Zhang Jing
Efficient Long Sequential Low-rank Adaptive Attention for Click-through rate Prediction
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In the context of burgeoning user historical behavior data, Accurate click-through rate(CTR) prediction requires effective modeling of lengthy user behavior sequences. As the volume of such data keeps swelling, the focus of research has shifted towards developing effective long-term behavior modeling methods to capture latent user interests. Nevertheless, the complexity introduced by large scale data brings about computational hurdles. There is a pressing need to strike a balance between achieving high model performance and meeting the strict response time requirements of online services. While existing retrieval-based methods (e.g., similarity filtering or attention approximation) achieve practical runtime efficiency, they inherently compromise information fidelity through aggressive sequence truncation or attention sparsification. This paper presents a novel attention mechanism. It overcomes the shortcomings of existing methods while ensuring computational efficiency. This mechanism learn compressed representation of sequence with length $L$ via low-rank projection matrices (rank $r \ll L$), reducing attention complexity from $O(L)$ to $O(r)$. It also integrates a uniquely designed loss function to preserve nonlinearity of attention. In the inference stage, the mechanism adopts matrix absorption and prestorage strategies. These strategies enable it to effectively satisfy online constraints. Comprehensive offline and online experiments demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms current state-of-the-art solutions.
Analyzing Nobel Prize Literature with Large Language Models
Oct 22, 2024
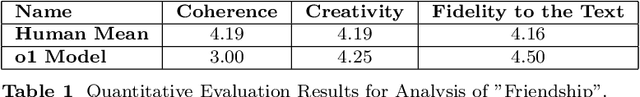
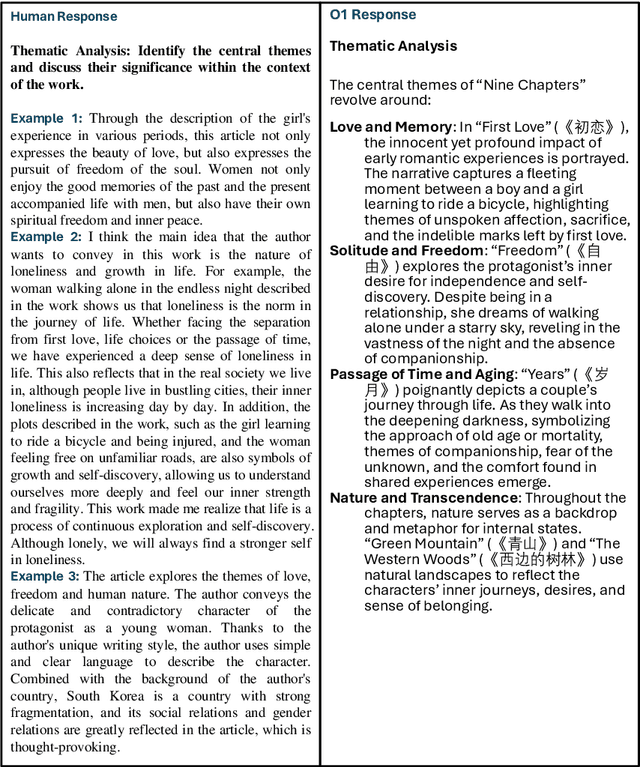
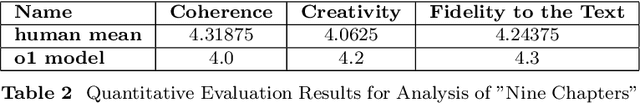
Abstract:This study examines the capabilities of advanced Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly the o1 model, in the context of literary analysis. The outputs of these models are compared directly to those produced by graduate-level human participants. By focusing on two Nobel Prize-winning short stories, 'Nine Chapters' by Han Kang, the 2024 laureate, and 'Friendship' by Jon Fosse, the 2023 laureate, the research explores the extent to which AI can engage with complex literary elements such as thematic analysis, intertextuality, cultural and historical contexts, linguistic and structural innovations, and character development. Given the Nobel Prize's prestige and its emphasis on cultural, historical, and linguistic richness, applying LLMs to these works provides a deeper understanding of both human and AI approaches to interpretation. The study uses qualitative and quantitative evaluations of coherence, creativity, and fidelity to the text, revealing the strengths and limitations of AI in tasks typically reserved for human expertise. While LLMs demonstrate strong analytical capabilities, particularly in structured tasks, they often fall short in emotional nuance and coherence, areas where human interpretation excels. This research underscores the potential for human-AI collaboration in the humanities, opening new opportunities in literary studies and beyond.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge