Zesheng Xu
Self-Supervised Unseen Object Instance Segmentation via Long-Term Robot Interaction
Feb 07, 2023



Abstract:We introduce a novel robotic system for improving unseen object instance segmentation in the real world by leveraging long-term robot interaction with objects. Previous approaches either grasp or push an object and then obtain the segmentation mask of the grasped or pushed object after one action. Instead, our system defers the decision on segmenting objects after a sequence of robot pushing actions. By applying multi-object tracking and video object segmentation on the images collected via robot pushing, our system can generate segmentation masks of all the objects in these images in a self-supervised way. These include images where objects are very close to each other, and segmentation errors usually occur on these images for existing object segmentation networks. We demonstrate the usefulness of our system by fine-tuning segmentation networks trained on synthetic data with real-world data collected by our system. We show that, after fine-tuning, the segmentation accuracy of the networks is significantly improved both in the same domain and across different domains. In addition, we verify that the fine-tuned networks improve top-down robotic grasping of unseen objects in the real world.
NeuralGrasps: Learning Implicit Representations for Grasps of Multiple Robotic Hands
Jul 06, 2022
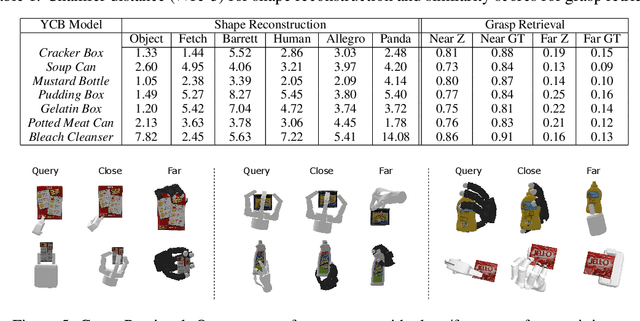
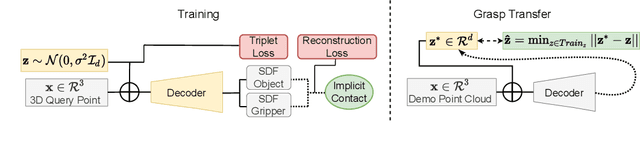
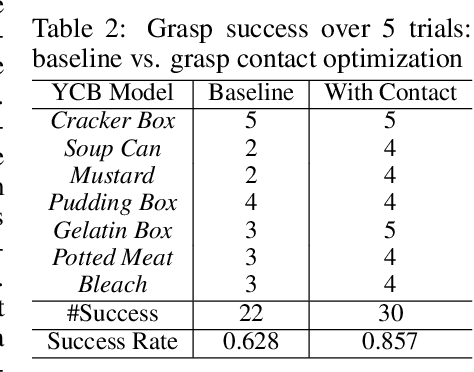
Abstract:We introduce a neural implicit representation for grasps of objects from multiple robotic hands. Different grasps across multiple robotic hands are encoded into a shared latent space. Each latent vector is learned to decode to the 3D shape of an object and the 3D shape of a robotic hand in a grasping pose in terms of the signed distance functions of the two 3D shapes. In addition, the distance metric in the latent space is learned to preserve the similarity between grasps across different robotic hands, where the similarity of grasps is defined according to contact regions of the robotic hands. This property enables our method to transfer grasps between different grippers including a human hand, and grasp transfer has the potential to share grasping skills between robots and enable robots to learn grasping skills from humans. Furthermore, the encoded signed distance functions of objects and grasps in our implicit representation can be used for 6D object pose estimation with grasping contact optimization from partial point clouds, which enables robotic grasping in the real world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge