Zhenhong Hu
AI for Equitable Tennis Training: Leveraging AI for Equitable and Accurate Classification of Tennis Skill Levels and Training Phases
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Numerous studies have demonstrated the manifold benefits of tennis, such as increasing overall physical and mental health. Unfortunately, many children and youth from low-income families are unable to engage in this sport mainly due to financial constraints such as private lesson expenses as well as logistical concerns to and back from such lessons and clinics. While several tennis self-training systems exist, they are often tailored for professionals and are prohibitively expensive. The present study aims to classify tennis players' skill levels and classify tennis strokes into phases characterized by motion attributes for a future development of an AI-based tennis self-training model for affordable and convenient applications running on devices used in daily life such as an iPhone or an Apple Watch for tennis skill improvement. We collected motion data, including Motion Yaw, Roll and Pitch from inertial measurement units (IMUs) worn by participating junior tennis players. For this pilot study, data from twelve participants were processed using Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithms. The SVM models demonstrated an overall accuracy of 77% in classifying players as beginners or intermediates, with low rates of false positives and false negatives, effectively distinguishing skill levels. Additionally, the tennis swings were successfully classified into five phases based on the collected motion data. These findings indicate that SVM-based classification can be a reliable foundation for developing an equitable and accessible AI-driven tennis training system.
Transparent AI: Developing an Explainable Interface for Predicting Postoperative Complications
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:Given the sheer volume of surgical procedures and the significant rate of postoperative fatalities, assessing and managing surgical complications has become a critical public health concern. Existing artificial intelligence (AI) tools for risk surveillance and diagnosis often lack adequate interpretability, fairness, and reproducibility. To address this, we proposed an Explainable AI (XAI) framework designed to answer five critical questions: why, why not, how, what if, and what else, with the goal of enhancing the explainability and transparency of AI models. We incorporated various techniques such as Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME), SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), counterfactual explanations, model cards, an interactive feature manipulation interface, and the identification of similar patients to address these questions. We showcased an XAI interface prototype that adheres to this framework for predicting major postoperative complications. This initial implementation has provided valuable insights into the vast explanatory potential of our XAI framework and represents an initial step towards its clinical adoption.
Global Contrastive Training for Multimodal Electronic Health Records with Language Supervision
Apr 10, 2024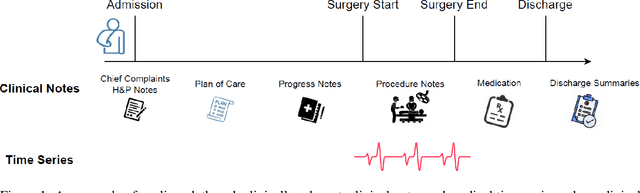
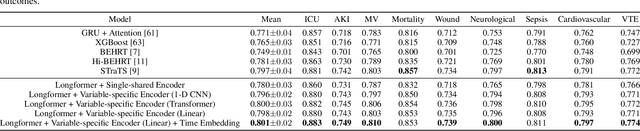
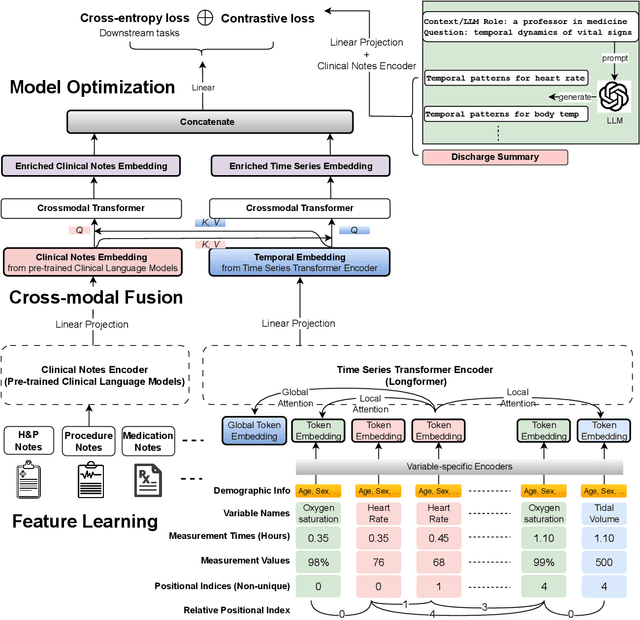
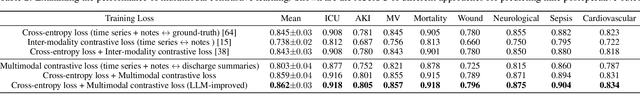
Abstract:Modern electronic health records (EHRs) hold immense promise in tracking personalized patient health trajectories through sequential deep learning, owing to their extensive breadth, scale, and temporal granularity. Nonetheless, how to effectively leverage multiple modalities from EHRs poses significant challenges, given its complex characteristics such as high dimensionality, multimodality, sparsity, varied recording frequencies, and temporal irregularities. To this end, this paper introduces a novel multimodal contrastive learning framework, specifically focusing on medical time series and clinical notes. To tackle the challenge of sparsity and irregular time intervals in medical time series, the framework integrates temporal cross-attention transformers with a dynamic embedding and tokenization scheme for learning multimodal feature representations. To harness the interconnected relationships between medical time series and clinical notes, the framework equips a global contrastive loss, aligning a patient's multimodal feature representations with the corresponding discharge summaries. Since discharge summaries uniquely pertain to individual patients and represent a holistic view of the patient's hospital stay, machine learning models are led to learn discriminative multimodal features via global contrasting. Extensive experiments with a real-world EHR dataset demonstrated that our framework outperformed state-of-the-art approaches on the exemplar task of predicting the occurrence of nine postoperative complications for more than 120,000 major inpatient surgeries using multimodal data from UF health system split among three hospitals (UF Health Gainesville, UF Health Jacksonville, and UF Health Jacksonville-North).
Federated learning model for predicting major postoperative complications
Apr 09, 2024
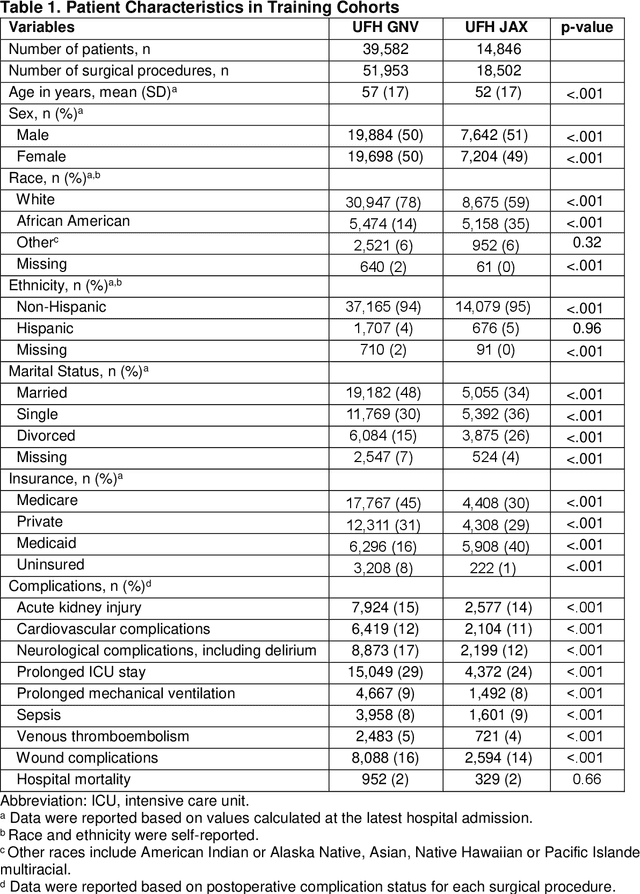


Abstract:Background: The accurate prediction of postoperative complication risk using Electronic Health Records (EHR) and artificial intelligence shows great potential. Training a robust artificial intelligence model typically requires large-scale and diverse datasets. In reality, collecting medical data often encounters challenges surrounding privacy protection. Methods: This retrospective cohort study includes adult patients who were admitted to UFH Gainesville (GNV) (n = 79,850) and Jacksonville (JAX) (n = 28,636) for any type of inpatient surgical procedure. Using perioperative and intraoperative features, we developed federated learning models to predict nine major postoperative complications (i.e., prolonged intensive care unit stay and mechanical ventilation). We compared federated learning models with local learning models trained on a single site and central learning models trained on pooled dataset from two centers. Results: Our federated learning models achieved the area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) values ranged from 0.81 for wound complications to 0.92 for prolonged ICU stay at UFH GNV center. At UFH JAX center, these values ranged from 0.73-0.74 for wound complications to 0.92-0.93 for hospital mortality. Federated learning models achieved comparable AUROC performance to central learning models, except for prolonged ICU stay, where the performance of federated learning models was slightly higher than central learning models at UFH GNV center, but slightly lower at UFH JAX center. In addition, our federated learning model obtained comparable performance to the best local learning model at each center, demonstrating strong generalizability. Conclusion: Federated learning is shown to be a useful tool to train robust and generalizable models from large scale data across multiple institutions where data protection barriers are high.
Temporal Cross-Attention for Dynamic Embedding and Tokenization of Multimodal Electronic Health Records
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:The breadth, scale, and temporal granularity of modern electronic health records (EHR) systems offers great potential for estimating personalized and contextual patient health trajectories using sequential deep learning. However, learning useful representations of EHR data is challenging due to its high dimensionality, sparsity, multimodality, irregular and variable-specific recording frequency, and timestamp duplication when multiple measurements are recorded simultaneously. Although recent efforts to fuse structured EHR and unstructured clinical notes suggest the potential for more accurate prediction of clinical outcomes, less focus has been placed on EHR embedding approaches that directly address temporal EHR challenges by learning time-aware representations from multimodal patient time series. In this paper, we introduce a dynamic embedding and tokenization framework for precise representation of multimodal clinical time series that combines novel methods for encoding time and sequential position with temporal cross-attention. Our embedding and tokenization framework, when integrated into a multitask transformer classifier with sliding window attention, outperformed baseline approaches on the exemplar task of predicting the occurrence of nine postoperative complications of more than 120,000 major inpatient surgeries using multimodal data from three hospitals and two academic health centers in the United States.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge