Zhanbo Xu
Uncertainty Set Prediction of Aggregated Wind Power Generation based on Bayesian LSTM and Spatio-Temporal Analysis
Oct 07, 2021



Abstract:Aggregated stochastic characteristics of geographically distributed wind generation will provide valuable information for secured and economical system operation in electricity markets. This paper focuses on the uncertainty set prediction of the aggregated generation of geographically distributed wind farms. A Spatio-temporal model is proposed to learn the dynamic features from partial observation in near-surface wind fields of neighboring wind farms. We use Bayesian LSTM, a probabilistic prediction model, to obtain the uncertainty set of the generation in individual wind farms. Then, spatial correlation between different wind farms is presented to correct the output results. Numerical testing results based on the actual data with 6 wind farms in northwest China show that the uncertainty set of aggregated wind generation of distributed wind farms is less volatile than that of a single wind farm.
Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for HVAC Control in Commercial Buildings
Jun 25, 2020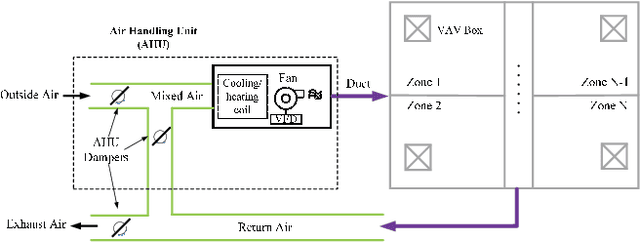
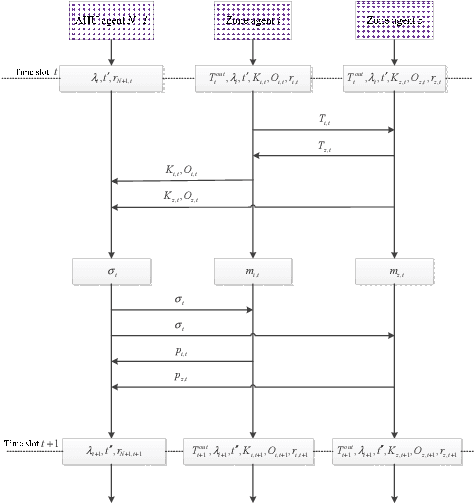
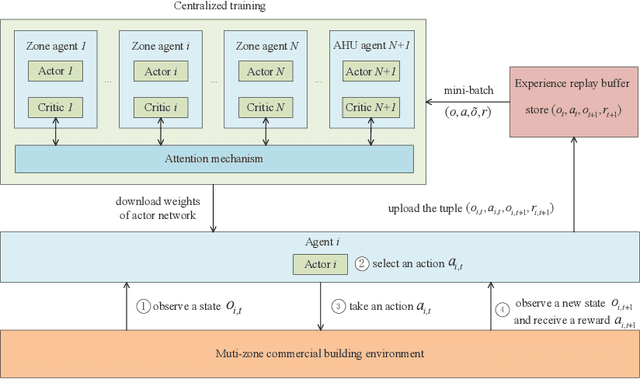
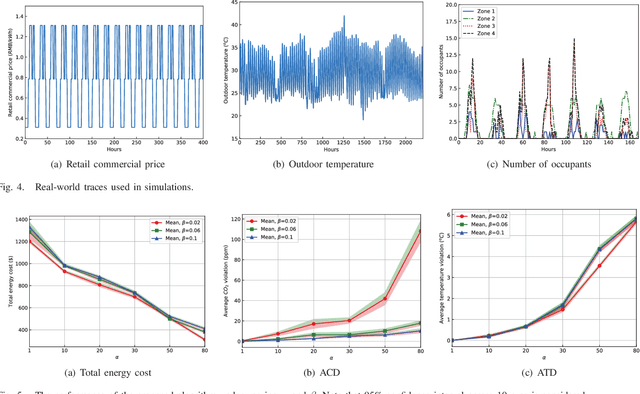
Abstract:In commercial buildings, about 40%-50% of the total electricity consumption is attributed to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, which places an economic burden on building operators. In this paper, we intend to minimize the energy cost of an HVAC system in a multi-zone commercial building under dynamic pricing with the consideration of random zone occupancy, thermal comfort, and indoor air quality comfort. Due to the existence of unknown thermal dynamics models, parameter uncertainties (e.g., outdoor temperature, electricity price, and number of occupants), spatially and temporally coupled constraints associated with indoor temperature and CO2 concentration, a large discrete solution space, and a non-convex and non-separable objective function, it is very challenging to achieve the above aim. To this end, the above energy cost minimization problem is reformulated as a Markov game. Then, an HVAC control algorithm is proposed to solve the Markov game based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning with attention mechanism. The proposed algorithm does not require any prior knowledge of uncertain parameters and can operate without knowing building thermal dynamics models. Simulation results based on real-world traces show the effectiveness, robustness and scalability of the proposed algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge