Yuequn Liu
An Identifiable Cost-Aware Causal Decision-Making Framework Using Counterfactual Reasoning
May 13, 2025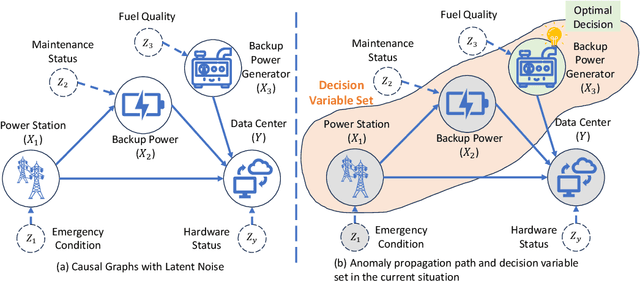
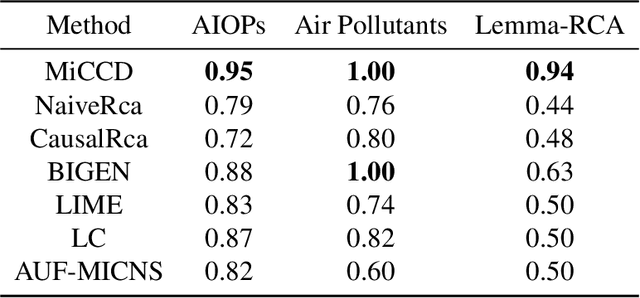
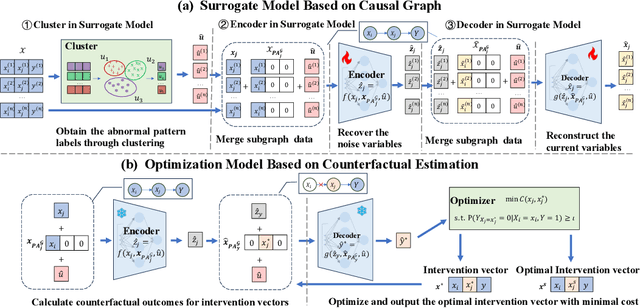
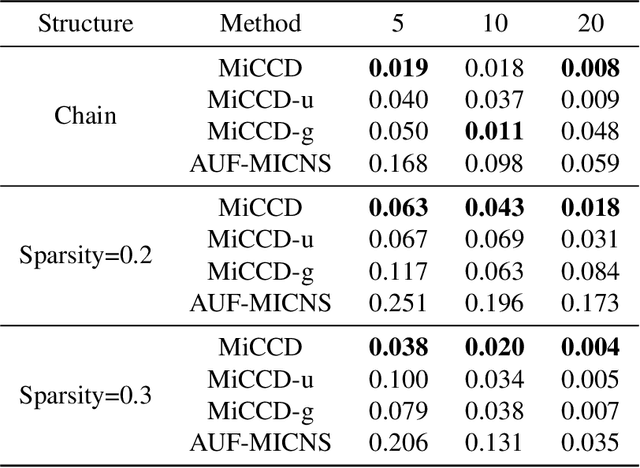
Abstract:Decision making under abnormal conditions is a critical process that involves evaluating the current state and determining the optimal action to restore the system to a normal state at an acceptable cost. However, in such scenarios, existing decision-making frameworks highly rely on reinforcement learning or root cause analysis, resulting in them frequently neglecting the cost of the actions or failing to incorporate causal mechanisms adequately. By relaxing the existing causal decision framework to solve the necessary cause, we propose a minimum-cost causal decision (MiCCD) framework via counterfactual reasoning to address the above challenges. Emphasis is placed on making counterfactual reasoning processes identifiable in the presence of a large amount of mixed anomaly data, as well as finding the optimal intervention state in a continuous decision space. Specifically, it formulates a surrogate model based on causal graphs, using abnormal pattern clustering labels as supervisory signals. This enables the approximation of the structural causal model among the variables and lays a foundation for identifiable counterfactual reasoning. With the causal structure approximated, we then established an optimization model based on counterfactual estimation. The Sequential Least Squares Programming (SLSQP) algorithm is further employed to optimize intervention strategies while taking costs into account. Experimental evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets reveal that MiCCD outperforms conventional methods across multiple metrics, including F1-score, cost efficiency, and ranking quality(nDCG@k values), thus validating its efficacy and broad applicability.
Disentangling Long-Short Term State Under Unknown Interventions for Online Time Series Forecasting
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Current methods for time series forecasting struggle in the online scenario, since it is difficult to preserve long-term dependency while adapting short-term changes when data are arriving sequentially. Although some recent methods solve this problem by controlling the updates of latent states, they cannot disentangle the long/short-term states, leading to the inability to effectively adapt to nonstationary. To tackle this challenge, we propose a general framework to disentangle long/short-term states for online time series forecasting. Our idea is inspired by the observations where short-term changes can be led by unknown interventions like abrupt policies in the stock market. Based on this insight, we formalize a data generation process with unknown interventions on short-term states. Under mild assumptions, we further leverage the independence of short-term states led by unknown interventions to establish the identification theory to achieve the disentanglement of long/short-term states. Built on this theory, we develop a long short-term disentanglement model (LSTD) to extract the long/short-term states with long/short-term encoders, respectively. Furthermore, the LSTD model incorporates a smooth constraint to preserve the long-term dependencies and an interrupted dependency constraint to enforce the forgetting of short-term dependencies, together boosting the disentanglement of long/short-term states. Experimental results on several benchmark datasets show that our \textbf{LSTD} model outperforms existing methods for online time series forecasting, validating its efficacy in real-world applications.
TNPAR: Topological Neural Poisson Auto-Regressive Model for Learning Granger Causal Structure from Event Sequences
Jun 25, 2023



Abstract:Learning Granger causality from event sequences is a challenging but essential task across various applications. Most existing methods rely on the assumption that event sequences are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). However, this i.i.d. assumption is often violated due to the inherent dependencies among the event sequences. Fortunately, in practice, we find these dependencies can be modeled by a topological network, suggesting a potential solution to the non-i.i.d. problem by introducing the prior topological network into Granger causal discovery. This observation prompts us to tackle two ensuing challenges: 1) how to model the event sequences while incorporating both the prior topological network and the latent Granger causal structure, and 2) how to learn the Granger causal structure. To this end, we devise a two-stage unified topological neural Poisson auto-regressive model. During the generation stage, we employ a variant of the neural Poisson process to model the event sequences, considering influences from both the topological network and the Granger causal structure. In the inference stage, we formulate an amortized inference algorithm to infer the latent Granger causal structure. We encapsulate these two stages within a unified likelihood function, providing an end-to-end framework for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge