Yunpeng Han
FashionSAP: Symbols and Attributes Prompt for Fine-grained Fashion Vision-Language Pre-training
Apr 11, 2023
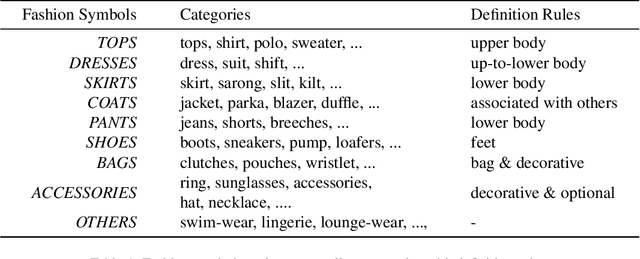
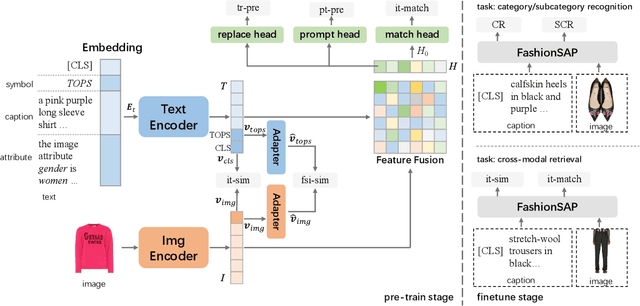
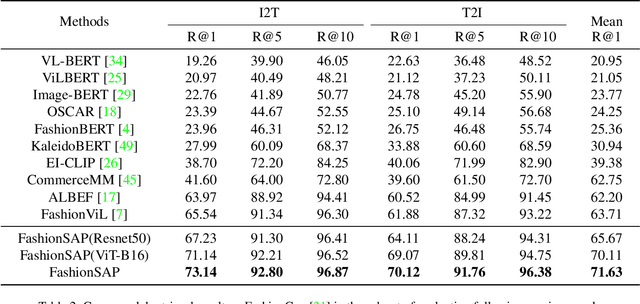
Abstract:Fashion vision-language pre-training models have shown efficacy for a wide range of downstream tasks. However, general vision-language pre-training models pay less attention to fine-grained domain features, while these features are important in distinguishing the specific domain tasks from general tasks. We propose a method for fine-grained fashion vision-language pre-training based on fashion Symbols and Attributes Prompt (FashionSAP) to model fine-grained multi-modalities fashion attributes and characteristics. Firstly, we propose the fashion symbols, a novel abstract fashion concept layer, to represent different fashion items and to generalize various kinds of fine-grained fashion features, making modelling fine-grained attributes more effective. Secondly, the attributes prompt method is proposed to make the model learn specific attributes of fashion items explicitly. We design proper prompt templates according to the format of fashion data. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on two public fashion benchmarks, i.e., FashionGen and FashionIQ, and FashionSAP gets SOTA performances for four popular fashion tasks. The ablation study also shows the proposed abstract fashion symbols, and the attribute prompt method enables the model to acquire fine-grained semantics in the fashion domain effectively. The obvious performance gains from FashionSAP provide a new baseline for future fashion task research.
Replacement as a Self-supervision for Fine-grained Vision-language Pre-training
Mar 09, 2023



Abstract:Fine-grained supervision based on object annotations has been widely used for vision and language pre-training (VLP). However, in real-world application scenarios, aligned multi-modal data is usually in the image-caption format, which only provides coarse-grained supervision. It is cost-expensive to collect object annotations and build object annotation pre-extractor for different scenarios. In this paper, we propose a fine-grained self-supervision signal without object annotations from a replacement perspective. First, we propose a homonym sentence rewriting (HSR) algorithm to provide token-level supervision. The algorithm replaces a verb/noun/adjective/quantifier word of the caption with its homonyms from WordNet. Correspondingly, we propose a replacement vision-language modeling (RVLM) framework to exploit the token-level supervision. Two replaced modeling tasks, i.e., replaced language contrastive (RLC) and replaced language modeling (RLM), are proposed to learn the fine-grained alignment. Extensive experiments on several downstream tasks demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method.
VLDeformer: Learning Visual-Semantic Embeddings by Vision-Language Transformer Decomposing
Oct 20, 2021



Abstract:Vision-language transformers (VL transformers) have shown impressive accuracy in cross-modal retrieval. However, most of the existing VL transformers use early-interaction dataflow that computes a joint representation for the text-image input. In the retrieval stage, such models need to infer on all the matched text-image combinations, which causes high computing costs. The goal of this paper is to decompose the early-interaction dataflow inside the pre-trained VL transformer to achieve acceleration while maintaining its outstanding accuracy. To achieve this, we propose a novel Vision-language Transformer Decomposing (VLDeformer) to modify the VL transformer as an individual encoder for a single image or text through contrastive learning, which accelerates retrieval speed by thousands of times. Meanwhile, we propose to compose bi-modal hard negatives for the contrastive learning objective, which enables the VLDeformer to maintain the outstanding accuracy of the backbone VL transformer. Extensive experiments on COCO and Flickr30k datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method. Considering both effectiveness and efficiency, VLDeformer provides a superior selection for cross-modal retrieval in the similar pre-training datascale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge