Yueyang Zhou
Transferable Graph Condensation from the Causal Perspective
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The increasing scale of graph datasets has significantly improved the performance of graph representation learning methods, but it has also introduced substantial training challenges. Graph dataset condensation techniques have emerged to compress large datasets into smaller yet information-rich datasets, while maintaining similar test performance. However, these methods strictly require downstream applications to match the original dataset and task, which often fails in cross-task and cross-domain scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a novel causal-invariance-based and transferable graph dataset condensation method, named \textbf{TGCC}, providing effective and transferable condensed datasets. Specifically, to preserve domain-invariant knowledge, we first extract domain causal-invariant features from the spatial domain of the graph using causal interventions. Then, to fully capture the structural and feature information of the original graph, we perform enhanced condensation operations. Finally, through spectral-domain enhanced contrastive learning, we inject the causal-invariant features into the condensed graph, ensuring that the compressed graph retains the causal information of the original graph. Experimental results on five public datasets and our novel \textbf{FinReport} dataset demonstrate that TGCC achieves up to a 13.41\% improvement in cross-task and cross-domain complex scenarios compared to existing methods, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on 5 out of 6 datasets in the single dataset and task scenario.
PEER: Expertizing Domain-Specific Tasks with a Multi-Agent Framework and Tuning Methods
Jul 10, 2024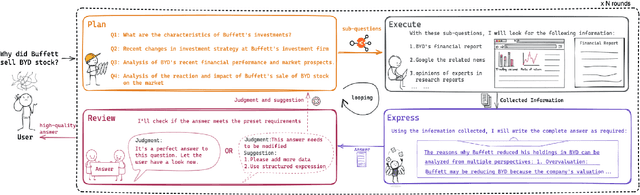

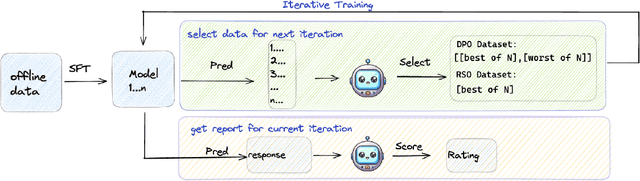
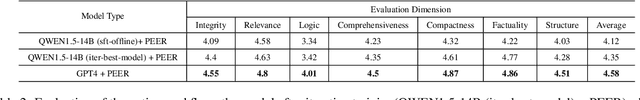
Abstract:In domain-specific applications, GPT-4, augmented with precise prompts or Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), shows notable potential but faces the critical tri-lemma of performance, cost, and data privacy. High performance requires sophisticated processing techniques, yet managing multiple agents within a complex workflow often proves costly and challenging. To address this, we introduce the PEER (Plan, Execute, Express, Review) multi-agent framework. This systematizes domain-specific tasks by integrating precise question decomposition, advanced information retrieval, comprehensive summarization, and rigorous self-assessment. Given the concerns of cost and data privacy, enterprises are shifting from proprietary models like GPT-4 to custom models, striking a balance between cost, security, and performance. We developed industrial practices leveraging online data and user feedback for efficient model tuning. This study provides best practice guidelines for applying multi-agent systems in domain-specific problem-solving and implementing effective agent tuning strategies. Our empirical studies, particularly in the financial question-answering domain, demonstrate that our approach achieves 95.0% of GPT-4's performance, while effectively managing costs and ensuring data privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge