Zhengqiu He
Improving Neural Relation Extraction with Positive and Unlabeled Learning
Nov 28, 2019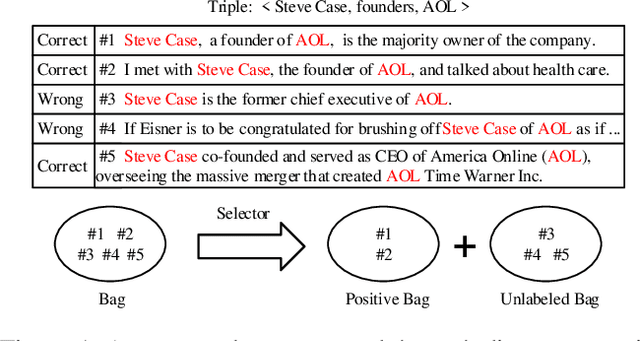
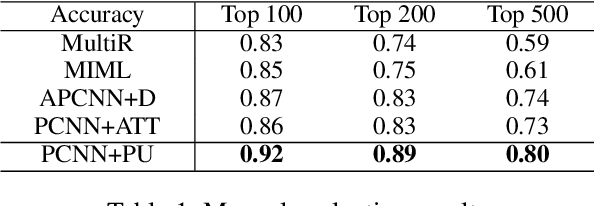
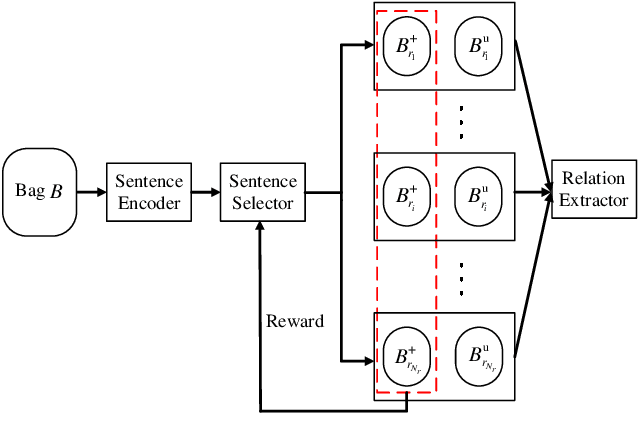
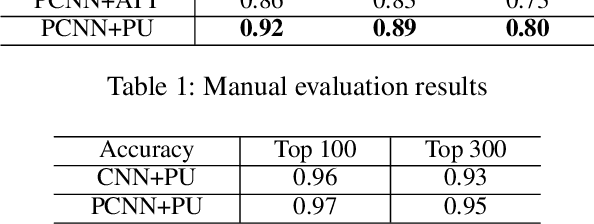
Abstract:We present a novel approach to improve the performance of distant supervision relation extraction with Positive and Unlabeled (PU) Learning. This approach first applies reinforcement learning to decide whether a sentence is positive to a given relation, and then positive and unlabeled bags are constructed. In contrast to most previous studies, which mainly use selected positive instances only, we make full use of unlabeled instances and propose two new representations for positive and unlabeled bags. These two representations are then combined in an appropriate way to make bag-level prediction. Experimental results on a widely used real-world dataset demonstrate that this new approach indeed achieves significant and consistent improvements as compared to several competitive baselines.
CCKS 2019 Shared Task on Inter-Personal Relationship Extraction
Aug 29, 2019



Abstract:The CCKS2019 shared task was devoted to inter-personal relationship extraction. Given two person entities and at least one sentence containing these two entities, participating teams are asked to predict the relationship between the entities according to a given relation list. This year, 358 teams from various universities and organizations participated in this task. In this paper, we present the task definition, the description of data and the evaluation methodology used during this shared task. We also present a brief overview of the various methods adopted by the participating teams. Finally, we present the evaluation results.
IPRE: a Dataset for Inter-Personal Relationship Extraction
Aug 10, 2019



Abstract:Inter-personal relationship is the basis of human society. In order to automatically identify the relations between persons from texts, we need annotated data for training systems. However, there is a lack of a massive amount of such data so far. To address this situation, we introduce IPRE, a new dataset for inter-personal relationship extraction which aims to facilitate information extraction and knowledge graph construction research. In total, IPRE has over 41,000 labeled sentences for 34 types of relations, including about 9,000 sentences annotated by workers. Our data is the first dataset for inter-personal relationship extraction. Additionally, we define three evaluation tasks based on IPRE and provide the baseline systems for further comparison in future work.
SEE: Syntax-aware Entity Embedding for Neural Relation Extraction
Jan 11, 2018



Abstract:Distant supervised relation extraction is an efficient approach to scale relation extraction to very large corpora, and has been widely used to find novel relational facts from plain text. Recent studies on neural relation extraction have shown great progress on this task via modeling the sentences in low-dimensional spaces, but seldom considered syntax information to model the entities. In this paper, we propose to learn syntax-aware entity embedding for neural relation extraction. First, we encode the context of entities on a dependency tree as sentence-level entity embedding based on tree-GRU. Then, we utilize both intra-sentence and inter-sentence attentions to obtain sentence set-level entity embedding over all sentences containing the focus entity pair. Finally, we combine both sentence embedding and entity embedding for relation classification. We conduct experiments on a widely used real-world dataset and the experimental results show that our model can make full use of all informative instances and achieve state-of-the-art performance of relation extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge