Yufan Xue
Method for making multi-attribute decisions in wargames by combining intuitionistic fuzzy numbers with reinforcement learning
Sep 06, 2021



Abstract:Researchers are increasingly focusing on intelligent games as a hot research area.The article proposes an algorithm that combines the multi-attribute management and reinforcement learning methods, and that combined their effect on wargaming, it solves the problem of the agent's low rate of winning against specific rules and its inability to quickly converge during intelligent wargame training.At the same time, this paper studied a multi-attribute decision making and reinforcement learning algorithm in a wargame simulation environment, and obtained data on red and blue conflict.Calculate the weight of each attribute based on the intuitionistic fuzzy number weight calculations. Then determine the threat posed by each opponent's chess pieces.Using the red side reinforcement learning reward function, the AC framework is trained on the reward function, and an algorithm combining multi-attribute decision-making with reinforcement learning is obtained. A simulation experiment confirms that the algorithm of multi-attribute decision-making combined with reinforcement learning presented in this paper is significantly more intelligent than the pure reinforcement learning algorithm.By resolving the shortcomings of the agent's neural network, coupled with sparse rewards in large-map combat games, this robust algorithm effectively reduces the difficulties of convergence. It is also the first time in this field that an algorithm design for intelligent wargaming combines multi-attribute decision making with reinforcement learning.Attempt interdisciplinary cross-innovation in the academic field, like designing intelligent wargames and improving reinforcement learning algorithms.
Generating Realistic Training Images Based on Tonality-Alignment Generative Adversarial Networks for Hand Pose Estimation
Nov 27, 2018
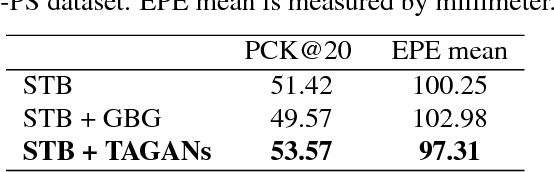


Abstract:Hand pose estimation from a monocular RGB image is an important but challenging task. The main factor affecting its performance is the lack of a sufficiently large training dataset with accurate hand-keypoint annotations. In this work, we circumvent this problem by proposing an effective method for generating realistic hand poses and show that state-of-the-art algorithms for hand pose estimation can be greatly improved by utilizing the generated hand poses as training data. Specifically, we first adopt an augmented reality (AR) simulator to synthesize hand poses with accurate hand-keypoint labels. Although the synthetic hand poses come with precise joint labels, eliminating the need of manual annotations, they look unnatural and are not the ideal training data. To produce more realistic hand poses, we propose to blend a synthetic hand pose with a real background, such as arms and sleeves. To this end, we develop tonality-alignment generative adversarial networks (TAGANs), which align the tonality and color distributions between synthetic hand poses and real backgrounds, and can generate high quality hand poses. We evaluate TAGAN on three benchmarks, including the RHP, STB, and CMU-PS hand pose datasets. With the aid of the synthesized poses, our method performs favorably against the state-of-the-arts in both $2$D and $3$D hand pose estimations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge