Zhanlin Sun
Relation-Gated Domain Adaptation for Relation Extraction
Dec 16, 2019



Abstract:Relation extraction aims to extract relational facts from sentences. Previous models mainly rely on manually labeled datasets, seed instances or human-crafted patterns, and distant supervision. However, the human annotation is expensive, while human-crafted patterns suffer from semantic drift and distant supervision samples are usually noisy. Domain adaptation methods enable leveraging labeled data from a different but related domain. However, different domains usually have various textual relation descriptions and different label space (the source label space is usually a superset of the target label space). To solve these problems, we propose a novel model of relation-gated adversarial learning for relation extraction, which extends the adversarial based domain adaptation. Experimental results have shown that the proposed approach outperforms previous domain adaptation methods regarding partial domain adaptation and can improve the accuracy of distance supervised relation extraction through fine-tuning.
Transfer Learning for Relation Extraction via Relation-Gated Adversarial Learning
Aug 22, 2019



Abstract:Relation extraction aims to extract relational facts from sentences. Previous models mainly rely on manually labeled datasets, seed instances or human-crafted patterns, and distant supervision. However, the human annotation is expensive, while human-crafted patterns suffer from semantic drift and distant supervision samples are usually noisy. Domain adaptation methods enable leveraging labeled data from a different but related domain. However, different domains usually have various textual relation descriptions and different label space (the source label space is usually a superset of the target label space). To solve these problems, we propose a novel model of relation-gated adversarial learning for relation extraction, which extends the adversarial based domain adaptation. Experimental results have shown that the proposed approach outperforms previous domain adaptation methods regarding partial domain adaptation and can improve the accuracy of distance supervised relation extraction through fine-tuning.
Improving Few-shot Text Classification via Pretrained Language Representations
Aug 22, 2019

Abstract:Text classification tends to be difficult when the data is deficient or when it is required to adapt to unseen classes. In such challenging scenarios, recent studies have often used meta-learning to simulate the few-shot task, thus negating explicit common linguistic features across tasks. Deep language representations have proven to be very effective forms of unsupervised pretraining, yielding contextualized features that capture linguistic properties and benefit downstream natural language understanding tasks. However, the effect of pretrained language representation for few-shot learning on text classification tasks is still not well understood. In this study, we design a few-shot learning model with pretrained language representations and report the empirical results. We show that our approach is not only simple but also produces state-of-the-art performance on a well-studied sentiment classification dataset. It can thus be further suggested that pretraining could be a promising solution for few shot learning of many other NLP tasks. The code and the dataset to replicate the experiments are made available at https://github.com/zxlzr/FewShotNLP.
Capturing Evolution Genes for Time Series Data
May 10, 2019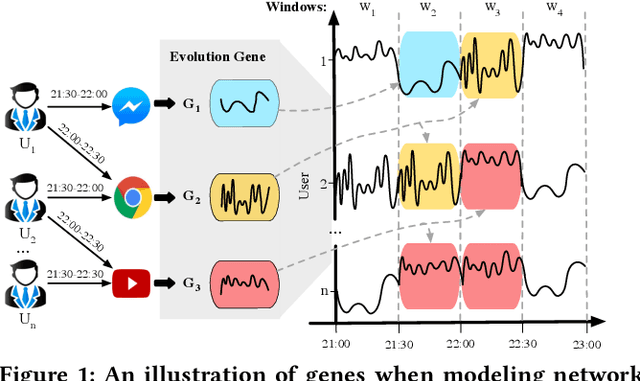
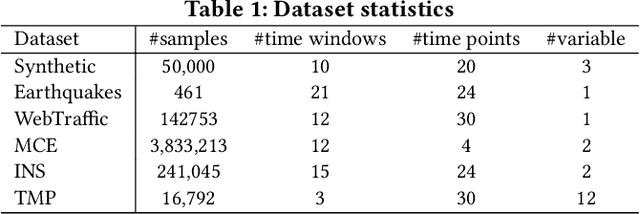
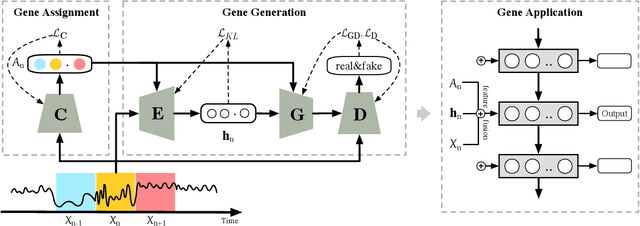
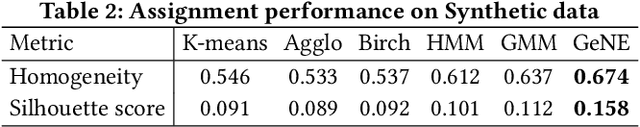
Abstract:The modeling of time series is becoming increasingly critical in a wide variety of applications. Overall, data evolves by following different patterns, which are generally caused by different user behaviors. Given a time series, we define the evolution gene to capture the latent user behaviors and to describe how the behaviors lead to the generation of time series. In particular, we propose a uniform framework that recognizes different evolution genes of segments by learning a classifier, and adopt an adversarial generator to implement the evolution gene by estimating the segments' distribution. Experimental results based on a synthetic dataset and five real-world datasets show that our approach can not only achieve a good prediction results (e.g., averagely +10.56% in terms of F1), but is also able to provide explanations of the results.
Long-tail Relation Extraction via Knowledge Graph Embeddings and Graph Convolution Networks
Mar 04, 2019



Abstract:We propose a distance supervised relation extraction approach for long-tailed, imbalanced data which is prevalent in real-world settings. Here, the challenge is to learn accurate "few-shot" models for classes existing at the tail of the class distribution, for which little data is available. Inspired by the rich semantic correlations between classes at the long tail and those at the head, we take advantage of the knowledge from data-rich classes at the head of the distribution to boost the performance of the data-poor classes at the tail. First, we propose to leverage implicit relational knowledge among class labels from knowledge graph embeddings and learn explicit relational knowledge using graph convolution networks. Second, we integrate that relational knowledge into relation extraction model by coarse-to-fine knowledge-aware attention mechanism. We demonstrate our results for a large-scale benchmark dataset which show that our approach significantly outperforms other baselines, especially for long-tail relations.
Attention-Based Capsule Networks with Dynamic Routing for Relation Extraction
Dec 29, 2018



Abstract:A capsule is a group of neurons, whose activity vector represents the instantiation parameters of a specific type of entity. In this paper, we explore the capsule networks used for relation extraction in a multi-instance multi-label learning framework and propose a novel neural approach based on capsule networks with attention mechanisms. We evaluate our method with different benchmarks, and it is demonstrated that our method improves the precision of the predicted relations. Particularly, we show that capsule networks improve multiple entity pairs relation extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge