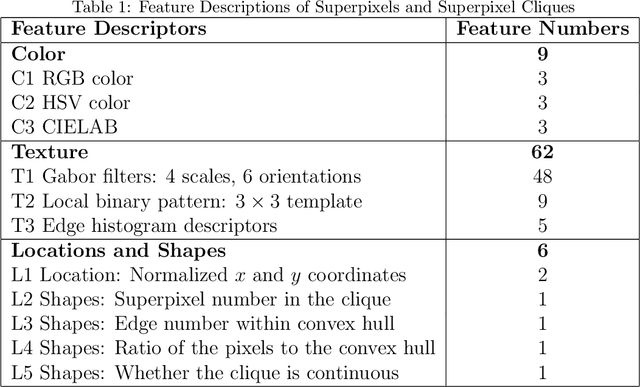
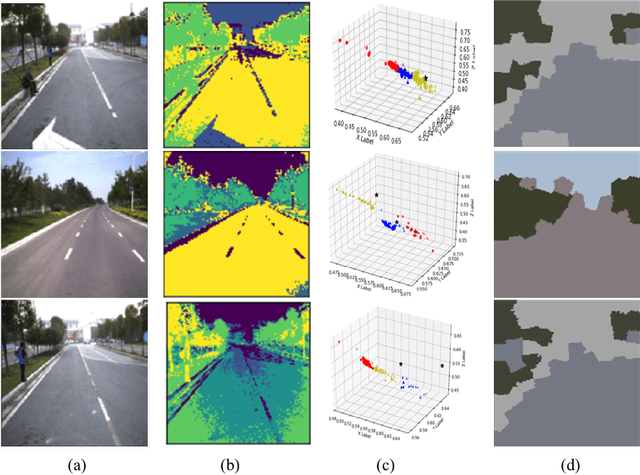

Abstract:Scene models construction based on image rendering is a hot topic in the computer vision community. In this paper, we propose a framework to construct road scene models based on 3D corridor structures. The construction of scene models consists of two successive stages: road detection and scene construction. The road detection is implemented via a new superpixel Markov random field (MRF) algorithm. The data fidelity term of the energy function is jointly computed using the superpixel features of color, texture and location. The smoothness term is defined by the interaction of spatio-temporally adjacent superpixels. The control points of road boundaries are generated with the constraint of vanishing point. Subsequently, the road scene models are constructed, where the foreground and background regions are modeled independently. Numerous applications are developed based on the proposed framework, e.g., traffic scenes simulation. The experiments and comparisons are conducted for both the road detection and scene construction stages, which prove the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge