Zhaorong Li
Beyond Conditional Computation: Retrieval-Augmented Genomic Foundation Models with Gengram
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Current genomic foundation models (GFMs) rely on extensive neural computation to implicitly approximate conserved biological motifs from single-nucleotide inputs. We propose Gengram, a conditional memory module that introduces an explicit and highly efficient lookup primitive for multi-base motifs via a genomic-specific hashing scheme, establishing genomic "syntax". Integrated into the backbone of state-of-the-art GFMs, Gengram achieves substantial gains (up to 14%) across several functional genomics tasks. The module demonstrates robust architectural generalization, while further inspection of Gengram's latent space reveals the emergence of meaningful representations that align closely with fundamental biological knowledge. By establishing structured motif memory as a modeling primitive, Gengram simultaneously boosts empirical performance and mechanistic interpretability, providing a scalable and biology-aligned pathway for the next generation of GFMs. The code is available at https://github.com/zhejianglab/Genos, and the model checkpoint is available at https://huggingface.co/ZhejiangLab/Gengram.
KG-MTT-BERT: Knowledge Graph Enhanced BERT for Multi-Type Medical Text Classification
Oct 08, 2022



Abstract:Medical text learning has recently emerged as a promising area to improve healthcare due to the wide adoption of electronic health record (EHR) systems. The complexity of the medical text such as diverse length, mixed text types, and full of medical jargon, poses a great challenge for developing effective deep learning models. BERT has presented state-of-the-art results in many NLP tasks, such as text classification and question answering. However, the standalone BERT model cannot deal with the complexity of the medical text, especially the lengthy clinical notes. Herein, we develop a new model called KG-MTT-BERT (Knowledge Graph Enhanced Multi-Type Text BERT) by extending the BERT model for long and multi-type text with the integration of the medical knowledge graph. Our model can outperform all baselines and other state-of-the-art models in diagnosis-related group (DRG) classification, which requires comprehensive medical text for accurate classification. We also demonstrated that our model can effectively handle multi-type text and the integration of medical knowledge graph can significantly improve the performance.
Extracting Actionability from Machine Learning Models by Sub-optimal Deterministic Planning
Nov 03, 2016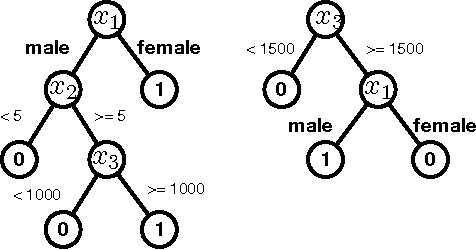
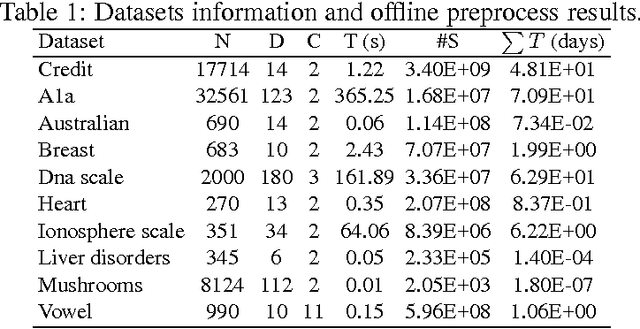
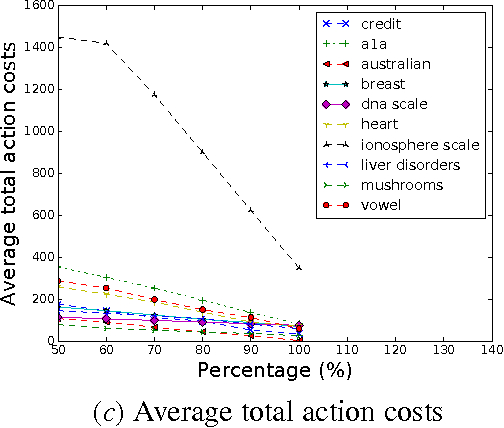
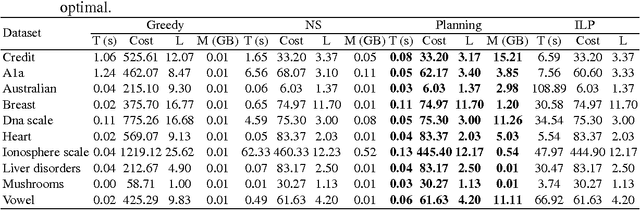
Abstract:A main focus of machine learning research has been improving the generalization accuracy and efficiency of prediction models. Many models such as SVM, random forest, and deep neural nets have been proposed and achieved great success. However, what emerges as missing in many applications is actionability, i.e., the ability to turn prediction results into actions. For example, in applications such as customer relationship management, clinical prediction, and advertisement, the users need not only accurate prediction, but also actionable instructions which can transfer an input to a desirable goal (e.g., higher profit repays, lower morbidity rates, higher ads hit rates). Existing effort in deriving such actionable knowledge is few and limited to simple action models which restricted to only change one attribute for each action. The dilemma is that in many real applications those action models are often more complex and harder to extract an optimal solution. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that achieves actionability by combining learning with planning, two core areas of AI. In particular, we propose a framework to extract actionable knowledge from random forest, one of the most widely used and best off-the-shelf classifiers. We formulate the actionability problem to a sub-optimal action planning (SOAP) problem, which is to find a plan to alter certain features of a given input so that the random forest would yield a desirable output, while minimizing the total costs of actions. Technically, the SOAP problem is formulated in the SAS+ planning formalism, and solved using a Max-SAT based approach. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed approach on a personal credit dataset and other benchmarks. Our work represents a new application of automated planning on an emerging and challenging machine learning paradigm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge